| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
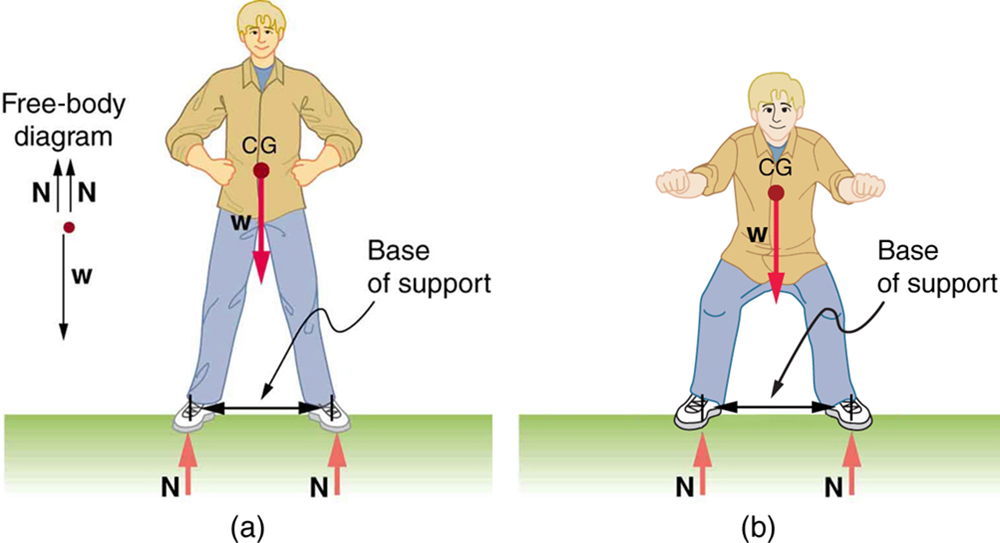
When we consider how far a system in stable equilibrium can be displaced before it becomes unstable, we find that some systems in stable equilibrium are more stable than others. The pencil in [link] and the person in [link] (a) are in stable equilibrium, but become unstable for relatively small displacements to the side. The critical point is reached when the cg is no longer above the base of support. Additionally, since the cg of a person’s body is above the pivots in the hips, displacements must be quickly controlled. This control is a central nervous system function that is developed when we learn to hold our bodies erect as infants. For increased stability while standing, the feet should be spread apart, giving a larger base of support. Stability is also increased by lowering one’s center of gravity by bending the knees, as when a football player prepares to receive a ball or braces themselves for a tackle. A cane, a crutch, or a walker increases the stability of the user, even more as the base of support widens. Usually, the cg of a female is lower (closer to the ground) than a male. Young children have their center of gravity between their shoulders, which increases the challenge of learning to walk.
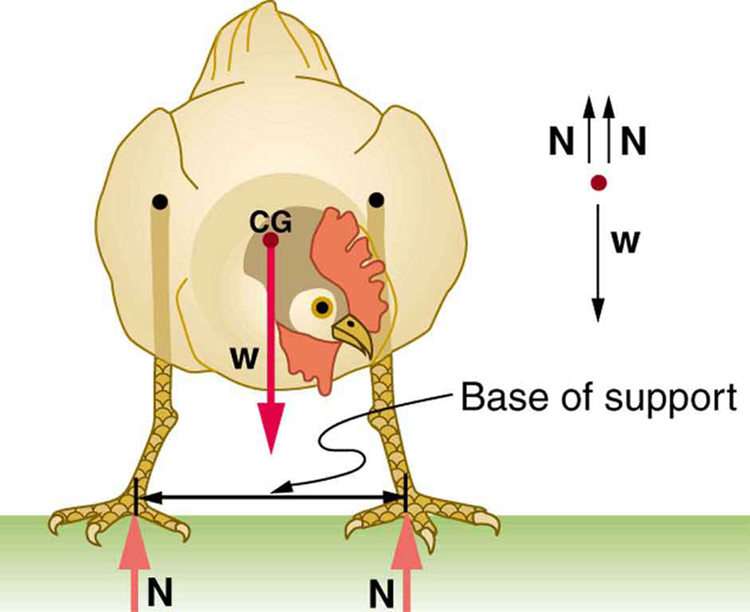
Animals such as chickens have easier systems to control. [link] shows that the cg of a chicken lies below its hip joints and between its widely separated and broad feet. Even relatively large displacements of the chicken’s cg are stable and result in restoring forces and torques that return the cg to its equilibrium position with little effort on the chicken’s part. Not all birds are like chickens, of course. Some birds, such as the flamingo, have balance systems that are almost as sophisticated as that of humans.
[link] shows that the cg of a chicken is below the hip joints and lies above a broad base of support formed by widely-separated and large feet. Hence, the chicken is in very stable equilibrium, since a relatively large displacement is needed to render it unstable. The body of the chicken is supported from above by the hips and acts as a pendulum between the hips. Therefore, the chicken is stable for front-to-back displacements as well as for side-to-side displacements.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Une: physics for the health professions' conversation and receive update notifications?