| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
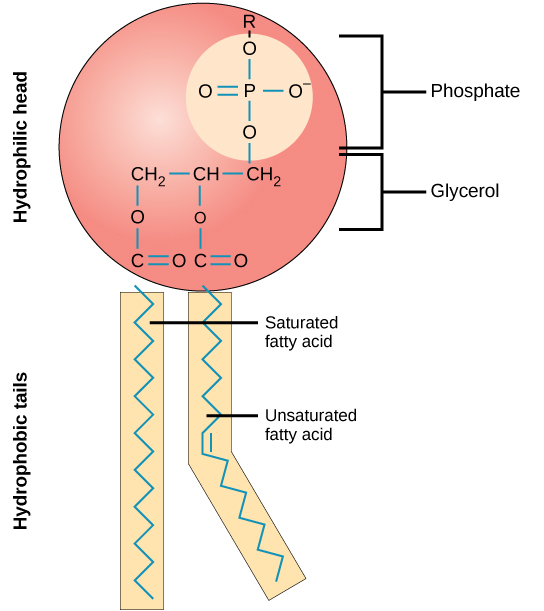
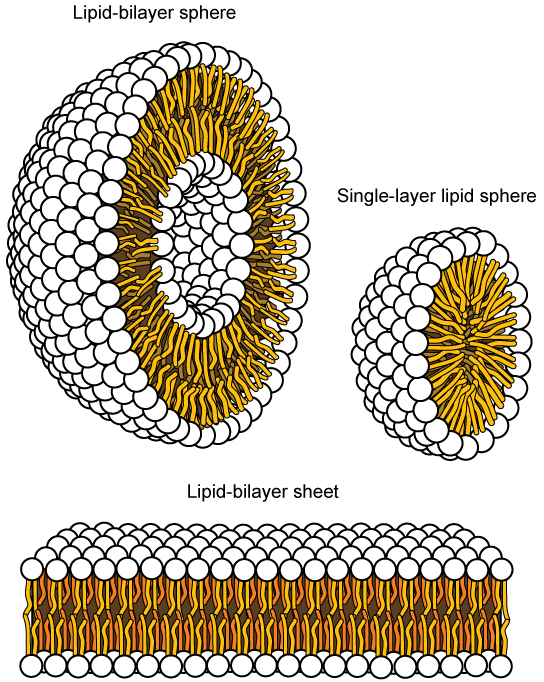
This characteristic is vital to the structure of a plasma membrane because, in water, phospholipids tend to become arranged with their hydrophobic tails facing each other and their hydrophilic heads facing out. In this way, they form a lipid bilayer—a barrier composed of a double layer of phospholipids that separates the water and other materials on one side of the barrier from the water and other materials on the other side. In fact, phospholipids heated in an aqueous solution tend to spontaneously form small spheres or droplets (called micelles or liposomes), with their hydrophilic heads forming the exterior and their hydrophobic tails on the inside ( [link] ).
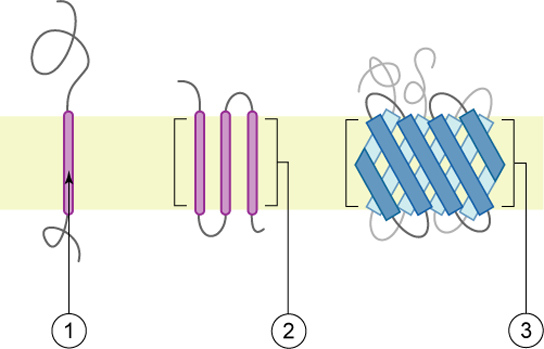
Proteins make up the second major component of plasma membranes. Integral proteins (some specialized types are called integrins) are, as their name suggests, integrated completely into the membrane structure, and their hydrophobic membrane-spanning regions interact with the hydrophobic region of the the phospholipid bilayer ( [link] ). Single-pass integral membrane proteins usually have a hydrophobic transmembrane segment that consists of 20–25 amino acids. Some span only part of the membrane—associating with a single layer—while others stretch from one side of the membrane to the other, and are exposed on either side. Some complex proteins are composed of up to 12 segments of a single protein, which are extensively folded and embedded in the membrane ( [link] ). This type of protein has a hydrophilic region or regions, and one or several mildly hydrophobic regions. This arrangement of regions of the protein tends to orient the protein alongside the phospholipids, with the hydrophobic region of the protein adjacent to the tails of the phospholipids and the hydrophilic region or regions of the protein protruding from the membrane and in contact with the cytosol or extracellular fluid.
Peripheral proteins are found on the exterior and interior surfaces of membranes, attached either to integral proteins or to phospholipids. Peripheral proteins, along with integral proteins, may serve as enzymes, as structural attachments for the fibers of the cytoskeleton, or as part of the cell’s recognition sites. These are sometimes referred to as “cell-specific” proteins. The body recognizes its own proteins and attacks foreign proteins associated with invasive pathogens.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology 2015' conversation and receive update notifications?