| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
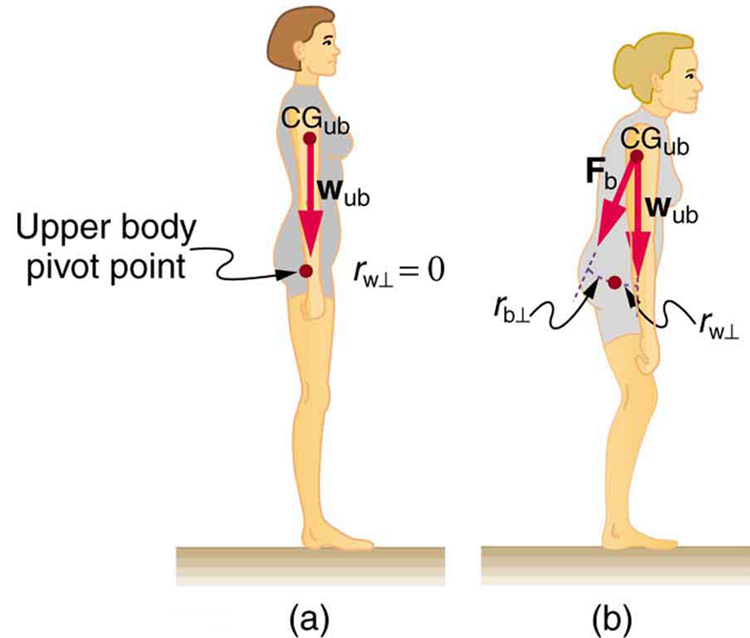
[link] shows how bad posture causes back strain. In part (a), we see a person with good posture. Note that her upper body’s cg is directly above the pivot point in the hips, which in turn is directly above the base of support at her feet. Because of this, her upper body’s weight exerts no torque about the hips. The only force needed is a vertical force at the hips equal to the weight supported. No muscle action is required, since the bones are rigid and transmit this force from the floor. This is a position of unstable equilibrium, but only small forces are needed to bring the upper body back to vertical if it is slightly displaced. Bad posture is shown in part (b); we see that the upper body’s cg is in front of the pivot in the hips. This creates a clockwise torque around the hips that is counteracted by muscles in the lower back. These muscles must exert large forces, since they have typically small mechanical advantages. (In other words, the perpendicular lever arm for the muscles is much smaller than for the cg.) Poor posture can also cause muscle strain for people sitting at their desks using computers. Special chairs are available that allow the body’s CG to be more easily situated above the seat, to reduce back pain. Prolonged muscle action produces muscle strain. Note that the cg of the entire body is still directly above the base of support in part (b) of [link] . This is compulsory; otherwise the person would not be in equilibrium. We lean forward for the same reason when carrying a load on our backs, to the side when carrying a load in one arm, and backward when carrying a load in front of us, as seen in [link] .
You have probably been warned against lifting objects with your back. This action, even more than bad posture, can cause muscle strain and damage discs and vertebrae, since abnormally large forces are created in the back muscles and spine.
Consider the person lifting a heavy box with his back, shown in [link] . (a) Calculate the magnitude of the force in the back muscles that is needed to support the upper body plus the box and compare this with his weight. The mass of the upper body is 55.0 kg and the mass of the box is 30.0 kg. (b) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the vertebrae on the spine at the indicated pivot point. Again, data in the figure may be taken to be accurate to three significant figures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Une: physics for the health professions' conversation and receive update notifications?