| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The kingdom of animals is informally divided into invertebrate animals, those without a backbone, and vertebrate animals, those with a backbone. Although in general we are most familiar with vertebrate animals, the vast majority of animal species, about 95 percent, are invertebrates. Invertebrates include a huge diversity of animals, millions of species in about 32 phyla, which we can just begin to touch on here.
The sponges and the cnidarians represent the simplest of animals. Sponges appear to represent an early stage of multicellularity in the animal clade. Although they have specialized cells for particular functions, they lack true tissues in which specialized cells are organized into functional groups. Sponges are similar to what might have been the ancestor of animals: colonial, flagellated protists. The cnidarians, or the jellyfish and their kin, are the simplest animal group that displays true tissues, although they possess only two tissue layers.
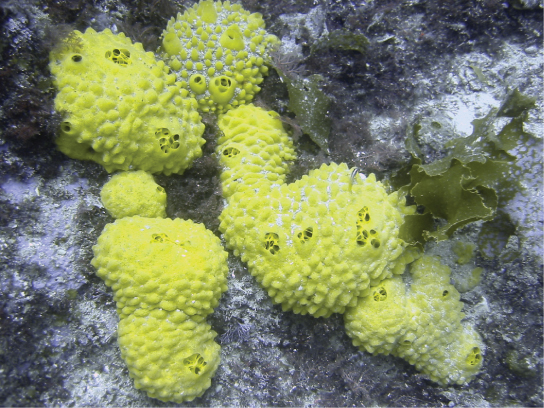
Animals in subkingdom Parazoa represent the simplest animals and include the sponges, or phylum Porifera ( [link] ). All sponges are aquatic and the majority of species are marine. Sponges live in intimate contact with water, which plays a role in their feeding, gas exchange, and excretion. Much of the body structure of the sponge is dedicated to moving water through the body so it can filter out food, absorb dissolved oxygen, and eliminate wastes.

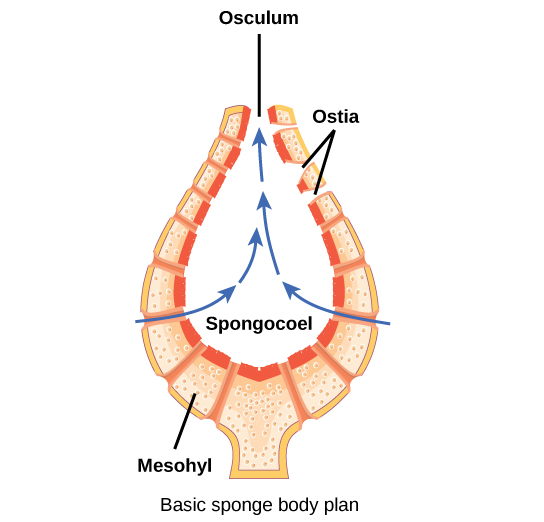
The body of the simplest sponges takes the shape of a cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel . Water enters the spongocoel from numerous pores in the body wall. Water flows out through a large opening called the osculum ( [link] ). However, sponges exhibit a diversity of body forms, which vary in the size and branching of the spongocoel, the number of osculi, and where the cells that filter food from the water are located.
Sponges consist of an outer layer of flattened cells and an inner layer of cells called choanocytes separated by a jelly-like substance called mesohyl . The mesohyl contains embedded amoeboid cells that secrete tiny needles called spicules or protein fibers that help give the sponge its structural strength. The cell body of the choanocyte is embedded in mesohyl but protruding into the spongocoel is a mesh-like collar surrounding a single flagellum. The beating of flagella from all choanocytes moves water through the sponge. Food particles are trapped in mucus produced by the sieve-like collar of the choanocytes and are ingested by phagocytosis. This process is called intracellular digestion . Amoebocytes take up nutrients repackaged in food vacuoles of the choanocytes and deliver them to other cells within the sponge.
Despite their lack of complexity, sponges are clearly successful organisms, having persisted on Earth for more than half a billion years. Lacking a true digestive system, sponges depend on the intracellular digestive processes of their choanocytes for their energy intake. The limit of this type of digestion is that food particles must be smaller than individual cells. Gas exchange, circulation, and excretion occur by diffusion between cells and the water.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for slcc biol 1010' conversation and receive update notifications?