| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Population, when unchecked, increases in a geometrical ratio. Subsistence increases only in an arithmetical ratio. A slight acquaintance with numbers will show the immensity of the first power in comparison of the second.Thomas Robert Malthus. An Essay on the Principle of Population , (1798)
Mathematical approaches to understanding animal population dynamics, which you learned about earlier in the semester, can be applied to human population growth. Malthus recognized long ago that exponential population growth might be a problem if resources increase non-exponentially. Resources can be increased by technology and other modifications to the environment. In fact, humans are not unique in their ability to alter their environment. For example, beaver dams alter the stream environment where they are built. Humans, however, have the ability to alter their environment to increase its carrying capacity sometimes to the detriment of other species (e.g., via artificial selection for crops that have a higher yield). Earth’s human population is growing rapidly, to the extent that some worry about the ability of the earth’s environment to sustain this population, as long-term exponential growth carries the potential risks of famine, disease, and large-scale death.
Although humans have increased the carrying capacity of their environment, the technologies used to achieve this transformation have caused unprecedented changes to Earth’s environment, altering ecosystems to the point where some may be in danger of collapse. The depletion of the ozone layer, erosion due to acid rain, and damage from global climate change are caused by human activities. The ultimate effect of these changes on our carrying capacity is unknown. As some point out, it is likely that the negative effects of increasing carrying capacity will outweigh the positive ones—the carrying capacity of the world for human beings might actually decrease.
The world’s human population is currently experiencing exponential growth even though human reproduction is far below its biotic potential ( [link] ). To reach its biotic potential, all females would have to become pregnant every nine months or so during their reproductive years. Also, resources would have to be such that the environment would support such growth. Neither of these two conditions exists. In spite of this fact, human population is still growing exponentially.
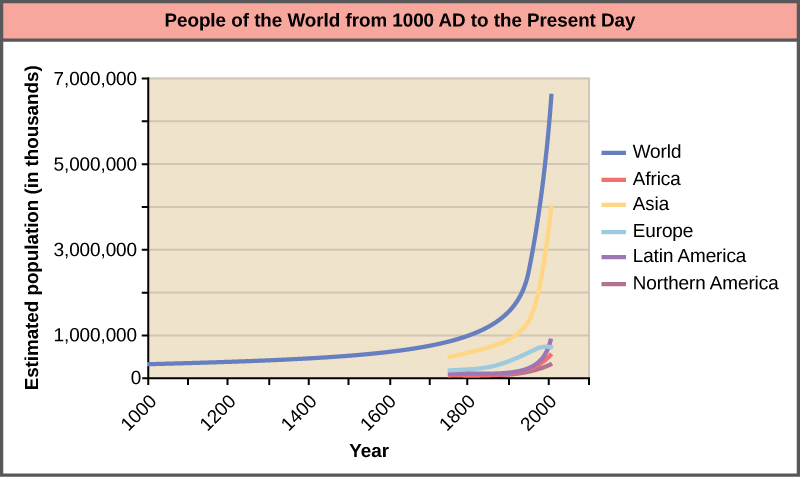
A consequence of exponential human population growth is the time that it takes to add a particular number of humans to the Earth is becoming shorter. [link] shows that 123 years were necessary to add 1 billion humans in 1930, but it only took 24 years to add two billion people between 1975 and 1999. As already discussed, at some point it would appear that our ability to increase our carrying capacity indefinitely on a finite world is uncertain. Without new technological advances, the human growth rate has been predicted to slow in the coming decades. However, the population will still be increasing and the threat of overpopulation remains.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?