| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most nematodes have four nerve cords that run along the length of the body on the top, bottom, and sides. The nerve cords fuse in a ring around the pharynx, to form a head ganglion or “brain” of the worm, as well as at the posterior end to form the tail ganglion. Beneath the epidermis lies a layer of longitudinal muscles that permits only side-to-side, wave-like undulation of the body.
View this video to see nematodes move about and feed on bacteria.
Nematodes employ a diversity of sexual reproductive strategies depending on the species; they may be monoecious, dioecious (separate sexes), or may reproduce asexually by parthenogenesis. Caenorhabditis elegans is nearly unique among animals in having both self-fertilizing hermaphrodites and a male sex that can mate with the hermaphrodite.
The name “arthropoda” means “jointed legs,” which aptly describes each of the enormous number of species belonging to this phylum. Arthropoda dominate the animal kingdom with an estimated 85 percent of known species, with many still undiscovered or undescribed. The principal characteristics of all the animals in this phylum are functional segmentation of the body and the presence of jointed appendages ( [link] ). As members of Ecdysozoa, arthropods also have an exoskeleton made principally of chitin. Arthropoda is the largest phylum in the animal world in terms of numbers of species, and insects form the single largest group within this phylum. Arthropods are true coelomate animals and exhibit prostostomic development.

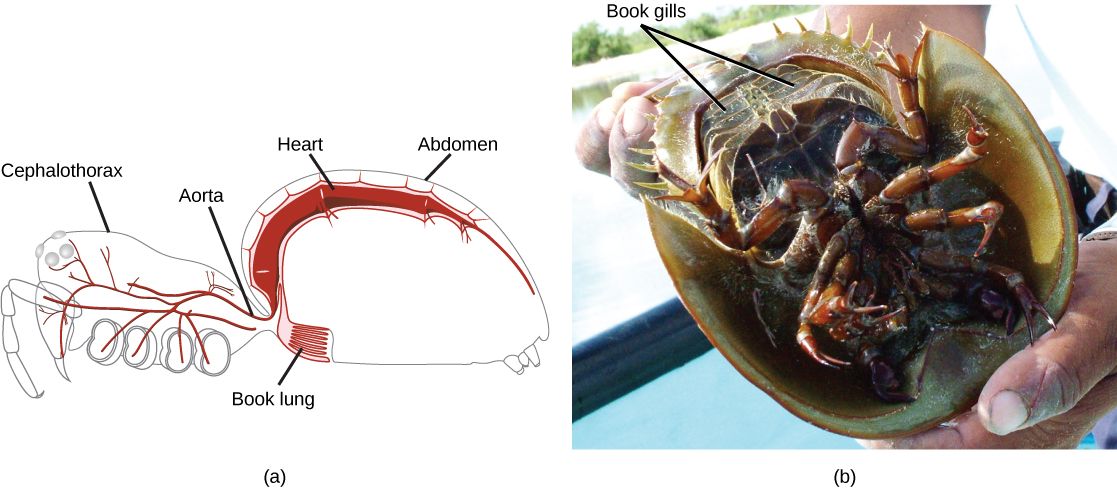
A unique feature of arthropods is the presence of a segmented body with fusion of certain sets of segments to give rise to functional segments. Fused segments may form a head, thorax, and abdomen, or a cephalothorax and abdomen, or a head and trunk. The coelom takes the form of a hemocoel (or blood cavity). The open circulatory system, in which blood bathes the internal organs rather than circulating in vessels, is regulated by a two-chambered heart. Respiratory systems vary, depending on the group of arthropod: Insects and myriapods use a series of tubes ( tracheae ) that branch throughout the body, open to the outside through openings called spiracles , and perform gas exchange directly between the cells and air in the tracheae. Aquatic crustaceans use gills, arachnids employ “book lungs,” and aquatic chelicerates use “book gills.” The book lungs of arachnids are internal stacks of alternating air pockets and hemocoel tissue shaped like the pages of a book. The book gills of crustaceans are external structures similar to book lungs with stacks of leaf-like structures that exchange gases with the surrounding water ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nsc 1406: contemporary biology' conversation and receive update notifications?