| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
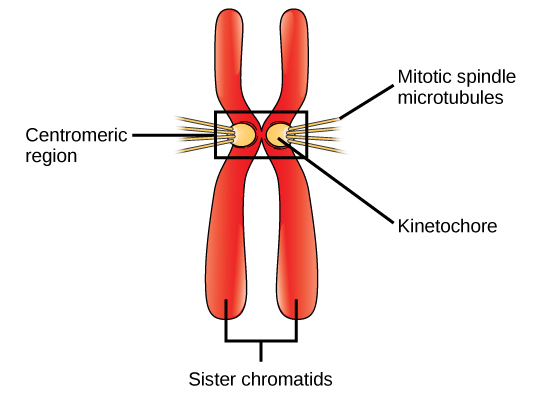
During metaphase , all the chromosomes are aligned in a plane called the metaphase plate , or the equatorial plane, midway between the two poles of the cell. The sister chromatids are still tightly attached to each other by cohesin proteins. At this time, the chromosomes are maximally condensed.
During anaphase , the cohesin proteins degrade, and the sister chromatids separate at the centromere. Each chromatid, now called a chromosome, is pulled rapidly toward the centrosome to which its microtubule is attached. The cell becomes visibly elongated (oval shaped) as the polar microtubules slide against each other at the metaphase plate where they overlap.
During telophase , the chromosomes reach the opposite poles and begin to decondense (unravel), relaxing into a chromatin configuration. The mitotic spindles are depolymerized into tubulin monomers that will be used to assemble cytoskeletal components for each daughter cell. Nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and cytokinesis occurs.
Cytokinesis , or “cell motion,” is part of telophase, during which cell division is completed via the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells. Division is not complete until the cell components have been apportioned and completely separated into the two daughter cells. Although the stages of mitosis are similar for most eukaryotes, the process of cytokinesis is quite different for eukaryotes that have cell walls, such as plant cells.
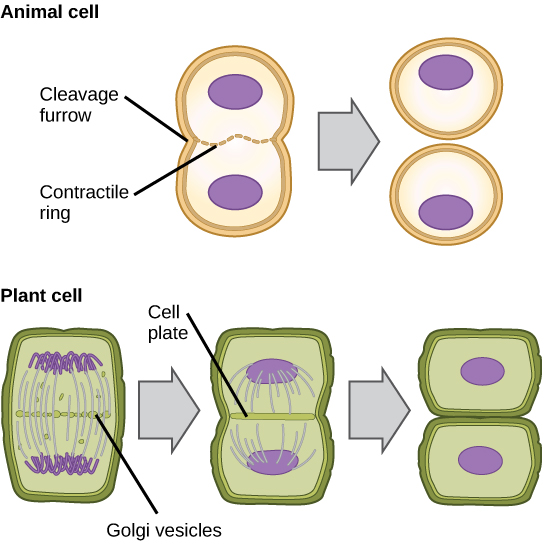
In cells such as animal cells that lack cell walls, cytokinesis follows the onset of anaphase. A contractile ring composed of actin filaments forms just inside the plasma membrane at the former metaphase plate. The actin filaments pull the equator of the cell inward, forming a fissure. This fissure, or “crack,” is called the cleavage furrow . The furrow deepens as the actin ring contracts, and eventually the membrane is cleaved in two ( [link] ).
In plant cells, a new cell wall must form between the daughter cells. During interphase, the Golgi apparatus accumulates enzymes, structural proteins, and glucose molecules prior to breaking into vesicles and dispersing throughout the dividing cell. During telophase, these Golgi vesicles are moved to the metaphase plate. There, the vesicles fuse from the center toward the cell walls; this structure is called a cell plate . As more vesicles fuse, the cell plate enlarges until it merges with the cell walls at the periphery of the cell. Enzymes use the glucose that has accumulated between the membrane layers to build a new cell wall. The Golgi membranes become parts of the plasma membrane on either side of the new cell wall ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?