| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Fig 1 - A force can change the course (direction) of a moving object.
Fig 2 - A force can halt a moving object.
Fig 3 - A force change the shape of an object.
Fig 4 - A force can change the speed of a moving object.
Fig 5 - A force can make an object rotate.
1. Contact forces
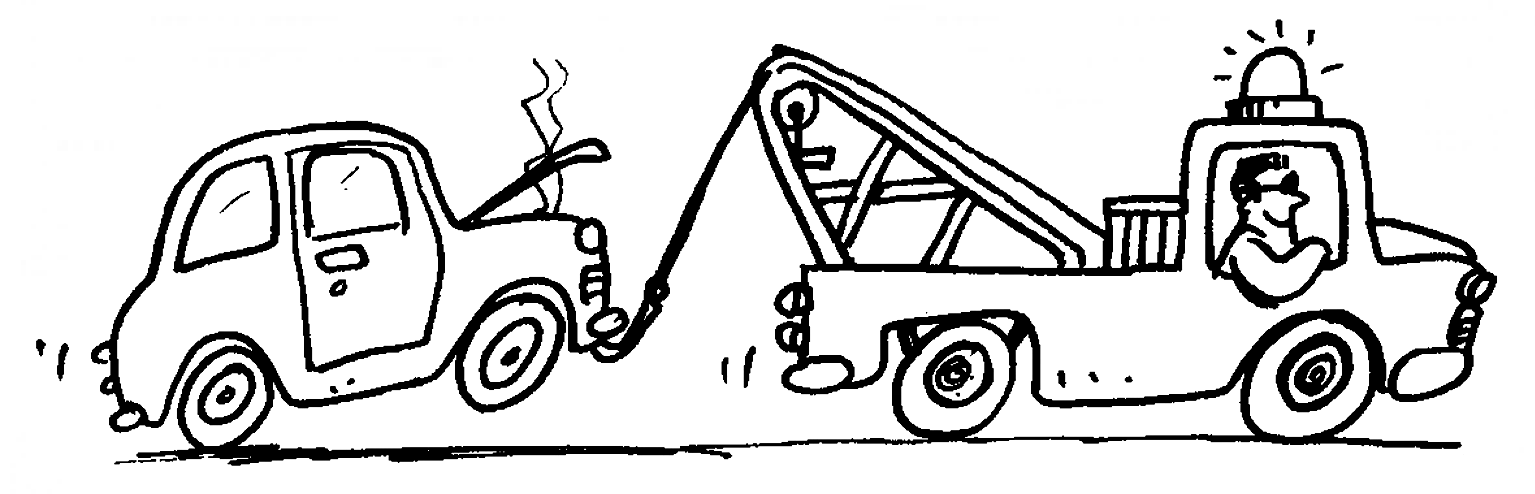
The vehicle in the illustration has broken down and cannot move by itself. The tow truck has to pull it.
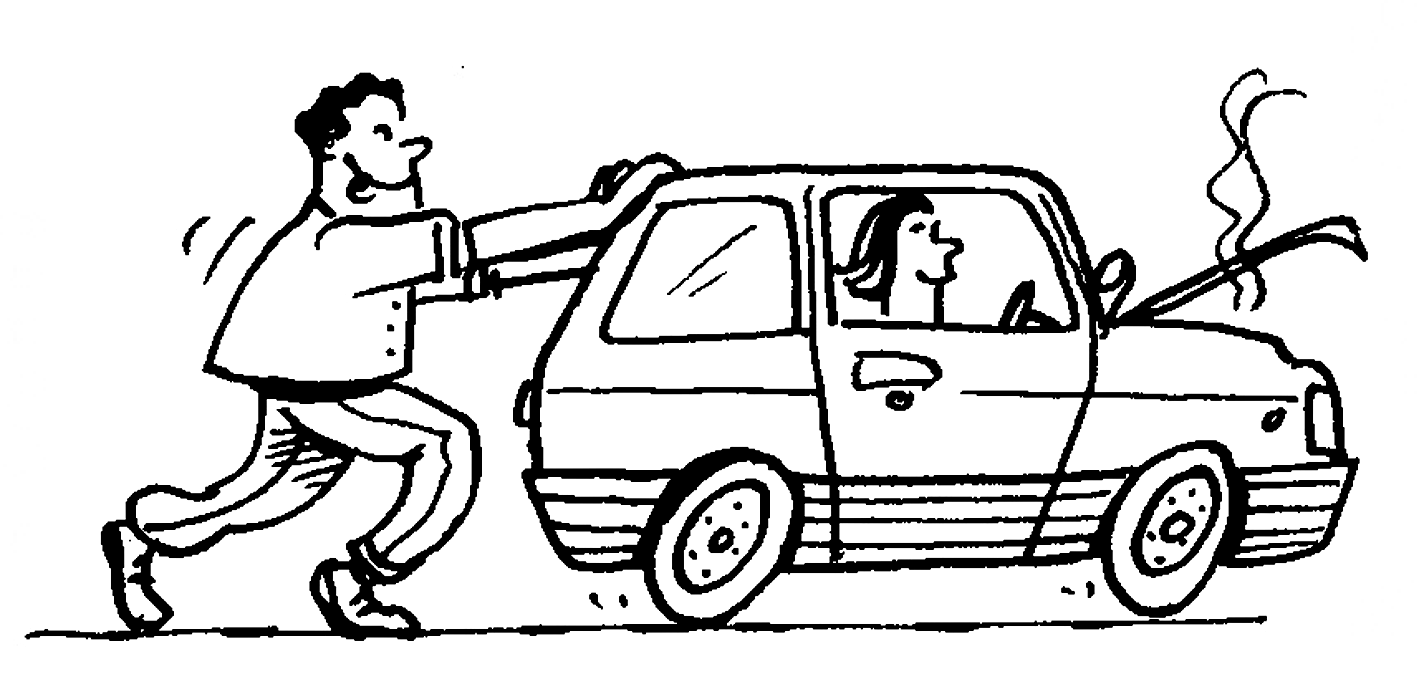
This car also cannot move by itself. The man has to push it.
When something has to be pulled or pushed, we say that we must exert force on it. You use the force of thrust to push something away from you, or the force of attraction to pull something towards you.
Examine the following illustrations and indicate whether they show forces of thrust or of attraction.
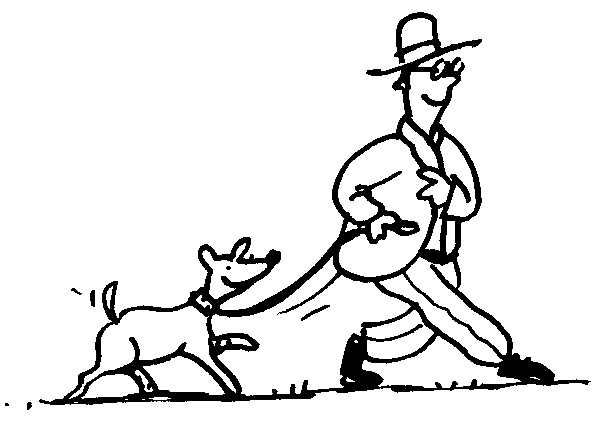




We cannot see force, but we know that it is there because we observe its effect. The above illustrations show that force can move a stationary object.
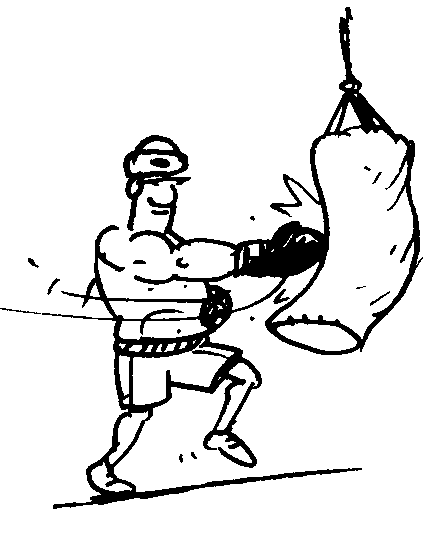
The following illustrations show more of the effect of forces. Are you able to identify them?
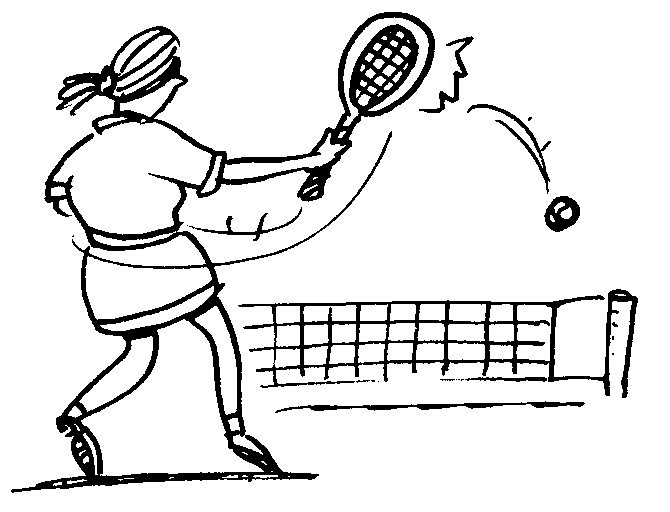
Fig. 1: The tennis player hits the ball away from her.
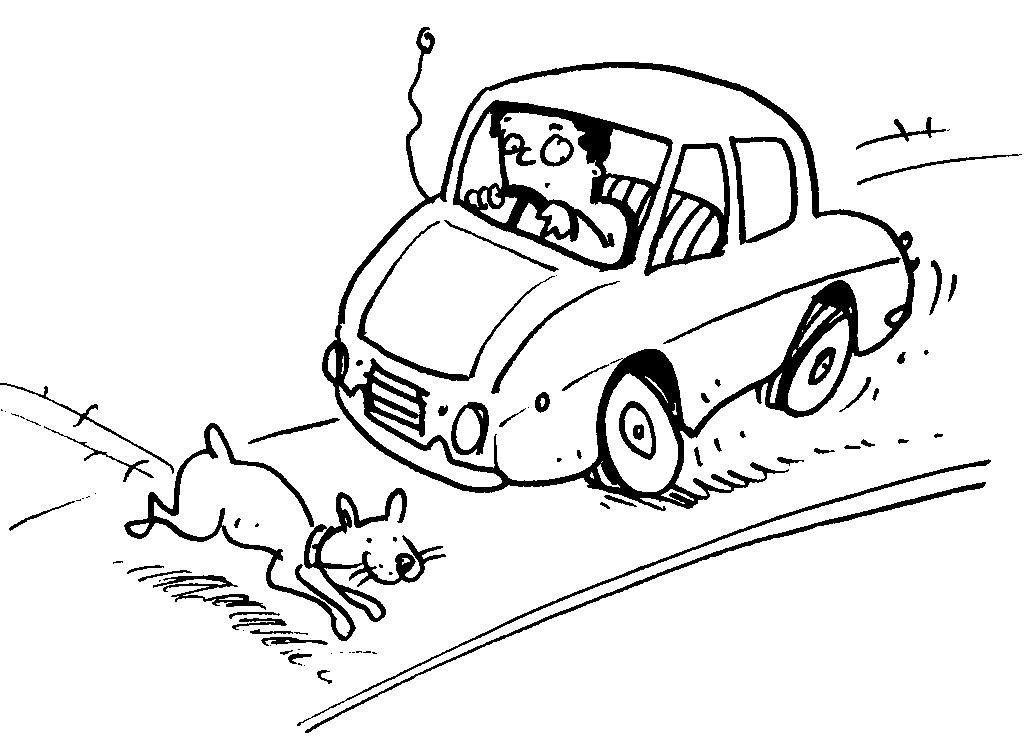
Fig. 2: The driver uses the brakes to stop the car.

Fig. 3 The force of attraction is exerted on the elastic band.
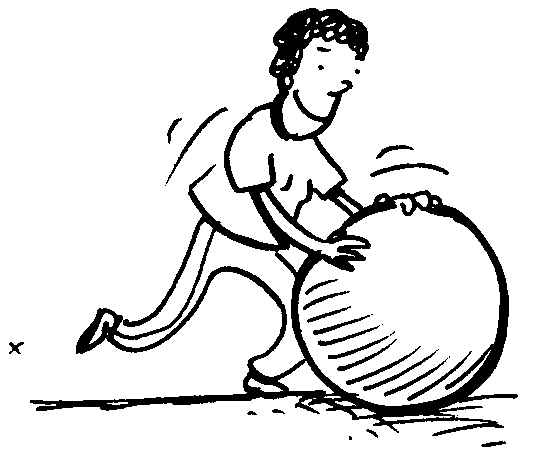

Fig. 4: The force of thrust in the same direction as the motion is exerted on the rolling ball.
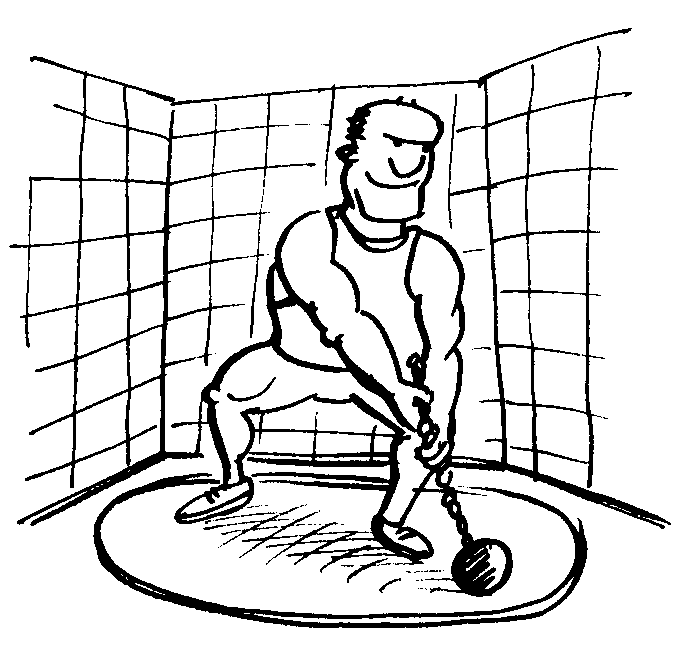
Fig. 5: The athlete swings the hammer to rotate it around him
Note down your deductions:
Fig 1: _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Fig 2: _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Fig 3: _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Fig 4: _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Fig 5: _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
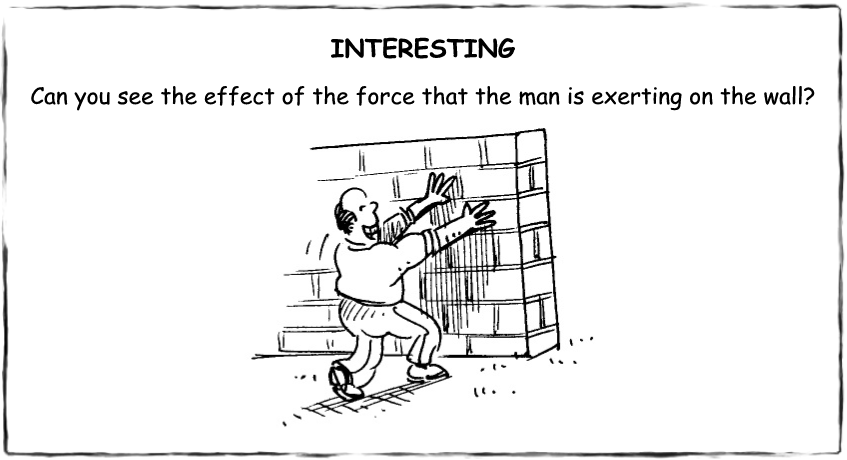
Sometimes the effect of force is not visible. When you push against a wall, you are using force, but the effect cannot be seen. But when there is an egg between your hand and the wall, you will be able to observe that you have exerted force quite plainly!
2. Forces that operate over distance:
It is even possible to bring objects into motion or to change the direction of the motion without any contact. Forces that affect objects without making contact are identified as forces that operate over distance.
Three kinds of force can have an effect without any contact with objects:
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner evaluates data and communicates findings: generalises in terms of relevant aspects and describes how the data support the generalisation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?