| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The oscillations of a system in which the net force can be described by Hooke’s law are of special importance, because they are very common. They are also the simplest oscillatory systems. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is the name given to oscillatory motion for a system where the net force can be described by Hooke’s law, and such a system is called a simple harmonic oscillator . If the net force can be described by Hooke’s law and there is no damping (by friction or other non-conservative forces), then a simple harmonic oscillator will oscillate with equal displacement on either side of the equilibrium position, as shown for an object on a spring in [link] . The maximum displacement from equilibrium is called the amplitude . The units for amplitude and displacement are the same, but depend on the type of oscillation. For the object on the spring, the units of amplitude and displacement are meters; whereas for sound oscillations, they have units of pressure (and other types of oscillations have yet other units). Because amplitude is the maximum displacement, it is related to the energy in the oscillation.
Find a bowl or basin that is shaped like a hemisphere on the inside. Place a marble inside the bowl and tilt the bowl periodically so the marble rolls from the bottom of the bowl to equally high points on the sides of the bowl. Get a feel for the force required to maintain this periodic motion. What is the restoring force and what role does the force you apply play in the simple harmonic motion (SHM) of the marble?
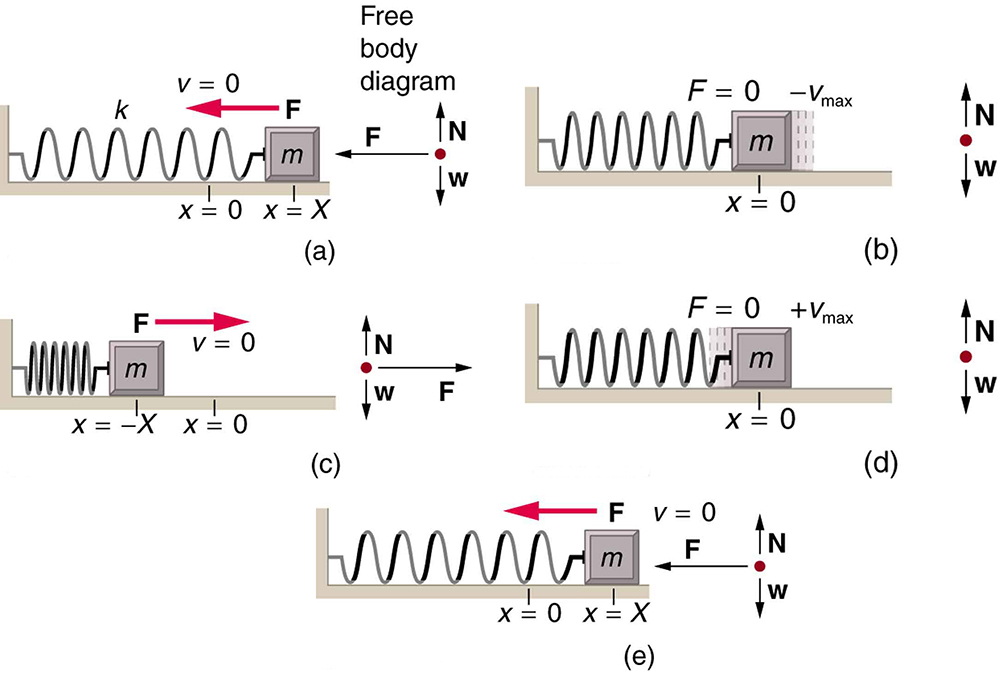
What is so significant about simple harmonic motion? One special thing is that the period and frequency of a simple harmonic oscillator are independent of amplitude. The string of a guitar, for example, will oscillate with the same frequency whether plucked gently or hard. Because the period is constant, a simple harmonic oscillator can be used as a clock.
Two important factors do affect the period of a simple harmonic oscillator. The period is related to how stiff the system is. A very stiff object has a large force constant , which causes the system to have a smaller period. For example, you can adjust a diving board’s stiffness—the stiffer it is, the faster it vibrates, and the shorter its period. Period also depends on the mass of the oscillating system. The more massive the system is, the longer the period. For example, a heavy person on a diving board bounces up and down more slowly than a light one.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics: physics of california' conversation and receive update notifications?