| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
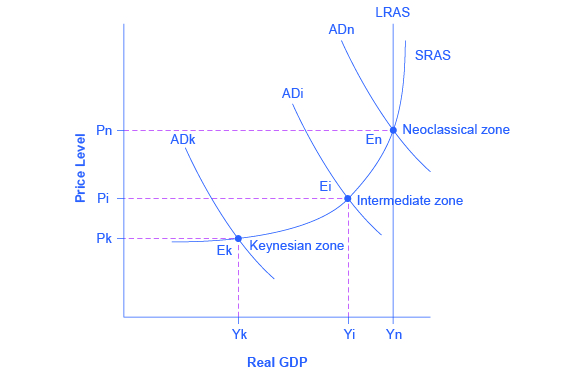
The simplified AD/AS model that we have used so far is fully consistent with Keynes’s original model. More recent research, though, has indicated that in the real world, an aggregate supply curve is more curved than the right angle used in this chapter. Rather, the real-world AS curve is very flat at levels of output far below potential (“the Keynesian zone”), very steep at levels of output above potential (“the neoclassical zone”) and curved in between (“the intermediate zone”). This is illustrated in [link] . The typical aggregate supply curve leads to the concept of the Phillips curve.
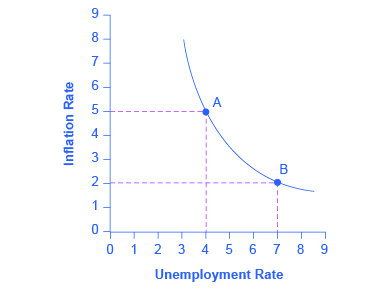
In the 1950s, A.W. Phillips , an economist at the London School of Economics, was studying the Keynesian analytical framework. The Keynesian theory implied that during a recession inflationary pressures are low, but when the level of output is at or even pushing beyond potential GDP, the economy is at greater risk for inflation. Phillips analyzed 60 years of British data and did find that tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, which became known as a Phillips curve . [link] shows a theoretical Phillips curve, and the following Work It Out feature shows how the pattern appears for the United States.
Step 1. Go to this website to see the 2005 Economic Report of the President.
Step 2. Scroll down and locate Table B-63 in the Appendices. This table is titled “Changes in special consumer price indexes, 1960–2004.”
Step 3. Download the table in Excel by selecting the XLS option and then selecting the location in which to save the file.
Step 4. Open the downloaded Excel file.
Step 5. View the third column (labeled “Year to year”). This is the inflation rate, measured by the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index.
Step 6. Return to the website and scroll to locate the Appendix Table B-42 “Civilian unemployment rate, 1959–2004.
Step 7. Download the table in Excel.
Step 8. Open the downloaded Excel file and view the second column. This is the overall unemployment rate.
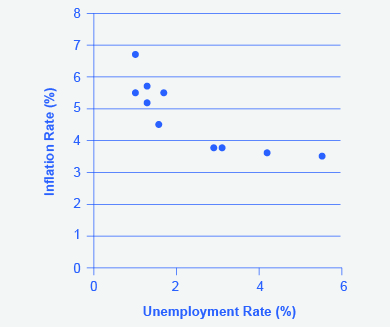
Step 9. Using the data available from these two tables, plot the Phillips curve for 1960–69, with unemployment rate on the x-axis and the inflation rate on the y-axis. Your graph should look like [link] .
Step 10. Plot the Phillips curve for 1960–1979. What does the graph look like? Do you still see the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment? Your graph should look like [link] .
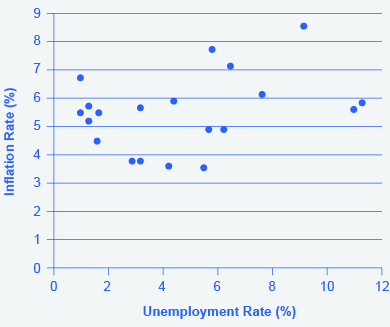
Over this longer period of time, the Phillips curve appears to have shifted out. There is no tradeoff any more.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of macroeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?