| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
I used a circle in my design. I am saying no more.
Use any round object to draw it, or a stencil, or a pair of compasses. At home you can use a plate if you want to draw a circle.
They are round and have no angles. Look at the circle below and then we’ll learn more about circles:
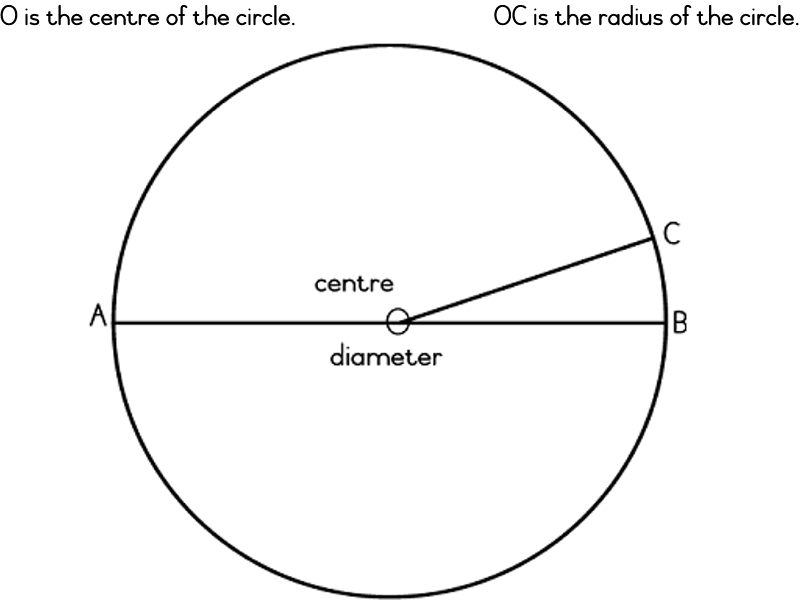
AB is the diameter. It halves the circle.
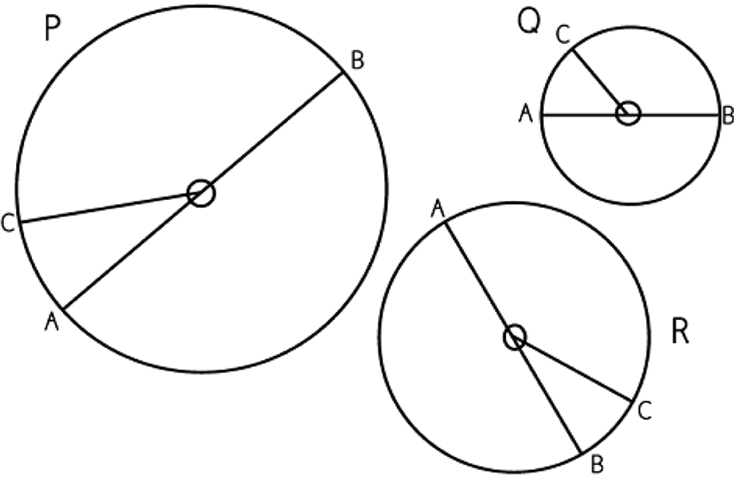
Circle P: Radius = _____cm Diameter = _____cm
Circle Q: Radius = _____cm Diameter = _____cm
Circle R: Radius = _____cm Diameter = _____cm
Now we know: 2 x Radius = Diameter and Diameter ÷ 2 = Radius
Circle W: Radius = 5cm Diameter = _____cm (Double)
Circle X: Radius = 8cm Diameter = _____cm
Circle Y: Diameter = 12cm Radius = _____cm (Halve)
Circle Z: Diameter = 22cm Radius = _____cm
Draw 2 circles that are exactly the same size. Cut out one of the circles. Fold it exactly in half and then in half again. Open it out and find the spot where the 4 folds cross in the centre. That is the centre of the circle. Lay it exactly on the other circle and push a pin down through the centre to make a mark on the circle below. Try it at home and come and show it to the class.
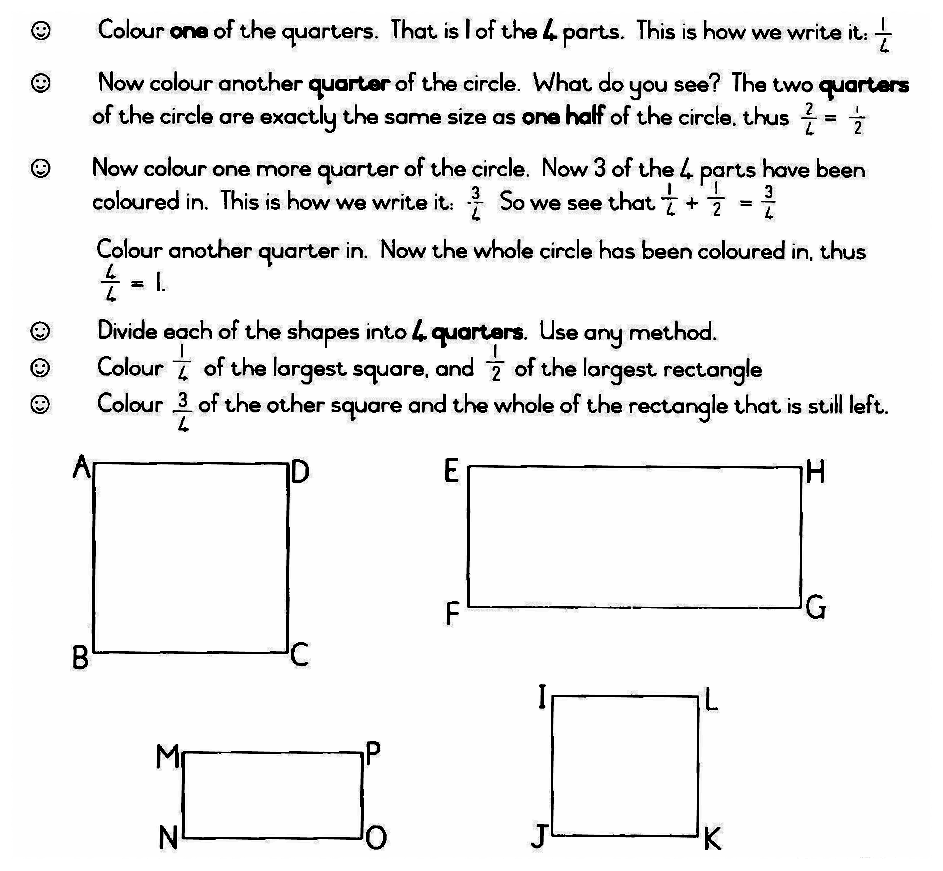

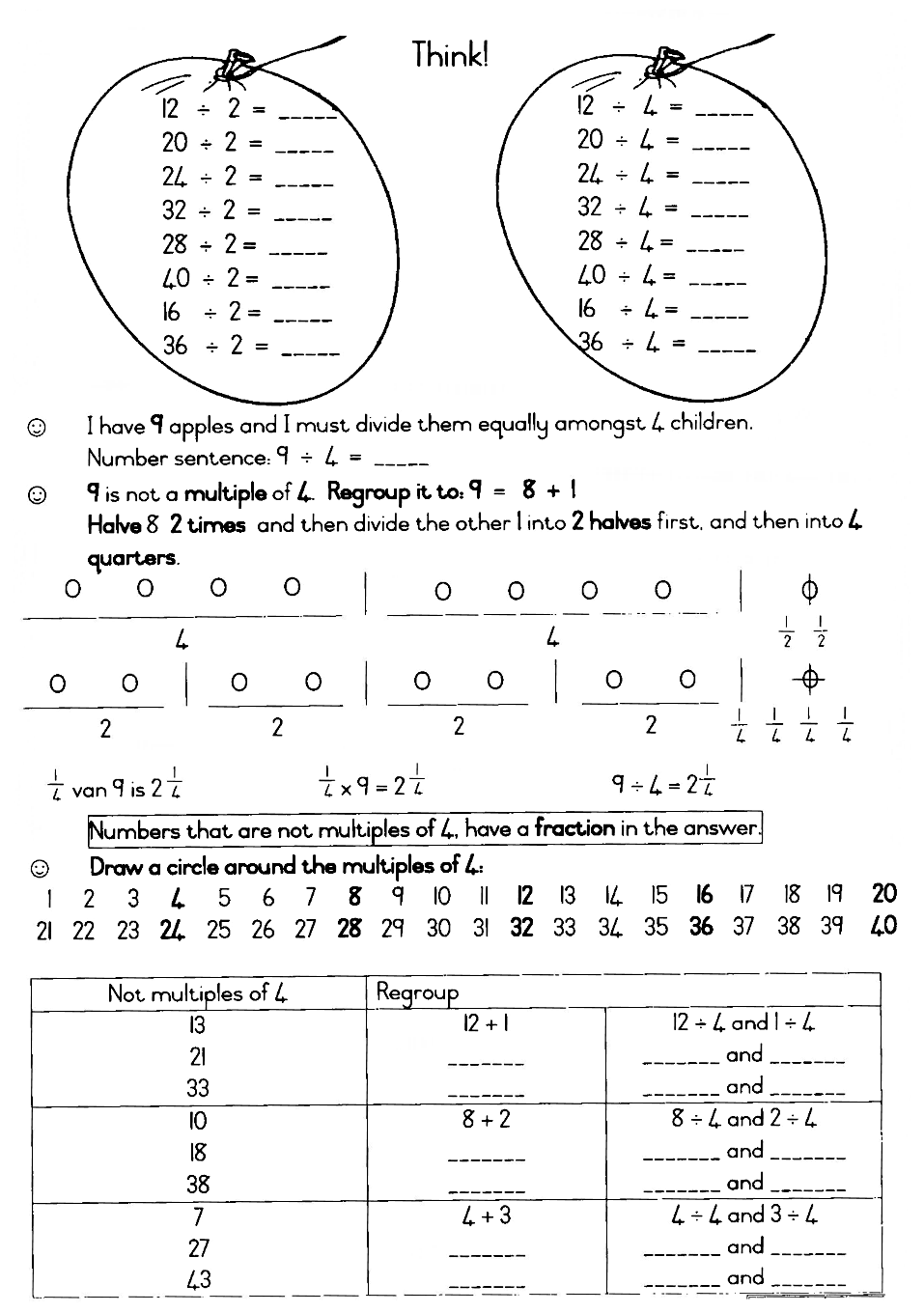
All multiples of 4 can easily be divided into quarters like this.
| 4 | 8 | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| 40 | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ | 4 |
| Multiples of 4 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 |
| ÷ 2 | 2 | 4 | ||||||||
| ÷ 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Number | Halve | Halve again | |
| 4080601008492 | 40 ÷ 4 = _____80 ÷ 4 = _____60 ÷ 4 = _____100 ÷ 4 = _____84 ÷ 4 = _____92 ÷ 4 = _____ |
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner orders, describes and compares numbers:
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner solves and explains solutions to practical problems that involve equal sharing and grouping and that lead to solutions that also include unitary and nonunitary fractions (e.g. ¼, ¾);
Assessment Standard 1.8: We know this when the learner can perform calculations, using appropriate symbols, to solve problems;
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses the following techniques:
1.10.1 building up and breaking down numbers;
1.10.2 doubling and halving;
1.10.3 number-lines;
1.10.4 rounding off in tens.
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner recognises, identifies and names two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in the environment and in pictures;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner observes and creates given and described two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects using concrete materials (e.g. building blocks, construction sets, cut-out two-dimensional shapes, clay, drinking straws);
Learning Outcome 4: The learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts.
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner investigates (alone and/or as a member of a group or team) and approximates.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?