| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
From their humble and still obscure beginning during the early Jurassic period (202–145.5 MYA), the angiosperms, or flowering plants, have successfully evolved to dominate most terrestrial ecosystems. Angiosperms include a staggering number of genera and species; with more than 260,000 species, the division is second only to insects in terms of diversification ( [link] ).

Angiosperm success is a result of two novel structures that ensure reproductive success: flowers and fruit. Flowers allowed plants to form cooperative evolutionary relationships with animals, in particular insects, to disperse their pollen to female gametophytes in a highly targeted way. Fruit protect the developing embryo and serve as an agent of dispersal. Different structures on fruit reflect the dispersal strategies that help with the spreading of seeds.
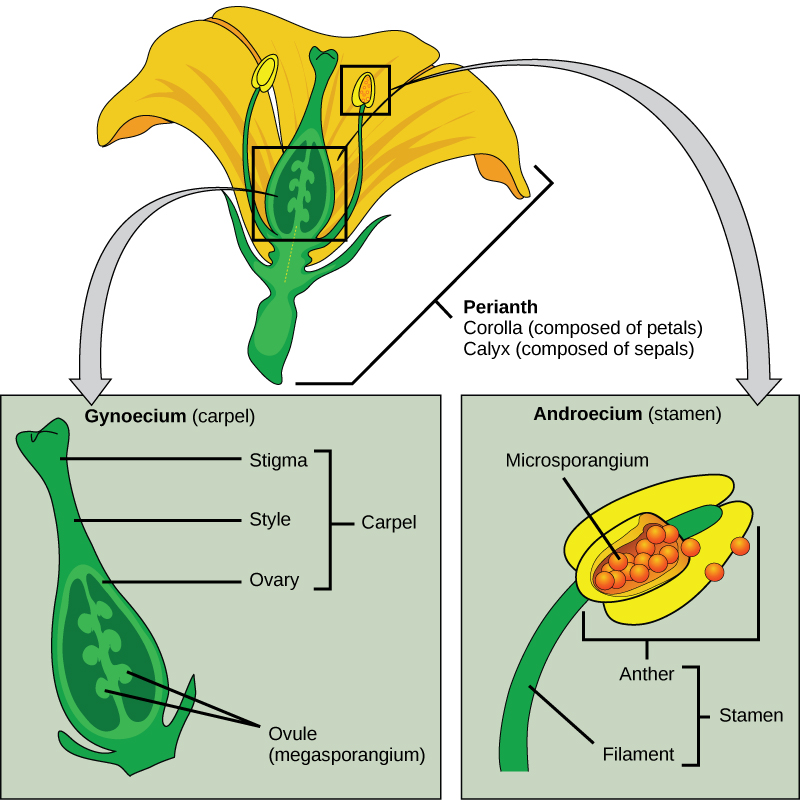
Flowers are modified leaves or sporophylls organized around a central stalk. Although they vary greatly in appearance, all flowers contain the same structures: sepals, petals, pistils, and stamens. A whorl of sepals (the calyx ) is located at the base of the peduncle, or stem, and encloses the floral bud before it opens. Sepals are usually photosynthetic organs, although there are some exceptions. For example, the corolla in lilies and tulips consists of three sepals and three petals that look virtually identical—this led botanists to coin the word tepal. Petals (collectively the corolla ) are located inside the whorl of sepals and usually display vivid colors to attract pollinators. Flowers pollinated by wind are usually small and dull. The sexual organs are located at the center of the flower.
As illustrated in [link] , the stigma, style, and ovary constitute the female organ, the carpel or pistil , which is also referred to as the gynoecium . A gynoecium may contain one or more carpels within a single flower. The megaspores and the female gametophytes are produced and protected by the thick tissues of the carpel. A long, thin structure called a style leads from the sticky stigma , where pollen is deposited, to the ovary enclosed in the carpel. The ovary houses one or more ovules that will each develop into a seed upon fertilization. The male reproductive organs, the androecium or stamens , surround the central carpel. Stamens are composed of a thin stalk called a filament and a sac-like structure, the anther , in which microspores are produced by meiosis and develop into pollen grains. The filament supports the anther.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nsc 1406: contemporary biology' conversation and receive update notifications?