| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The topics chosen for the modules in Grade 1 are all related to stories which reflect the learners’ experience in the world in which they are growing up. They are relevant to both boys and girls.
Much depends on the number of times the learners hear the stories and rhymes and the provision made for the repetition of the vocabulary introduced. At first this is done classically. As the learners become more familiar with English they can communicate with a friend. Eventually they will want to tell the teacher and answer questions about the texts.
The educators must keep in mind that there may be many/some learners in the class who are still only at the listening stage, but with the necessary encouragement and praise they will soon join in and begin speaking in English.
It is suggested that the average learners complete all eight modules during the year, finishing ± two modules per term.
Allow the slower learners to proceed at their own pace when doing the written activities but expose them to all the listening and speaking activities with the class.
The quick learners can be extended and given more tasks and activities to complete.
Tim and Tina are off on a shopping spree on a rainy day in winter. They visit many different kinds of shops. Learners colour articles which boys/girls would like to buy. They answer yes or no to questions and complete a graph about the traffic.
This module lends itself to the discussion of such issues as job opportunities for all including disabled persons; the acquiring of wealth; the results of unemployment.

| LO 1.1.5 | LO 2.1 | LO 2.5 | LO 6.6 |
Mom said, “Look at all the cars!”
Tim said, “Look at all the trucks and lorries.”
Tina said, “Look at all the buses and trains.”
Dad said, “Look at all the . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
| LO 1.3 | LO 4.2 | LO 5.1.2 |

| LO 1.1.5 | LO 2.1 | LO 3.5 |
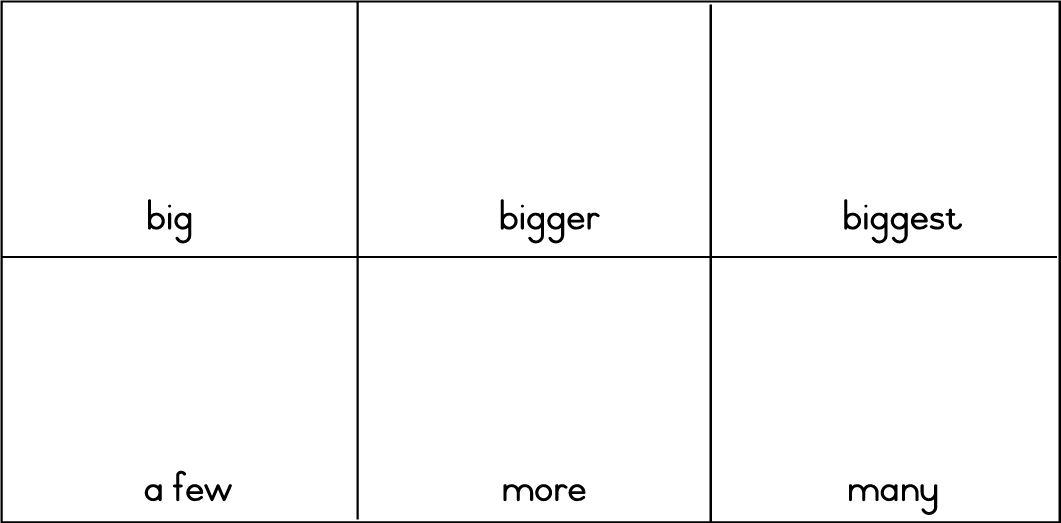
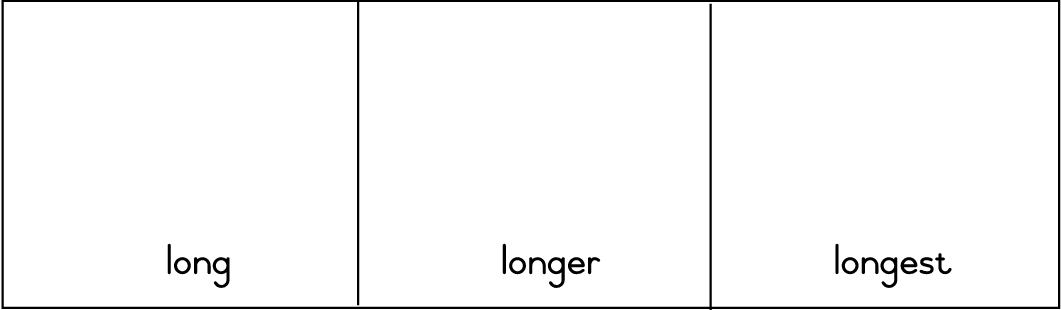
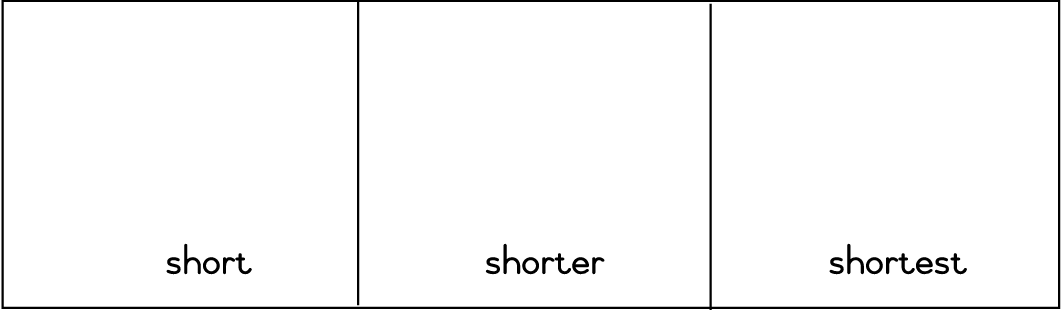
| LO 1.1.3 | LO 6.10 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner understands short, simple stories:
1.1.3 draws a picture of the story;
1.1.5 answers simple, literal ‘yes/no’ and open questions with one-word answers;
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner understands simple oral instructions by responding physically;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner responds appropriately to simple questions with single words or formulaic phrases;
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner expresses self in simple ways if given an oral structure;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.2: We know this when the learner uses simple, familiar words to complete sentence frames.
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.1: We know this when the learner understands concepts and vocabulary relating to:
5.1.2 number;
Learning Outcome 6: GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY : The learner knows and is able to use the sounds, vocabulary and grammar of the language to create and interpret texts.
Assessment Standard 6.6: We know this when the learner understands negative forms in oral texts;
Assessment Standard 6.10: We know this when the learner understands some adjectives and adverbs in oral texts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English first additional language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?