| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. Answers may vary from one individual to another:
| CONTAINER | ESTIMATED VOLUME | CORRECT VOLUME |
| Coffee mug | 250 mℓ | 270 mℓ |
| Kettle | 1 litre | 1,704 litre |
| Tea pot | 400 mℓ | 592 mℓ |
Assignment 7:
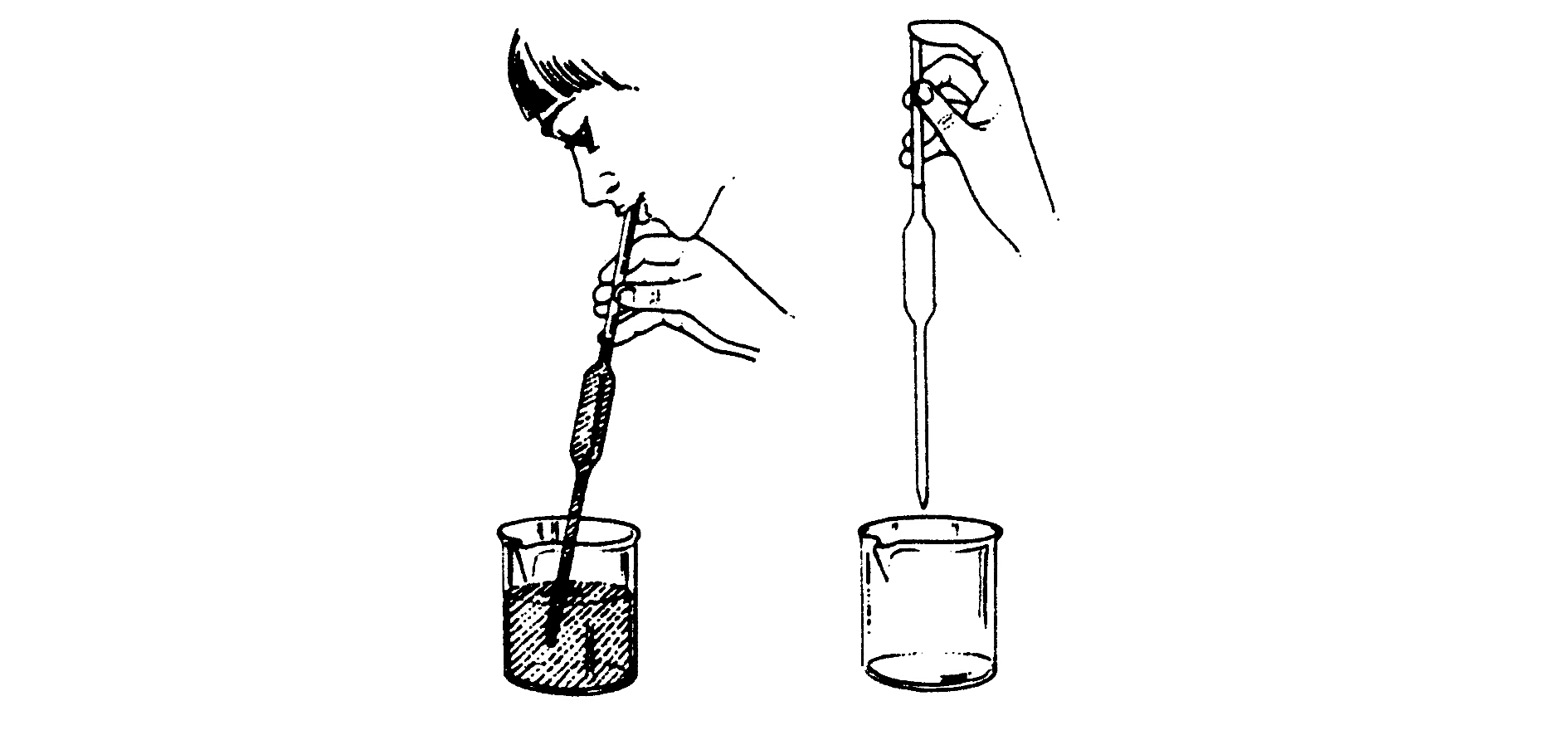
You sip up the liquid and put your finger on the top end as quickly as possible. Then you lift your finger and let the water drain until the meniscus is level with the line. You use it when you want to measure exactly 25 mℓ or 50 mℓ (or any size of the pipette) to add to something.
MEASURING WITH THE HELP OF A MEASURING CYLINDER
Volume refers to the contents of particular spaces. When you buy a cold drink, you pay for a particular amount of liquid that fills a specific space.
This amount of cold drink can also be described as the volume of cold drink.
Volumes can be measured with the help of a measuring cylinder, a burette or a pipette.
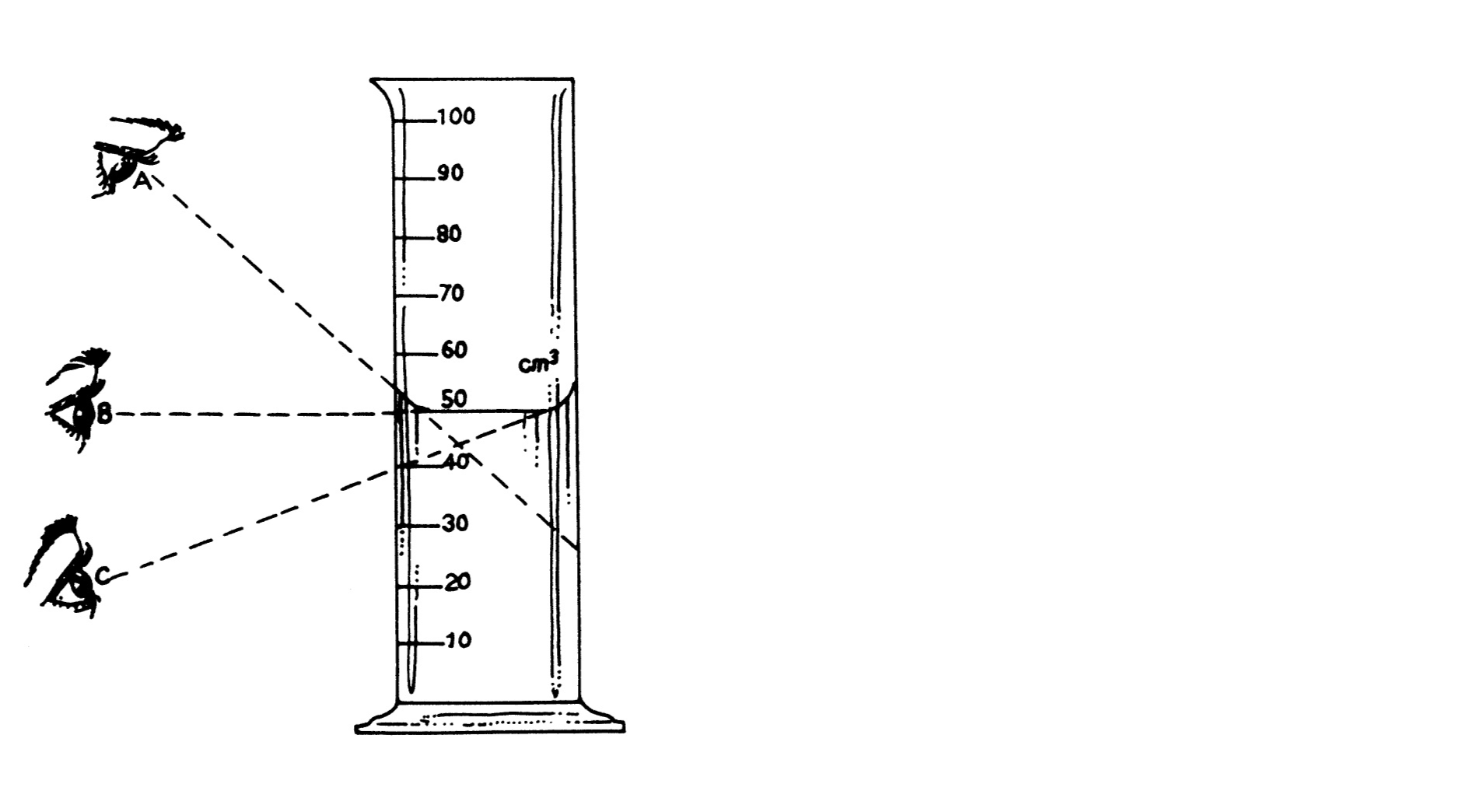
By using a measuring cylinder frequently, you will develop your skill in estimating correctly.
1. Use a typical measuring cylinder to measure the volume of the following containers (and to see how accurate your estimation is):
| Container | Estimated volume | Correct volume |
| Coffee mug | __________________ | __________________ |
| Kettle | __________________ | __________________ |
| Teapot | __________________ | __________________ |
Two basic rules have to be considered for taking a correct reading from a measuring cylinder:
Explain what a meniscus is, using your own words:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
MEASURING WITH THE HELP OF A PIPETTE
Study the following illustration to get to know a pipette:
ASSIGNMENT 7
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
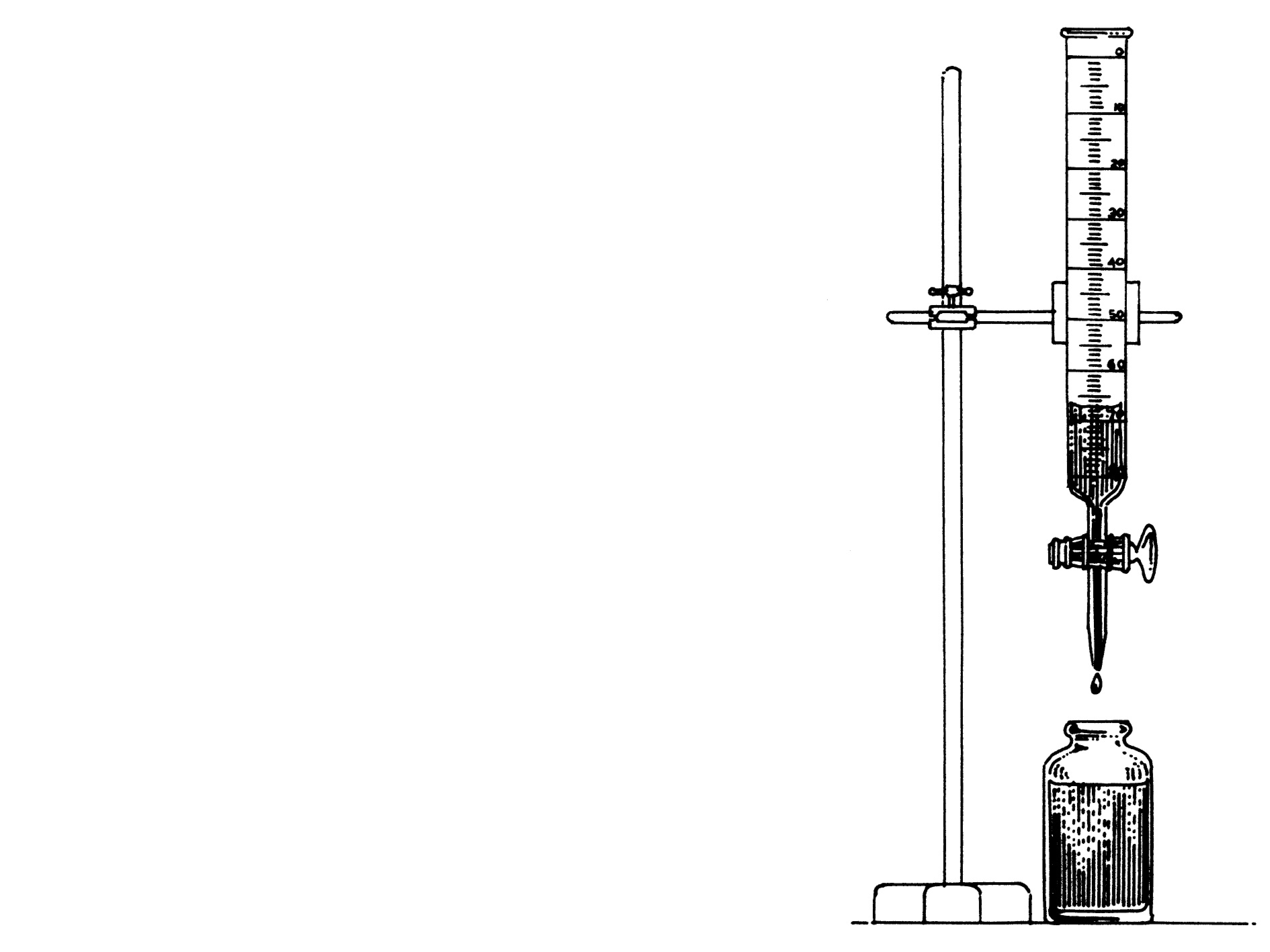
MEASURING WITH THE HELP OF A BURETTE:
A burette is used to measure liquid volume.
It is particularly suitable for measuring volumes smaller than 50 cm.
Burettes are calibrated (marked in divisions) from top to bottom and usually are more accurate than measuring cylinders.
The amount of liquid that is tapped from a burette can simply be read from the burette by checking the level of the meniscus.
Now use the burette to measure the following volumes:
| Object | Estimated volume | Correct volume |
| Teaspoon | __________________ | __________________ |
| Soup spoon | __________________ | __________________ |
| Tablespoon | __________________ | __________________ |
| Ladle | __________________ | __________________ |
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner plans investigations: plans simple tests and comparisons and considers how to conduct these properly.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner interprets information by identifying key ideas in text, finding patterns in recorded data, and making inferences from information in various forms (e.g. pictures, diagrams, text).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?