| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Radiation makes it impossible to stand close to a hot lava flow. Calculate the rate of heat transfer by radiation from of fresh lava into surroundings, assuming lava’s emissivity is 1.00.
(a) Calculate the rate of heat transfer by radiation from a car radiator at into a environment, if the radiator has an emissivity of 0.750 and a surface area. (b) Is this a significant fraction of the heat transfer by an automobile engine? To answer this, assume a horsepower of and the efficiency of automobile engines as 25%.
Find the net rate of heat transfer by radiation from a skier standing in the shade, given the following. She is completely clothed in white (head to foot, including a ski mask), the clothes have an emissivity of 0.200 and a surface temperature of , the surroundings are at , and her surface area is .
Suppose you walk into a sauna that has an ambient temperature of . (a) Calculate the rate of heat transfer to you by radiation given your skin temperature is , the emissivity of skin is 0.98, and the surface area of your body is . (b) If all other forms of heat transfer are balanced (the net heat transfer is zero), at what rate will your body temperature increase if your mass is 75.0 kg?
Thermography is a technique for measuring radiant heat and detecting variations in surface temperatures that may be medically, environmentally, or militarily meaningful.(a) What is the percent increase in the rate of heat transfer by radiation from a given area at a temperature of compared with that at , such as on a person’s skin? (b) What is the percent increase in the rate of heat transfer by radiation from a given area at a temperature of compared with that at , such as for warm and cool automobile hoods?
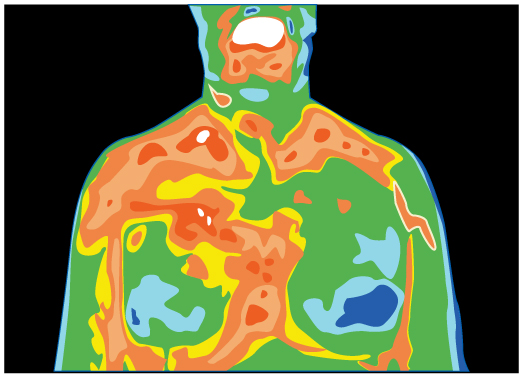
(a) 1.31%
(b) 20.5%
The Sun radiates like a perfect black body with an emissivity of exactly 1. (a) Calculate the surface temperature of the Sun, given that it is a sphere with a radius that radiates into 3-K space. (b) How much power does the Sun radiate per square meter of its surface? (c) How much power in watts per square meter is that value at the distance of Earth, away? (This number is called the solar constant.)
A large body of lava from a volcano has stopped flowing and is slowly cooling. The interior of the lava is at , its surface is at , and the surroundings are at . (a) Calculate the rate at which energy is transferred by radiation from of surface lava into the surroundings, assuming the emissivity is 1.00. (b) Suppose heat conduction to the surface occurs at the same rate. What is the thickness of the lava between the surface and the interior, assuming that the lava’s conductivity is the same as that of brick?
(a)
(b) 4.2 cm
Calculate the temperature the entire sky would have to be in order to transfer energy by radiation at —about the rate at which the Sun radiates when it is directly overhead on a clear day. This value is the effective temperature of the sky, a kind of average that takes account of the fact that the Sun occupies only a small part of the sky but is much hotter than the rest. Assume that the body receiving the energy has a temperature of .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 105: adventures in physics' conversation and receive update notifications?