| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If two identical waves, each having an intensity of , interfere perfectly constructively, what is the intensity of the resulting wave?
Strategy
We know from Superposition and Interference that when two identical waves, which have equal amplitudes , interfere perfectly constructively, the resulting wave has an amplitude of . Because a wave’s intensity is proportional to amplitude squared, the intensity of the resulting wave is four times as great as in the individual waves.
Solution
Discussion
The intensity goes up by a factor of 4 when the amplitude doubles. This answer is a little disquieting. The two individual waves each have intensities of , yet their sum has an intensity of , which may appear to violate conservation of energy. This violation, of course, cannot happen. What does happen is intriguing. The area over which the intensity is is much less than the area covered by the two waves before they interfered. There are other areas where the intensity is zero. The addition of waves is not as simple as our first look in Superposition and Interference suggested. We actually get a pattern of both constructive interference and destructive interference whenever two waves are added. For example, if we have two stereo speakers putting out each, there will be places in the room where the intensity is , other places where the intensity is zero, and others in between. [link] shows what this interference might look like. We will pursue interference patterns elsewhere in this text.
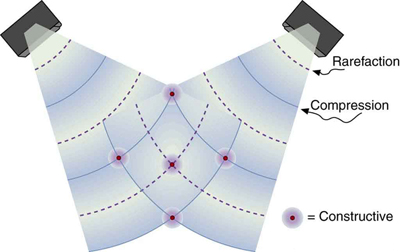
Which measurement of a wave is most important when determining the wave's intensity?
Amplitude, because a wave’s energy is directly proportional to its amplitude squared.
Intensity is defined to be the power per unit area:
and has units of .
Two identical waves undergo pure constructive interference. Is the resultant intensity twice that of the individual waves? Explain your answer.
Circular water waves decrease in amplitude as they move away from where a rock is dropped. Explain why.
Medical Application
Ultrasound of intensity is produced by the rectangular head of a medical imaging device measuring 3.00 by 5.00 cm. What is its power output?
0.225 W
The low-frequency speaker of a stereo set has a surface area of and produces 1W of acoustical power. What is the intensity at the speaker? If the speaker projects sound uniformly in all directions, at what distance from the speaker is the intensity ?
To increase intensity of a wave by a factor of 50, by what factor should the amplitude be increased?
7.07
Engineering Application
A device called an insolation meter is used to measure the intensity of sunlight has an area of 100 cm 2 and registers 6.50 W. What is the intensity in ?
Astronomy Application
Energy from the Sun arrives at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere with an intensity of How long does it take for to arrive on an area of ?
16.0 d
Suppose you have a device that extracts energy from ocean breakers in direct proportion to their intensity. If the device produces 10.0 kW of power on a day when the breakers are 1.20 m high, how much will it produce when they are 0.600 m high?
2.50 kW
Engineering Application
(a) A photovoltaic array of (solar cells) is 10.0% efficient in gathering solar energy and converting it to electricity. If the average intensity of sunlight on one day is what area should your array have to gather energy at the rate of 100 W? (b) What is the maximum cost of the array if it must pay for itself in two years of operation averaging 10.0 hours per day? Assume that it earns money at the rate of 9.00 ¢ per kilowatt-hour.
A microphone receiving a pure sound tone feeds an oscilloscope, producing a wave on its screen. If the sound intensity is originally but is turned up until the amplitude increases by 30.0%, what is the new intensity?
Medical Application
(a) What is the intensity in of a laser beam used to burn away cancerous tissue that, when 90.0% absorbed, puts 500 J of energy into a circular spot 2.00 mm in diameter in 4.00 s? (b) Discuss how this intensity compares to the average intensity of sunlight (about ) and the implications that would have if the laser beam entered your eye. Note how your answer depends on the time duration of the exposure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics: physics of california' conversation and receive update notifications?