| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Work in groups of four. Each group will need a raybox (or torch) with slit, triangular glass prism and protractor. If you do not have a raybox, use a torch and stick two pieces of tape over the lens so that only a thin beam of light is visible.
Aim:
To investigate total internal reflection.
Method:
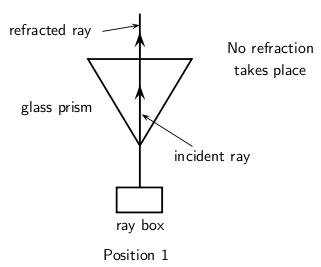
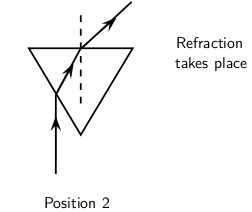
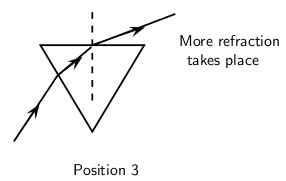
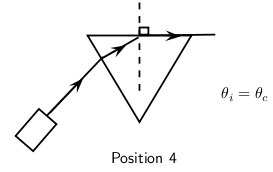
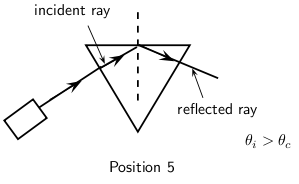
When we increase the angle of incidence, we reach a point where the angle of refraction is 90 and the refracted ray runs along the surface of the medium. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle.
The critical angle is the angle of incidence where the angle of reflection is 90 . The light must shine from a dense to a less dense medium.
If the angle of incidence is bigger than this critical angle, the refracted ray will not emerge from the medium, but will be reflected back into the medium. This is called total internal reflection.
Total internal reflection takes place when
Total internal reflection takes place when light is reflected back into the medium because the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
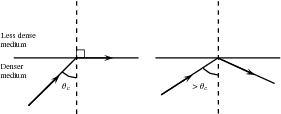
Each medium has its own unique critical angle. For example, the critical angle for glass is 42 , and that of water is 48,8 . We can calculate the critical angle for any medium.
Now we shall learn how to derive the value of the critical angle for two given media. The process is fairly simple and involves just the use of Snell's Law that we have already studied. To recap, Snell's Law states:
where is the refractive index of material 1, is the refractive index of material 2, is the angle of incidence and is the angle of refraction. For total internal reflection we know that the angle of incidence is the critical angle. So,
However, we also know that the angle of refraction at the critical angle is 90 . So we have:
We can then write Snell's Law as:
Solving for gives:
Khan academy video on refraction - 1
Given that the refractive indices of air and water are 1 and 1,33, respectively, find the critical angle.
We know that the critical angle is given by:
The critical angle for light travelling from water to air is .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?