| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity 1:
To recognise, visualise and name 3-dimensional objects in the environment [LO 3.1]
To describe, sort and compare them [LO 3.2]
Prisms, rectangular prisms, spheres, cylinders, pyramids, and other objects are found all round us.
1. Study the following three-dimensional objects in order to learn their names and be able to recognize and name similar objects in the world around us:
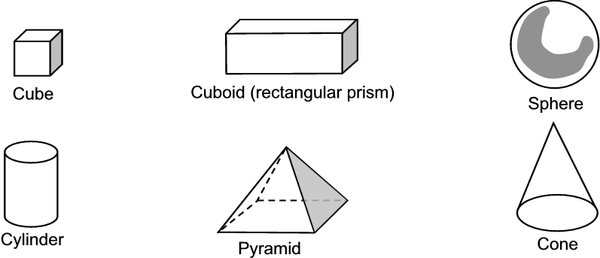
2. Objects in the world around us: now try to draw and name the 3-D objects:
| Item | Drawing | Geometrical name of the object |
| Cricket ball | ||
| Cube of sugar (lump) | ||
| Tin of dog-food |
| Ice-cream cone | ||
| Box of matches | ||
| Packet of cornflakes | ||
| Triangular box of sweets |
3. More shapes and objects.
3.1 Write each of the following solid objects under the correct geometrical heading: The sun; a string of spaghetti; a block of ice; an ordinary candle; the handle of a garden rake; a book; an orange; a brick; a block of margarine. Think of others and write them in the columns too, especially the columns that seem to be rather empty.
3.2 Compare your lists with those of your friends. If they have an item that you have not thought of, you may add it to your list.
| Sphere | Cylinder | Cube | Cuboid (rectangular prism) | Pyramid | Cone |
. Write the correct geometrical name next to each of the following:
5. Look at the objects again. How many surfaces are there? Are the surfaces flat or curved? What shape are the surfaces? Fill in the missing words to describe the objects:
| Object | Number of surfaces | Flat or curved surfaces | Shape of surfaces |
| A box of cornflakes | |||
| A ball | |||
| A cube of sugar | |||
| A candle | |||
| A pyramid | Sides:Base: |
Activity 2:
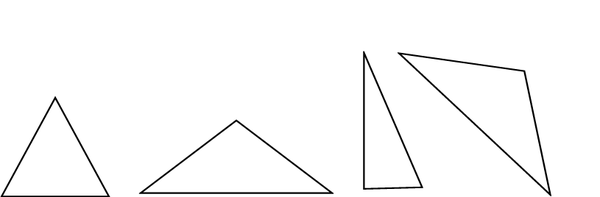
3 sides: Triangles
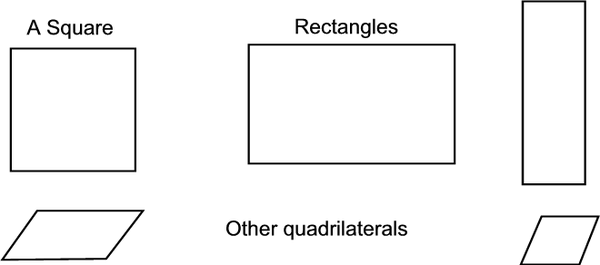
4 sides: Quadrilaterals
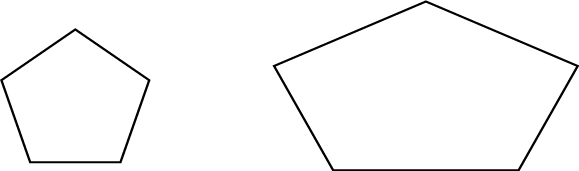
5 sides: Pentagons (when all the sides are equal in length, it is a regular pentagon; if they are different lengths, it is an irregular pentagon)
6 sides: Hexagons
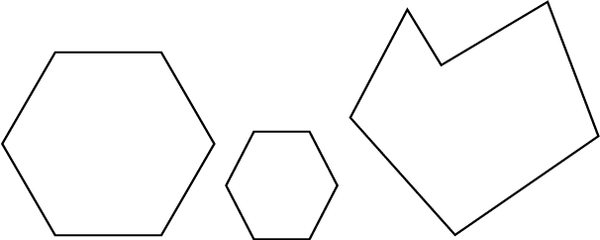
7 sides: Heptagons
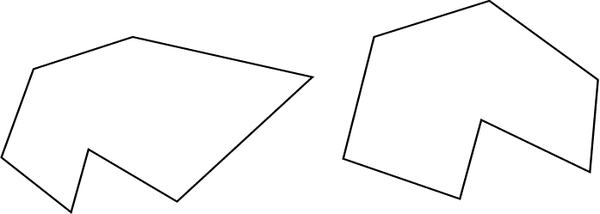
(Try to draw one regular heptagon.)
2. Circles
2.1 Circles are not polygons. Look at the circle below and compare it with the polygons that we have discussed:
3.1 The Circle
3.2 The Triangle
3.3 The Square

3.4 The Rectangle

3.5 The Octogon
4. Cut out the TANGRAM on the next page. Cut out all the shapes in it.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?