| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many complex circuits, such as the one in [link] , cannot be analyzed with the series-parallel techniques developed in Resistors in Series and Parallel and Electromotive Force: Terminal Voltage . There are, however, two circuit analysis rules that can be used to analyze any circuit, simple or complex. These rules are special cases of the laws of conservation of charge and conservation of energy. The rules are known as Kirchhoff’s rules , after their inventor Gustav Kirchhoff (1824–1887).
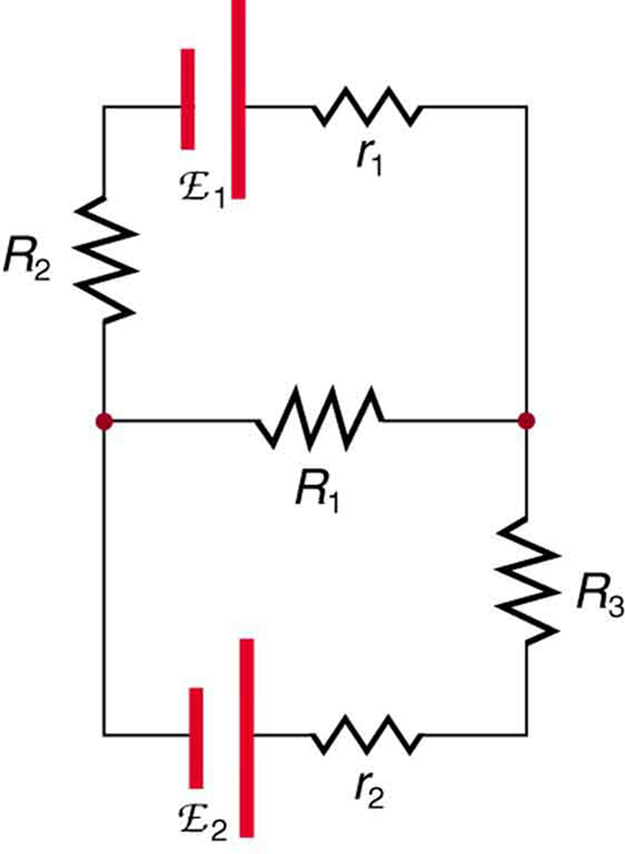
Explanations of the two rules will now be given, followed by problem-solving hints for applying Kirchhoff’s rules, and a worked example that uses them.
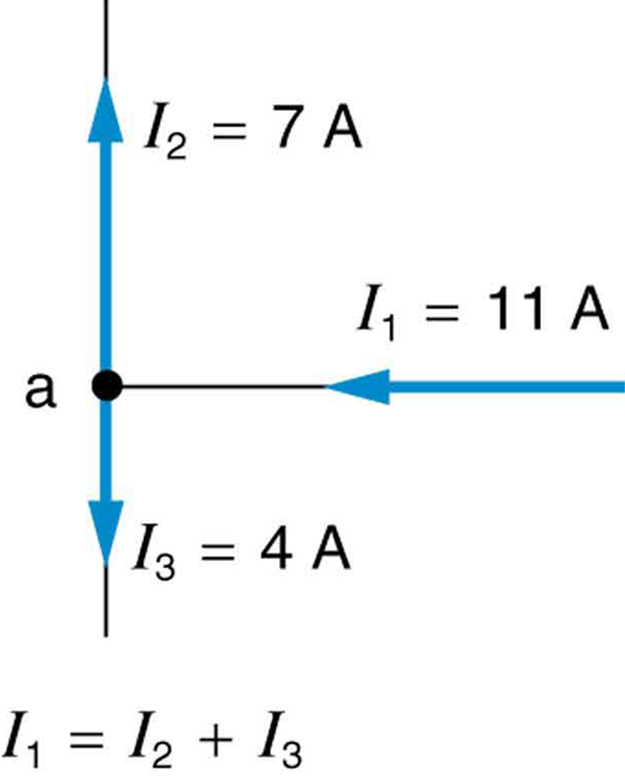
Kirchhoff’s first rule (the junction rule ) is an application of the conservation of charge to a junction; it is illustrated in [link] . Current is the flow of charge, and charge is conserved; thus, whatever charge flows into the junction must flow out. Kirchhoff’s first rule requires that (see figure). Equations like this can and will be used to analyze circuits and to solve circuit problems.
Kirchhoff’s rules for circuit analysis are applications of conservation laws to circuits. The first rule is the application of conservation of charge, while the second rule is the application of conservation of energy. Conservation laws, even used in a specific application, such as circuit analysis, are so basic as to form the foundation of that application.
Kirchhoff’s second rule (the loop rule ) is an application of conservation of energy. The loop rule is stated in terms of potential, , rather than potential energy, but the two are related since . Recall that emf is the potential difference of a source when no current is flowing. In a closed loop, whatever energy is supplied by emf must be transferred into other forms by devices in the loop, since there are no other ways in which energy can be transferred into or out of the circuit. [link] illustrates the changes in potential in a simple series circuit loop.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 101' conversation and receive update notifications?