| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Compliance with the contraceptive method is a strong contributor to the success or failure rate of any particular method. The only method that is completely effective at preventing conception is abstinence. The choice of contraceptive method depends on the goals of the woman or couple. Tubal ligation and vasectomy are considered permanent prevention, while other methods are reversible and provide short-term contraception.
Termination of an existing pregnancy can be spontaneous or voluntary. Spontaneous termination is a miscarriage and usually occurs very early in the pregnancy, usually within the first few weeks. This occurs when the fetus cannot develop properly and the gestation is naturally terminated. Voluntary termination of a pregnancy is an abortion. Laws regulating abortion vary between states and tend to view fetal viability as the criteria for allowing or preventing the procedure.
Infertility is the inability to conceive a child or carry a child to birth. About 75 percent of causes of infertility can be identified; these include diseases, such as sexually transmitted diseases that can cause scarring of the reproductive tubes in either men or women, or developmental problems frequently related to abnormal hormone levels in one of the individuals. Inadequate nutrition, especially starvation, can delay menstruation. Stress can also lead to infertility. Short-term stress can affect hormone levels, while long-term stress can delay puberty and cause less frequent menstrual cycles. Other factors that affect fertility include toxins (such as cadmium), tobacco smoking, marijuana use, gonadal injuries, and aging.
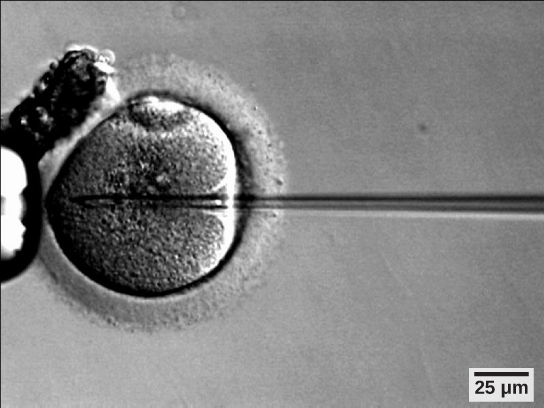
If infertility is identified, several assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are available to aid conception. A common type of ART is in vitro fertilization (IVF) where an egg and sperm are combined outside the body and then placed in the uterus. Eggs are obtained from the woman after extensive hormonal treatments that prepare mature eggs for fertilization and prepare the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg. Sperm are obtained from the man and they are combined with the eggs and supported through several cell divisions to ensure viability of the zygotes. When the embryos have reached the eight-cell stage, one or more is implanted into the woman’s uterus. If fertilization is not accomplished by simple IVF, a procedure that injects the sperm into an egg can be used. This is called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and is shown in [link] . IVF procedures produce a surplus of fertilized eggs and embryos that can be frozen and stored for future use. The procedures can also result in multiple births.
Human pregnancy begins with fertilization of an egg and proceeds through the three trimesters of gestation. The labor process has three stages (contractions, delivery of the fetus, expulsion of the placenta), each propelled by hormones. The first trimester lays down the basic structures of the body, including the limb buds, heart, eyes, and the liver. The second trimester continues the development of all of the organs and systems. The third trimester exhibits the greatest growth of the fetus and culminates in labor and delivery. Prevention of a pregnancy can be accomplished through a variety of methods including barriers, hormones, or other means. Assisted reproductive technologies may help individuals who have infertility problems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of georgia concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?