| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plants obtain inorganic elements from the soil, which serves as a natural medium for land plants. Soil is the outer loose layer that covers the surface of Earth. Soil quality is a major determinant, along with climate, of plant distribution and growth. Soil quality depends not only on the chemical composition of the soil, but also the topography (regional surface features) and the presence of living organisms. In agriculture, the history of the soil, such as the cultivating practices and previous crops, modify the characteristics and fertility of that soil.
Soil develops very slowly over long periods of time, and its formation results from natural and environmental forces acting on mineral, rock, and organic compounds. Soils can be divided into two groups: organic soils are those that are formed from sedimentation and primarily composed of organic matter, while those that are formed from the weathering of rocks and are primarily composed of inorganic material are called mineral soils . Mineral soils are predominant in terrestrial ecosystems, where soils may be covered by water for part of the year or exposed to the atmosphere.
Soil consists of these major components ( [link] ):
The amount of each of the four major components of soil depends on the amount of vegetation, soil compaction, and water present in the soil. A good healthy soil has sufficient air, water, minerals, and organic material to promote and sustain plant life.
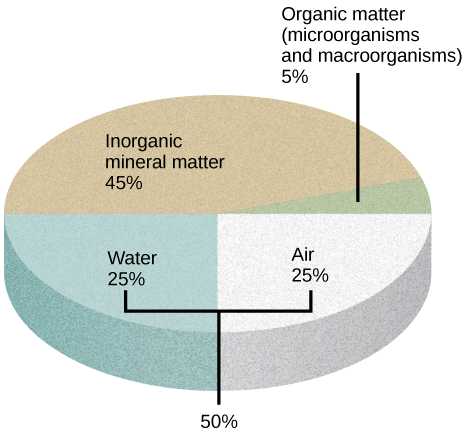
Soil compaction can result when soil is compressed by heavy machinery or even foot traffic. How might this compaction change the soil composition?
The organic material of soil, called humus , is made up of microorganisms (dead and alive), and dead animals and plants in varying stages of decay. Humus improves soil structure and provides plants with water and minerals. The inorganic material of soil consists of rock, slowly broken down into smaller particles that vary in size. Soil particles that are 0.1 to 2 mm in diameter are sand . Soil particles between 0.002 and 0.1 mm are called silt , and even smaller particles, less than 0.002 mm in diameter, are called clay . Some soils have no dominant particle size and contain a mixture of sand, silt, and humus; these soils are called loams .
Explore this interactive map from the USDA’s National Cooperative Soil Survey to access soil data for almost any region in the United States.
Soil formation is the consequence of a combination of biological, physical, and chemical processes. Soil should ideally contain 50 percent solid material and 50 percent pore space. About one-half of the pore space should contain water, and the other half should contain air. The organic component of soil serves as a cementing agent, returns nutrients to the plant, allows soil to store moisture, makes soil tillable for farming, and provides energy for soil microorganisms. Most soil microorganisms—bacteria, algae, or fungi—are dormant in dry soil, but become active once moisture is available.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology ii' conversation and receive update notifications?