| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

What do we mean when we say something is a wave? The most intuitive and easiest wave to imagine is the familiar water wave. More precisely, a wave is a disturbance that propagates, or moves from the place it was created. For water waves, the disturbance is in the surface of the water, perhaps created by a rock thrown into a pond or by a swimmer splashing the surface repeatedly. For sound waves, the disturbance is a change in air pressure, perhaps created by the oscillating cone inside a speaker. For earthquakes, there are several types of disturbances, including disturbance of Earth’s surface and pressure disturbances under the surface. Even radio waves are most easily understood using an analogy with water waves. Visualizing water waves is useful because there is more to it than just a mental image. Water waves exhibit characteristics common to all waves, such as amplitude, period, frequency and energy. All wave characteristics can be described by a small set of underlying principles.
A wave is a disturbance that propagates, or moves from the place it was created. The simplest waves repeat themselves for several cycles and are associated with simple harmonic motion. Let us start by considering the simplified water wave in [link] . The wave is an up and down disturbance of the water surface. It causes a sea gull to move up and down in simple harmonic motion as the wave crests and troughs (peaks and valleys) pass under the bird. The time for one complete up and down motion is the wave’s period . The wave’s frequency is , as usual. The wave itself moves to the right in the figure. This movement of the wave is actually the disturbance moving to the right, not the water itself (or the bird would move to the right). We define wave velocity to be the speed at which the disturbance moves. Wave velocity is sometimes also called the propagation velocity or propagation speed , because the disturbance propagates from one location to another.
Many people think that water waves push water from one direction to another. In fact, the particles of water tend to stay in one location, save for moving up and down due to the energy in the wave. The energy moves forward through the water, but the water stays in one place. If you feel yourself pushed in an ocean, what you feel is the energy of the wave, not a rush of water.
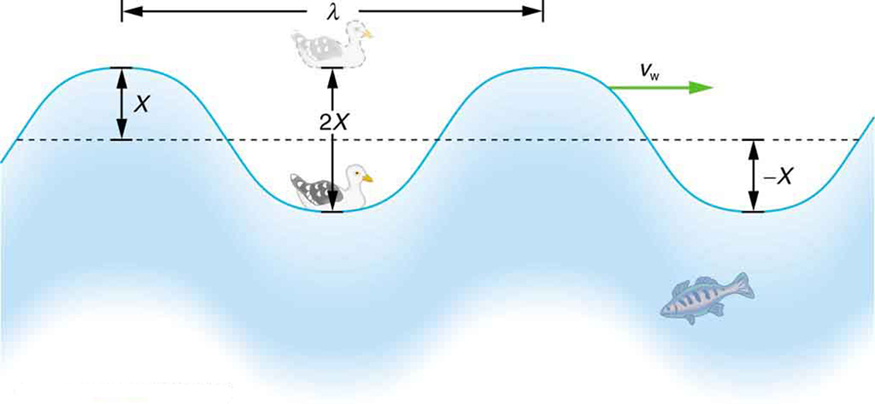
The water wave in the figure also has a length associated with it, called its wavelength , the distance between adjacent identical parts of a wave. ( is the distance parallel to the direction of propagation.) The speed of propagation is the distance the wave travels in a given time, which is one wavelength in the time of one period. In equation form, that is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics: physics of california' conversation and receive update notifications?