| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To illustrate this, imagine two full glasses of water. One has a single teaspoon of sugar in it, whereas the second one contains one-quarter cup of sugar. If the total volume of the solutions in both cups is the same, which cup contains more water? Because the large amount of sugar in the second cup takes up much more space than the teaspoon of sugar in the first cup, the first cup has more water in it.
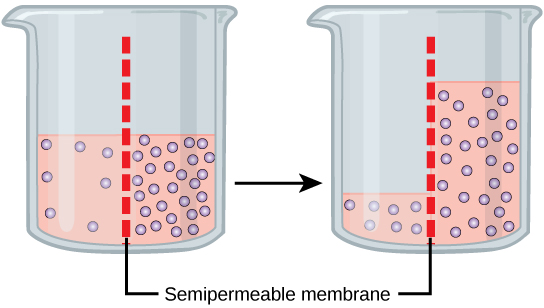
Returning to the beaker example, recall that it has a mixture of solutes on either side of the membrane. A principle of diffusion is that the molecules move around and will spread evenly throughout the medium if they can. However, only the material capable of getting through the membrane will diffuse through it. In this example, the solute cannot diffuse through the membrane, but the water can. Water has a concentration gradient in this system. Thus, water will diffuse down its concentration gradient, crossing the membrane to the side where it is less concentrated. This diffusion of water through the membrane—osmosis—will continue until the concentration gradient of water goes to zero or until the hydrostatic pressure of the water balances the osmotic pressure. Osmosis proceeds constantly in living systems.
Tonicity describes how an extracellular solution can change the volume of a cell by affecting osmosis. A solution's tonicity often directly correlates with the osmolarity of the solution. Osmolarity describes the total solute concentration of the solution. A solution with low osmolarity has a greater number of water molecules relative to the number of solute particles; a solution with high osmolarity has fewer water molecules with respect to solute particles. In a situation in which solutions of two different osmolarities are separated by a membrane permeable to water, though not to the solute, water will move from the side of the membrane with lower osmolarity (and more water) to the side with higher osmolarity (and less water). This effect makes sense if you remember that the solute cannot move across the membrane, and thus the only component in the system that can move—the water—moves along its own concentration gradient. An important distinction that concerns living systems is that osmolarity measures the number of particles (which may be molecules) in a solution. Therefore, a solution that is cloudy with cells may have a lower osmolarity than a solution that is clear, if the second solution contains more dissolved molecules than there are cells.
Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells. In a hypotonic situation, the extracellular fluid has lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell, and water enters the cell. (In living systems, the point of reference is always the cytoplasm, so the prefix hypo - means that the extracellular fluid has a lower concentration of solutes, or a lower osmolarity, than the cell cytoplasm.) It also means that the extracellular fluid has a higher concentration of water in the solution than does the cell. In this situation, water will follow its concentration gradient and enter the cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology 2015' conversation and receive update notifications?