| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many factors, typically physical or chemical in nature (abiotic), influence the mortality of a population regardless of its density, including weather, natural disasters, and pollution. An individual deer may be killed in a forest fire regardless of how many deer happen to be in that area. Its chances of survival are the same whether the population density is high or low. The same holds true for cold winter weather.
In real-life situations, population regulation is very complicated and density-dependent and independent factors can interact. A dense population that is reduced in a density-independent manner by some environmental factor(s) will be able to recover differently than a sparse population. For example, a population of deer affected by a harsh winter will recover faster if there are more deer remaining to reproduce.



It's easy to get lost in the discussion of dinosaurs and theories about why they went extinct 65 million years ago. Was it due to a meteor slamming into Earth near the coast of modern-day Mexico, or was it from some long-term weather cycle that is not yet understood? One hypothesis that will never be proposed is that humans had something to do with it. Mammals were small, insignificant creatures of the forest 65 million years ago, and no humans existed.
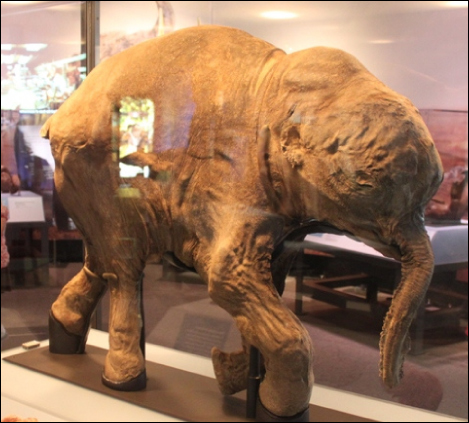
Woolly mammoths, however, began to go extinct about 10,000 years ago, when they shared the Earth with humans who were no different anatomically than humans today ( [link] ). Mammoths survived in isolated island populations as recently as 1700 BC. We know a lot about these animals from carcasses found frozen in the ice of Siberia and other regions of the north. Scientists have sequenced at least 50 percent of its genome and believe mammoths are between 98 and 99 percent identical to modern elephants.
It is commonly thought that climate change and human hunting led to their extinction. A 2008 study estimated that climate change reduced the mammoth’s range from 3,000,000 square miles 42,000 years ago to 310,000 square miles 6,000 years ago. David Nogués-Bravo et al., “Climate Change, Humans, and the Extinction of the Woolly Mammoth.” PLoS Biol 6 (April 2008): e79, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060079. It is also well documented that humans hunted these animals. A 2012 study showed that no single factor was exclusively responsible for the extinction of these magnificent creatures. G.M. MacDonald et al., “Pattern of Extinction of the Woolly Mammoth in Beringia.” Nature Communications 3, no. 893 (June 2012), doi:10.1038/ncomms1881. In addition to human hunting, climate change, and reduction of habitat, these scientists demonstrated another important factor in the mammoth’s extinction was the migration of humans across the Bering Strait to North America during the last ice age 20,000 years ago.
The maintenance of stable populations was and is very complex, with many interacting factors determining the outcome. It is important to remember that humans are also part of nature. Once we contributed to a species’ decline using primitive hunting technology only.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of georgia biology' conversation and receive update notifications?