| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Determine the value of each of the following.
>>(6*7)+4^2-2^4 (ans = 42)
>>((3^2+2^3)/(4^5-5^4))+((sqrt(64)-5^2)/(4^5+5^6+7^8)) (ans = 0.0426)
>>log10(10^2)+10^5 (ans = 100002)
>>exp(2)+2^3-log(exp(2)) (ans = 13.3891)
>>sin(2*pi)+cos(pi/4) (ans = 0.7071)
>>tan(pi/3)+cos(270*pi/180)+sin(270*pi/180)+cos(pi/3) (ans = 1.2321)
Solve the following system of equations:
>>A=[2 4; 1 5]
A =2 4
1 5>>B=[1; 2]
B =1
2>>Solution=A\B
Solution =-0.5000
0.5000
Evaluate y at 5.
>>p=[4 0 3 -1 0]
p =4 0 3 -1 0>>polyval(p,5)
ans =2570>>
Given below is Load-Gage Length data for a type 304 stainless steel that underwent a tensile test. Original specimen diameter is 12.7 mm. Introduction to Materials Science for Engineers by J. F. Shackelford, Macmillan Publishing Company. © 1985, (p.304)
| Load [N] | Gage Length [mm] |
|---|---|
| 0.000 | 50.8000 |
| 4890 | 50.8102 |
| 9779 | 50.8203 |
| 14670 | 50.8305 |
| 19560 | 50.8406 |
| 24450 | 50.8508 |
| 27620 | 50.8610 |
| 29390 | 50.8711 |
| 32680 | 50.9016 |
| 33950 | 50.9270 |
| 34580 | 50.9524 |
| 35220 | 50.9778 |
| 35720 | 51.0032 |
| 40540 | 51.816 |
| 48390 | 53.340 |
| 59030 | 55.880 |
| 65870 | 58.420 |
| 69420 | 60.960 |
| 69670 (maximum) | 61.468 |
| 68150 | 63.500 |
| 60810 (fracture) | 66.040 (after fracture) |
First, we need to enter the data sets. Because it is rather a large table, using Variable Editor is more convenient. See the figures below:
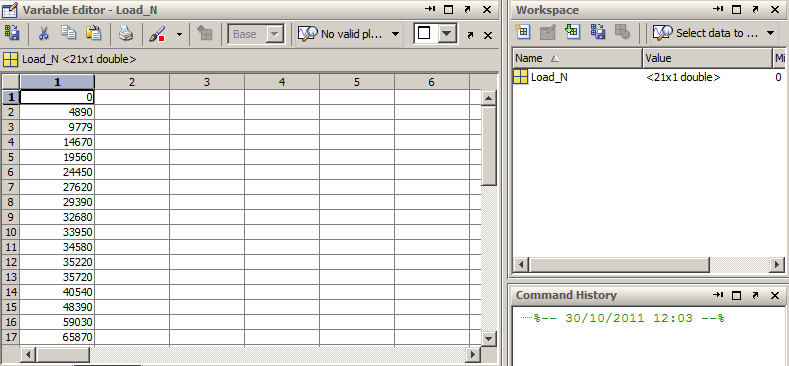
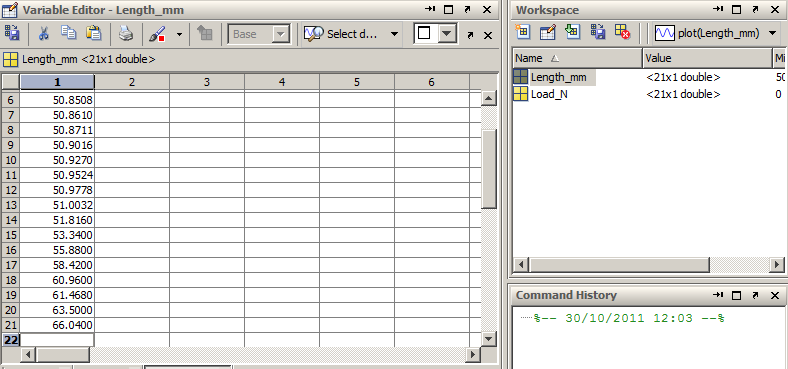
Next, we will calculate the cross-sectional area.
Area=pi/4*(0.0127^2)
Area =1.2668e-004
Now, we can find the Stress values with the following, note that we are obtaining results in MPa:
Sigma=(Load_N./Area)*10^(-6)
Sigma =0
38.602277.1964
115.8065154.4086
193.0108218.0351
232.0076257.9792
268.0047272.9780
278.0302281.9773
320.0269381.9955
465.9888519.9844
548.0085549.9820
537.9830480.0403
For strain calculation, we will first find the change in length:
Delta_L=Length_mm-50.800
Delta_L =0
0.01020.0203
0.03050.0406
0.05080.0610
0.07110.1016
0.12700.1524
0.17780.2032
1.01602.5400
5.08007.6200
10.160010.6680
12.700015.2400
Now we can determine Strain with the following:
Epsilon=Delta_L./50.800
Epsilon =0
0.00020.0004
0.00060.0008
0.00100.0012
0.00140.0020
0.00250.0030
0.00350.0040
0.02000.0500
0.10000.1500
0.20000.2100
0.25000.3000
The final results can be tabulated as foolows:
[Sigma Epsilon]
ans =0 0
38.6022 0.000277.1964 0.0004
115.8065 0.0006154.4086 0.0008
193.0108 0.0010218.0351 0.0012
232.0076 0.0014257.9792 0.0020
268.0047 0.0025272.9780 0.0030
278.0302 0.0035281.9773 0.0040
320.0269 0.0200381.9955 0.0500
465.9888 0.1000519.9844 0.1500
548.0085 0.2000549.9820 0.2100
537.9830 0.2500480.0403 0.3000

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'A brief introduction to engineering computation with matlab' conversation and receive update notifications?