| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
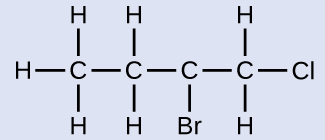
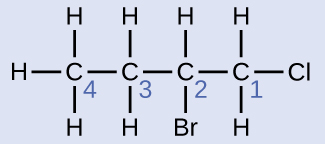
The four-carbon chain is numbered from the end with the chlorine atom. This puts the substituents on positions 1 and 2 (numbering from the other end would put the substituents on positions 3 and 4). Four carbon atoms means that the base name of this compound will be butane. The bromine at position 2 will be described by adding 2-bromo-; this will come at the beginning of the name, since bromo- comes before chloro- alphabetically. The chlorine at position 1 will be described by adding 1-chloro-, resulting in the name of the molecule being 2-bromo-1-chlorobutane.
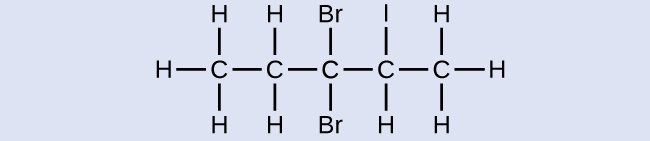
3,3-dibromo-2-iodopentane
We call a substituent that contains one less hydrogen than the corresponding alkane an alkyl group. The name of an alkyl group is obtained by dropping the suffix -ane of the alkane name and adding -yl :
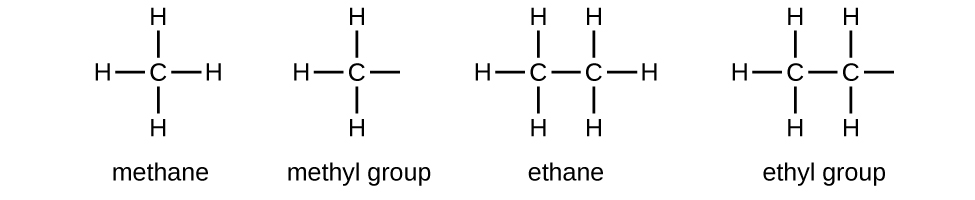
The open bonds in the methyl and ethyl groups indicate that these alkyl groups are bonded to another atom.
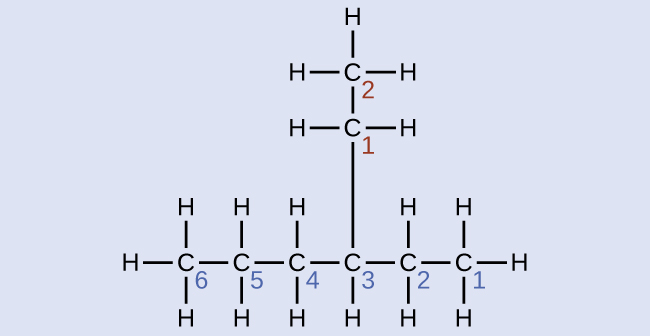
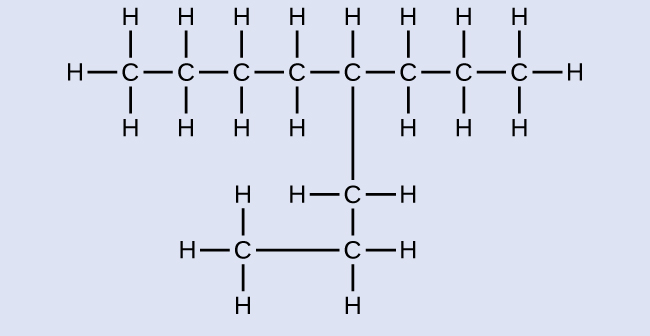
4-propyloctane
Some hydrocarbons can form more than one type of alkyl group when the hydrogen atoms that would be removed have different “environments” in the molecule. This diversity of possible alkyl groups can be identified in the following way: The four hydrogen atoms in a methane molecule are equivalent; they all have the same environment. They are equivalent because each is bonded to a carbon atom (the same carbon atom) that is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. (It may be easier to see the equivalency in the ball and stick models in [link] . Removal of any one of the four hydrogen atoms from methane forms a methyl group. Likewise, the six hydrogen atoms in ethane are equivalent ( [link] ) and removing any one of these hydrogen atoms produces an ethyl group. Each of the six hydrogen atoms is bonded to a carbon atom that is bonded to two other hydrogen atoms and a carbon atom. However, in both propane and 2–methylpropane, there are hydrogen atoms in two different environments, distinguished by the adjacent atoms or groups of atoms:
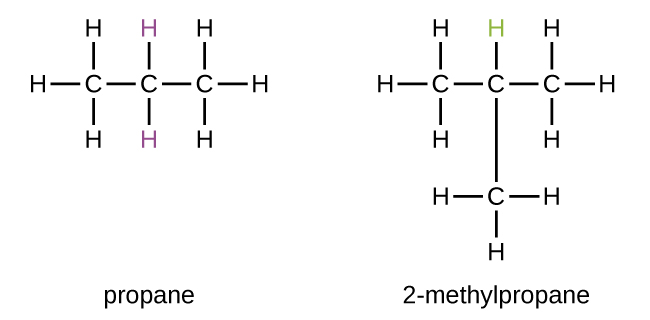
Each of the six equivalent hydrogen atoms of the first type in propane and each of the nine equivalent hydrogen atoms of that type in 2-methylpropane (all shown in black) are bonded to a carbon atom that is bonded to only one other carbon atom. The two purple hydrogen atoms in propane are of a second type. They differ from the six hydrogen atoms of the first type in that they are bonded to a carbon atom bonded to two other carbon atoms. The green hydrogen atom in 2-methylpropane differs from the other nine hydrogen atoms in that molecule and from the purple hydrogen atoms in propane. The green hydrogen atom in 2-methylpropane is bonded to a carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms. Two different alkyl groups can be formed from each of these molecules, depending on which hydrogen atom is removed. The names and structures of these and several other alkyl groups are listed in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?