| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
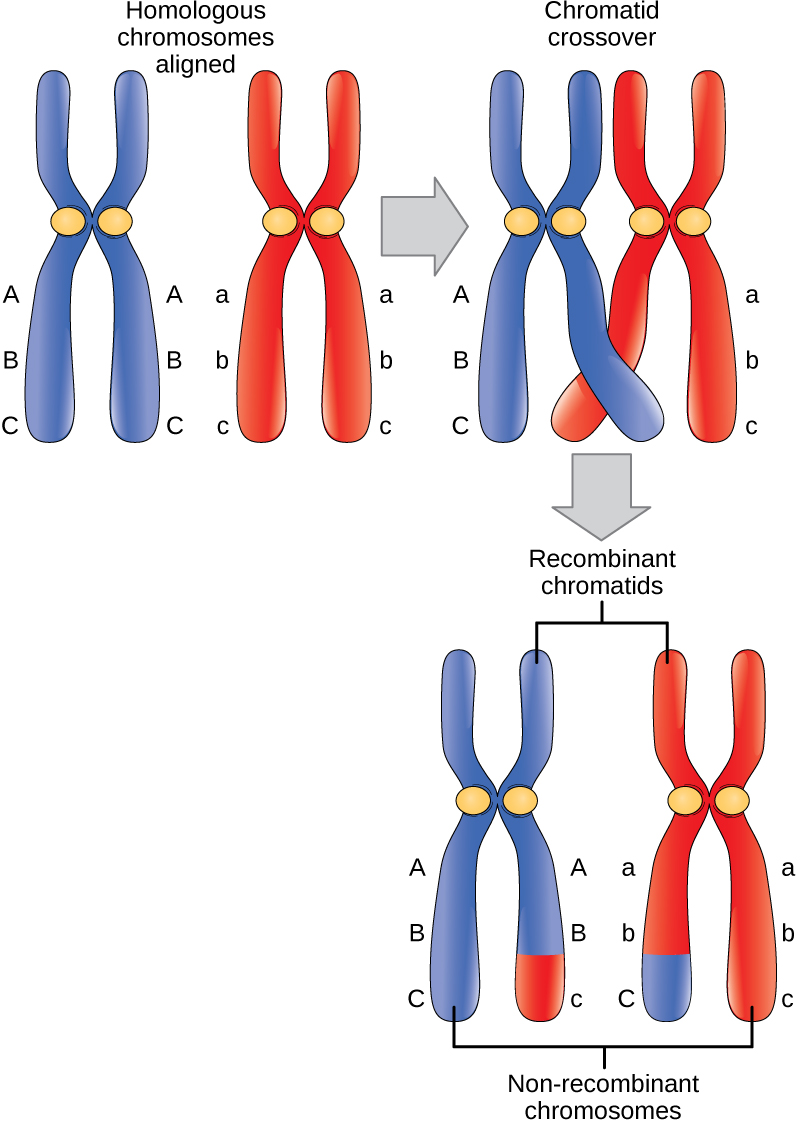
The crossover events are the first source of genetic variation in the nuclei produced by meiosis. A single crossover event between homologous non-sister chromatids leads to a reciprocal exchange of equivalent DNA between a maternal chromosome and a paternal chromosome. Now, when that sister chromatid is moved into a gamete cell it will carry some DNA from one parent of the individual and some DNA from the other parent. The sister recombinant chromatid has a combination of maternal and paternal genes that did not exist before the crossover. Multiple crossovers in an arm of the chromosome have the same effect, exchanging segments of DNA to create recombinant chromosomes.
The key event in prometaphase I is the attachment of the spindle fiber microtubules to the kinetochore proteins at the centromeres. Kinetochore proteins are multiprotein complexes that bind the centromeres of a chromosome to the microtubules of the mitotic spindle. Microtubules grow from centrosomes placed at opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules move toward the middle of the cell and attach to one of the two fused homologous chromosomes. The microtubules attach at each chromosomes' kinetochores. With each member of the homologous pair attached to opposite poles of the cell, in the next phase, the microtubules can pull the homologous pair apart. A spindle fiber that has attached to a kinetochore is called a kinetochore microtubule. At the end of prometaphase I, each tetrad is attached to microtubules from both poles, with one homologous chromosome facing each pole. The homologous chromosomes are still held together at chiasmata. In addition, the nuclear membrane has broken down entirely.
During metaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are arranged in the center of the cell with the kinetochores facing opposite poles. The homologous pairs orient themselves randomly at the equator. For example, if the two homologous members of chromosome 1 are labeled a and b, then the chromosomes could line up a-b, or b-a. This is important in determining the genes carried by a gamete, as each will only receive one of the two homologous chromosomes. Recall that homologous chromosomes are not identical. They contain slight differences in their genetic information, causing each gamete to have a unique genetic makeup.
This randomness is the physical basis for the creation of the second form of genetic variation in offspring. Consider that the homologous chromosomes of a sexually reproducing organism are originally inherited as two separate sets, one from each parent. Using humans as an example, one set of 23 chromosomes is present in the egg donated by the mother. The father provides the other set of 23 chromosomes in the sperm that fertilizes the egg. Every cell of the multicellular offspring has copies of the original two sets of homologous chromosomes. In prophase I of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes form the tetrads. In metaphase I, these pairs line up at the midway point between the two poles of the cell to form the metaphase plate. Because there is an equal chance that a microtubule fiber will encounter a maternally or paternally inherited chromosome, the arrangement of the tetrads at the metaphase plate is random. Any maternally inherited chromosome may face either pole. Any paternally inherited chromosome may also face either pole. The orientation of each tetrad is independent of the orientation of the other 22 tetrads.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Open genetics' conversation and receive update notifications?