| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

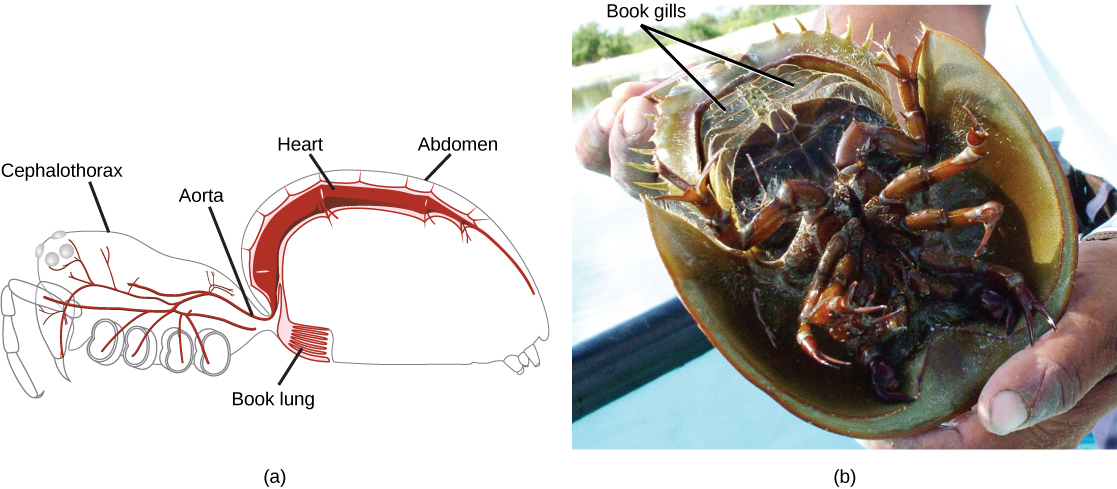
A unique feature of animals in the arthropod phylum is the presence of a segmented body and fusion of sets of segments that give rise to functional body regions called tagma. Tagma may be in the form of a head, thorax, and abdomen, or a cephalothorax and abdomen, or a head and trunk. A central cavity, called the hemocoel (or blood cavity), is present, and the open circulatory system is regulated by a tubular or single-chambered heart. Respiratory systems vary depending on the group of arthropod: insects and myriapods use a series of tubes (tracheae) that branch through the body, open to the outside through openings called spiracles, and perform gas exchange directly between the cells and air in the tracheae, whereas aquatic crustaceans utilize gills, terrestrial chelicerates employ book lungs, and aquatic chelicerates use book gills ( [link] ). The book lungs of arachnids (scorpions, spiders, ticks and mites) contain a vertical stack of hemocoel wall tissue that somewhat resembles the pages of a book. Between each of the "pages" of tissue is an air space. This allows both sides of the tissue to be in contact with the air at all times, greatly increasing the efficiency of gas exchange. The gills of crustaceans are filamentous structures that exchange gases with the surrounding water. Groups of arthropods also differ in the organs used for excretion, with crustaceans possessing green glands and insects using Malpighian tubules, which work in conjunction with the hindgut to reabsorb water while ridding the body of nitrogenous waste. The cuticle is the covering of an arthropod. It is made up of two layers: the epicuticle, which is a thin, waxy water-resistant outer layer containing no chitin, and the layer beneath it, the chitinous procuticle. Chitin is a tough, flexible polysaccharide. In order to grow, the arthropod must shed the exoskeleton during a process called ecdysis (“to strip off”); this is a cumbersome method of growth, and during this time, the animal is vulnerable to predation. The characteristic morphology of representative animals from each subphylum is described below.
The name Hexapoda denotes the presence of six legs (three pairs) in these animals as differentiated from the number of pairs present in other arthropods. Hexapods are characterized by the presence of a head, thorax, and abdomen, constituting three tagma. The thorax bears the wings as well as six legs in three pairs. Many of the common insects we encounter on a daily basis—including ants, cockroaches, butterflies, and flies—are examples of Hexapoda.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Animals' conversation and receive update notifications?