| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ACTIVITY 1
Discovering the volume and exterior surface area of prisms and formulating a formula for calculating this, and applying the discovered formulas in practical situations
[LO 3.8, 4.2, 4.3, 4.5]
1. Write the formulas for calculating the area and volume of each of the following figures:
1.1 Area of a square:
1.2 Area of a rectangle:
1.3 Area of a triangle:
1.4 Area of a circle:
1.5 Volume of a rectangular prism:
1.6 Volume of a cylinder:
2. Explain what you understand the following to be and sketch it.
2.1 rectangular prism:
Sketch:
2.2 triangular prism:
Sketch:
2.3 cube:
Sketch:
2.4 cylinder:
Sketch:
3. What do you understand by the word “volume”?
4. Name the standard unit of measurement for each of the following:
5. Study the following representations of nets.
5.1 Rectangular prism:
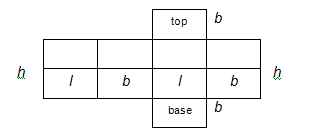
5.2 Triangular prism (this is not a proper pyramid):
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT
Date of submission:
1. Collect the following sweet containers: a rectangular prism, a triangular prism, a cube and a cylinder. Unfold each example so that the complete area is visible and paste each onto a separate sheet of cardboard.
2. Draw a net to represent each of the figures. Indicate the lengths of the sides.
3. Make use of your existing knowledge and determine the total surface area and volume of each example.
4. Work out a formula for calculating the total surface area and the volume of each figure. You may refer to sources for help.
ASSESSMENT RUBRIC: INVESTIGATION
| Criterion 1: | The net is constructed accurately. (CONSTRUCTION) |
| Criterion 2: | The surface areas and volumes are calculated correctly. (CALCULATIONS) |
| Criterion 3: | The deduction of formulas for surface areas and volumes is correct. (FORMULAS) |
| Criterion 4: | The application in practical situations is correct. (REPORT) |
| CRITERION | NOT ACHIEVED | AVERAGE ACHIEVEMENT | ACHIEVED | EXCEPTIONAL | MARKS |
| Construction | The nets are not well constructed. | The nets are constructed relatively well. | The nets are constructed well. | The nets are constructed to meet the requirements for a perfect net. | /20 |
| Calculations | The calculations are incorrect. | The calculations are partially correct. | The calculations are (70 – 90%) correct. | The calculations are (100%) correct. | /10 |
| Formulas | The formulas are not correct or mathematical. | The formulas are partially correct and mathematical. | The formulas are 99% correct. | The formulas are 100% correctly presented. | /10 |
| Report | The report is untidy. The applications (use of mathematics) is weak. | The report is fairly good, but the application is not altogether correct in every instance. | The report is well-presented and the application is correct. | The manner of presentation reveals that extra effort has gone into the exercise. | /10 |
| TOTAL | /50 |
| LO 3 |
| Space and Form (geometry)The learner is able to describe and represent features of and relationships between two-dimensional forms and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 3.2 describes and classifies geometric figures and three-dimensional objects in terms of properties in contexts inclusive of those that can be used to promote awareness of social, cultural and environmental issues, including:3.2.1 sides, angles and diagonals and their relationships, focusing on triangles and quadrilaterals (e.g. types of triangles and quadrilaterals); |
| 3.3 uses vocabulary to describe parallel lines that are cut by a transverse, perpendicular or intersection line, as well as triangles, with reference to angular relationships (e.g. vertically opposite, corresponding);3.4 uses a pair of compasses, a ruler and a protractor for accurately constructing geometric figures so that specific properties may be investigated and nets may be designed;3.5 designs and uses nets to make models of geometric three- dimensional objects that have been studied in the preceding grades and up till now;3.7 uses proportion to describe the effect of expansion and reduction on the properties of geometric figures;3.8 draws and interprets sketches of geometric three-dimensional objects from several perspectives, focusing on the retention of properties. |
| LO 4 |
| MeasuringThe learner is able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulas in a variety of contexts. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 4.1 solves more complicated problems involving time, inclusive of the ratio between time, distance and speed;4.2 solves problems involving the following:4.2.1 length;4.2.2 circumference and area of polygons and circles;4.2.3 volume and exterior area of rectangular prisms and cylinders; |
| 4.3 solves problems using a variety of strategies, including:4.3.1 estimation;4.3.2 calculation to at least two decimal points;4.3.3 use and converting between appropriate S.I. units; |
| 4.5 calculates the following with the use of appropriate formulas:4.5.1 circumference of polygons and circles;4.5.2 area of triangles, right angles and polygons by means of splitting up to triangles and right angles;4.5.3 volume of prisms with triangular and rectangular bases and cylinders; |
| 4.7 estimates, compares, measures and draws triangles accurately to within one degree. |
ACTIVITY 1
2. Learners supply.
3. Contents

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?