| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Observation by means of the microscope will reveal more wonderful things than those viewed in regard to mere structure and connection: for while the heart is still beating the contrary (i.e., in opposite directions in the different vessels) movement of the blood is observed in the vessels—though with difficulty—so that the circulation of the blood is clearly exposed.Marcello Malpighi, De Pulmonibus , 1661
Malpighi's work (mostly on frogs) outlined the finer microscopic details of circulation, following the work of Harvey, who described the circulatory system at a macroscopic level. In all animals, except a few simple types, the circulatory system is used to transport nutrients and gases through the body. Simple diffusion allows some water, nutrient, waste, and gas exchange into primitive animals that are only a few cell layers thick; however, bulk flow is the only method by which the entire body of larger more complex organisms is accessed.
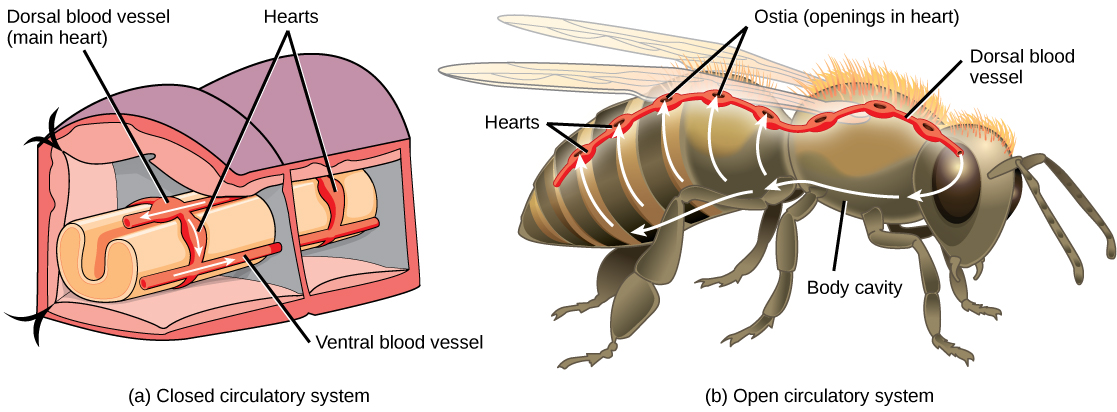
The circulatory system is effectively a network of cylindrical vessels: the arteries, veins, and capillaries that emanate from a pump, the heart. In all vertebrate organisms, as well as some invertebrates, this is a closed system, in which the blood is not free in a cavity. In a closed circulatory system , blood is contained inside blood vessels and circulates unidirectionally from the heart around the systemic circulatory route, then returns to the heart again, as illustrated in [link] a . As opposed to a closed system, arthropods—including insects, crustaceans, and most mollusks—have an open circulatory system, as illustrated in [link] b . In an open circulatory system , the fluid is not enclosed in the blood vessels but is pumped into a cavity called a hemocoel; rather than blood, this fluid is called hemolymph because the blood mixes with the interstitial fluid. As the heart beats and the animal moves, the hemolymph circulates around the organs within the body cavity and then reenters the hearts through openings called ostia. This movement allows for gas and nutrient exchange. An open circulatory system does not use as much energy as a closed system to operate or to maintain; however, there is a trade-off with the amount of blood that can be moved to highly metabolically active organs and tissues.
The circulatory system varies from simple systems in invertebrates to more complex systems in vertebrates. The simplest animals, such as the sponges (Porifera) and rotifers (Rotifera), do not need a circulatory system because diffusion allows adequate exchange of water, nutrients, and waste, as well as dissolved gases, as shown in [link] a . Organisms that are more complex but still only have two layers of cells in their body plan, such as jellies (Cnidaria) and comb jellies (Ctenophora) also use diffusion through their epidermis and internally through the gastrovascular compartment. Both their internal and external tissues are bathed in an aqueous environment and exchange fluids by diffusion on both sides, as illustrated in [link] b . Exchange of fluids is assisted by the pulsing of the jellyfish body.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?