| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space. The primary components of these materials are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Collectively, these materials are called the extracellular matrix ( [link] ). Not only does the extracellular matrix hold the cells together to form a tissue, but it also allows the cells within the tissue to communicate with each other.
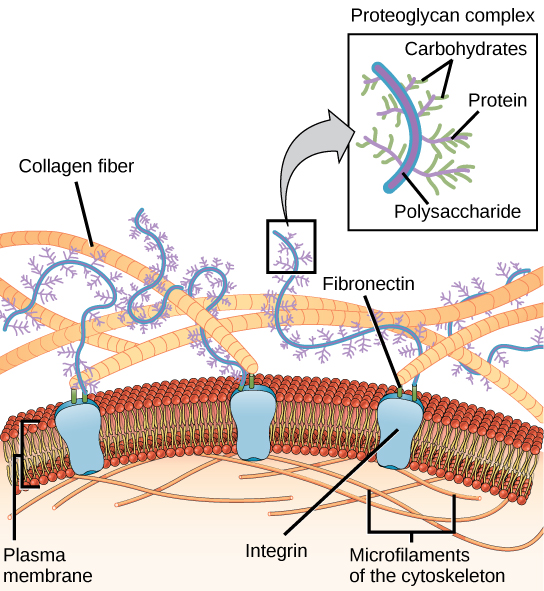
Blood clotting provides an example of the role of the extracellular matrix in cell communication. When the cells lining a blood vessel are damaged, they display a protein receptor called tissue factor. When tissue factor binds with another factor in the extracellular matrix, it causes platelets to adhere to the wall of the damaged blood vessel, stimulates adjacent smooth muscle cells in the blood vessel to contract (thus constricting the blood vessel), and initiates a series of steps that stimulate the platelets to produce clotting factors.
Cells can also communicate with each other by direct contact, referred to as intercellular junctions. There are some differences in the ways that plant and animal cells do this. Plasmodesmata (singular = plasmodesma) are junctions between plant cells, whereas animal cell contacts include tight and gap junctions, and desmosomes.
In general, long stretches of the plasma membranes of neighboring plant cells cannot touch one another because they are separated by the cell walls surrounding each cell. Plasmodesmata are numerous channels that pass between the cell walls of adjacent plant cells, connecting their cytoplasm and enabling signal molecules and nutrients to be transported from cell to cell ( [link] a ).
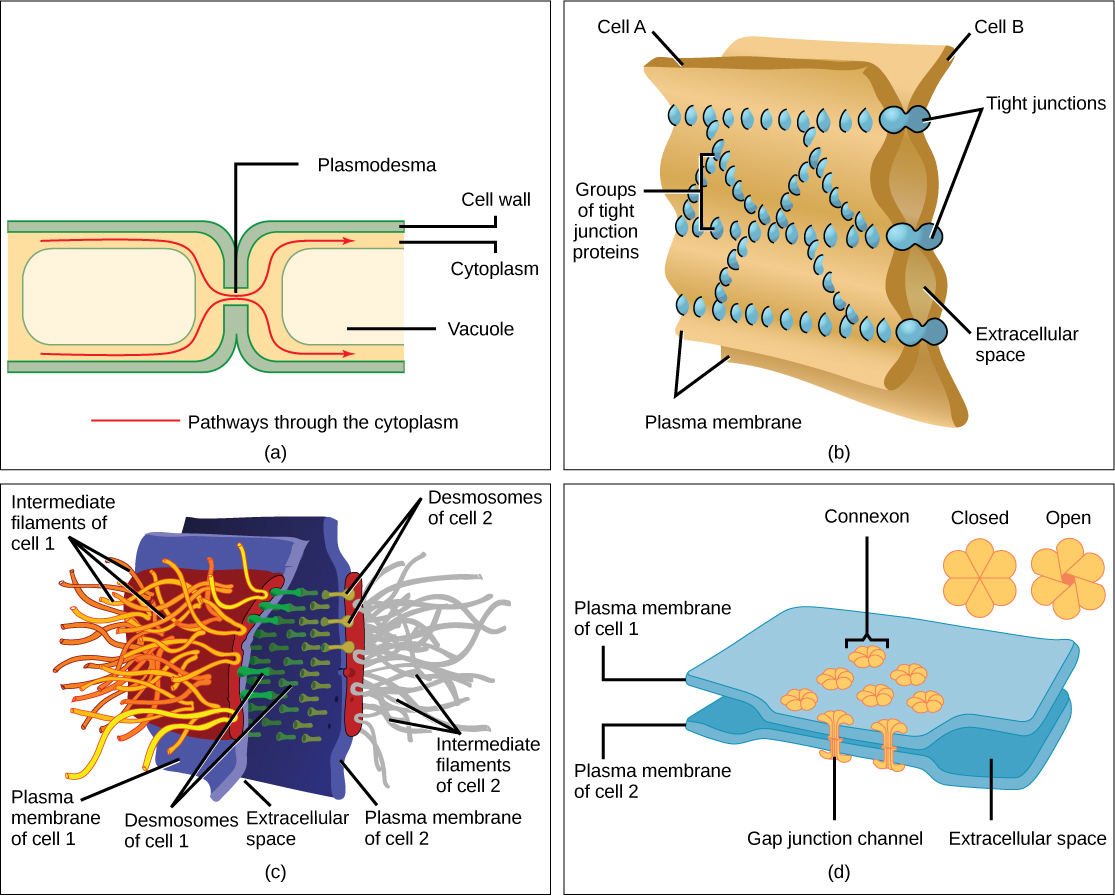
A tight junction is a watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells ( [link] b ). Proteins hold the cells tightly against each other. This tight adhesion prevents materials from leaking between the cells. Tight junctions are typically found in the epithelial tissue that lines internal organs and cavities, and composes most of the skin. For example, the tight junctions of the epithelial cells lining the urinary bladder prevent urine from leaking into the extracellular space.
Also found only in animal cells are desmosomes , which act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells ( [link] c ). They keep cells together in a sheet-like formation in organs and tissues that stretch, like the skin, heart, and muscles.
Gap junctions in animal cells are like plasmodesmata in plant cells in that they are channels between adjacent cells that allow for the transport of ions, nutrients, and other substances that enable cells to communicate ( [link] d ). Structurally, however, gap junctions and plasmodesmata differ.
| Components of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells and Their Functions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Component | Function | Present in Prokaryotes? | Present in Animal Cells? | Present in Plant Cells? |
| Plasma membrane | Separates cell from external environment; controls passage of organic molecules, ions, water, oxygen, and wastes into and out of the cell | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoplasm | Provides structure to cell; site of many metabolic reactions; medium in which organelles are found | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Nucleoid | Location of DNA | Yes | No | No |
| Nucleus | Cell organelle that houses DNA and directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins | No | Yes | Yes |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mitochondria | ATP production/cellular respiration | No | Yes | Yes |
| Peroxisomes | Oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids, and detoxifies poisons | No | Yes | Yes |
| Vesicles and vacuoles | Storage and transport; digestive function in plant cells | No | Yes | Yes |
| Centrosome | Unspecified role in cell division in animal cells; organizing center of microtubules in animal cells | No | Yes | No |
| Lysosomes | Digestion of macromolecules; recycling of worn-out organelles | No | Yes | No |
| Cell wall | Protection, structural support and maintenance of cell shape | Yes, primarily peptidoglycan in bacteria but not Archaea | No | Yes, primarily cellulose |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis | No | No | Yes |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids | No | Yes | Yes |
| Golgi apparatus | Modifies, sorts, tags, packages, and distributes lipids and proteins | No | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoskeleton | Maintains cell’s shape, secures organelles in specific positions, allows cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enables unicellular organisms to move independently | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Flagella | Cellular locomotion | Some | Some | No, except for some plant sperm. |
| Cilia | Cellular locomotion, movement of particles along extracellular surface of plasma membrane, and filtration | No | Some | No |
This table provides the components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and their respective functions.
Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, but a eukaryotic cell is typically larger than a prokaryotic cell, has a true nucleus (meaning its DNA is surrounded by a membrane), and has other membrane-bound organelles that allow for compartmentalization of functions. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The nucleolus within the nucleus is the site for ribosome assembly. Ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm or are attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane or endoplasmic reticulum. They perform protein synthesis. Mitochondria perform cellular respiration and produce ATP. Peroxisomes break down fatty acids, amino acids, and some toxins. Vesicles and vacuoles are storage and transport compartments. In plant cells, vacuoles also help break down macromolecules.
Animal cells also have a centrosome and lysosomes. The centrosome has two bodies, the centrioles, with an unknown role in cell division. Lysosomes are the digestive organelles of animal cells.
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole. The plant cell wall, whose primary component is cellulose, protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. The central vacuole expands, enlarging the cell without the need to produce more cytoplasm.
The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, as well as the plasma membrane. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport membrane lipids and proteins.
The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements. Microfilaments provide rigidity and shape to the cell, and facilitate cellular movements. Intermediate filaments bear tension and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place. Microtubules help the cell resist compression, serve as tracks for motor proteins that move vesicles through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell. They are also the structural elements of centrioles, flagella, and cilia.
Animal cells communicate through their extracellular matrices and are connected to each other by tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Plant cells are connected and communicate with each other by plasmodesmata.
[link] What structures does a plant cell have that an animal cell does not have? What structures does an animal cell have that a plant cell does not have?
[link] Plant cells have plasmodesmata, a cell wall, a large central vacuole, chloroplasts, and plastids. Animal cells have lysosomes and centrosomes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for the university of georgia' conversation and receive update notifications?