| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In general, populations of one species never live in isolation from populations of other species. The interacting populations occupying a given habitat form an ecological community. The number of species occupying the same habitat and their relative abundance is known as the diversity of the community. Areas with low species diversity, such as the glaciers of Antarctica, still contain a wide variety of living organisms, whereas the diversity of tropical rainforests is so great that it cannot be accurately assessed. Scientists study ecology at the community level to understand how species interact with each other and compete for the same resources.
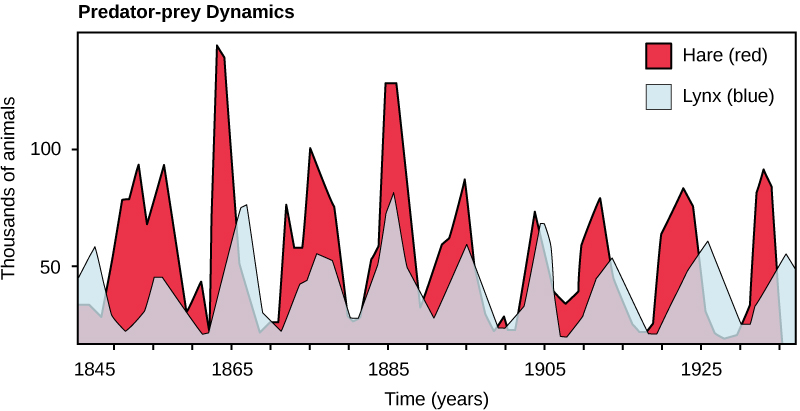
Perhaps the classical example of species interaction is the predator-prey relationship. The narrowest definition of the predator-prey interaction describes individuals of one population that kill and then consume the individuals of another population. Population sizes of predators and prey in a community are not constant over time, and they may vary in cycles that appear to be related. The most often cited example of predator-prey population dynamics is seen in the cycling of the lynx (predator) and the snowshoe hare (prey), using 100 years of trapping data from North America ( [link] ). This cycling of predator and prey population sizes has a period of approximately ten years, with the predator population lagging one to two years behind the prey population. An apparent explanation for this pattern is that as the hare numbers increase, there is more food available for the lynx, allowing the lynx population to increase as well. When the lynx population grows to a threshold level, however, they kill so many hares that hare numbers begin to decline, followed by a decline in the lynx population because of scarcity of food. When the lynx population is low, the hare population size begins to increase due, in part, to low predation pressure, starting the cycle anew.
Predation and predator avoidance are strong selective agents. Any heritable character that allows an individual of a prey population to better evade its predators will be represented in greater numbers in later generations. Likewise, traits that allow a predator to more efficiently locate and capture its prey will lead to a greater number of offspring and an increase in the commonness of the trait within the population. Such ecological relationships between specific populations lead to adaptations that are driven by reciprocal evolutionary responses in those populations. Species have evolved numerous mechanisms to escape predation and herbivory (the consumption of plants for food). Defenses may be mechanical, chemical, physical, or behavioral.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for the university of georgia' conversation and receive update notifications?