| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One-Way ANOVA: Four sororities took a random sample of sisters regarding their grade means for the past term. The results are shown below:
| MEAN GRADES FOR FOUR SORORITIES | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sorority 1 | Sorority 2 | Sorority 3 | Sorority 4 |
| 2.17 | 2.63 | 2.63 | 3.79 |
| 1.85 | 1.77 | 3.78 | 3.45 |
| 2.83 | 3.25 | 4.00 | 3.08 |
| 1.69 | 1.86 | 2.55 | 2.26 |
| 3.33 | 2.21 | 2.45 | 3.18 |
Using a significance level of 1%, is there a difference in mean grades among the sororities?
Let
,
,
,
be the population means of the sororities. Remember that the null
hypothesis claims that the sorority groups are from the same normal distribution.The alternate hypothesis says that at least two of the sorority groups come from
populations with different normal distributions. Notice that the four sample sizes areeach size 5.
: Not all of the means are equal.
Distribution for the test:
where and
Calculate the test statistic:
Graph:
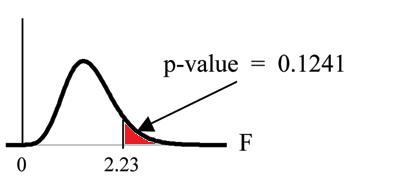
Probability statement:
Compare and the :
Make a decision: Since , you cannot reject .
Conclusion: There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a difference among the mean grades for the sororities.
TI-83+ or TI 84: Put the data into lists L1, L2, L3, and L4. Press
STAT and
arrow over to
TESTS . Arrow down to
F:ANOVA . Press
ENTER and Enter
(
L1,L2,L3,L4 ). The F statistic is 2.2303 and the
is 0.1241.
(under
"Factor" ) and
(under
Error ).
A fourth grade class is studying the environment. One of the assignments is to grow bean plants in different soils. Tommy chose to grow his beanplants in soil found outside his classroom mixed with dryer lint. Tara chose to grow her bean plants in potting soil bought at the local nursery. Nick chose to grow his beanplants in soil from his mother's garden. No chemicals were used on the plants, only water. They were grown inside the classroom next to a large window. Each childgrew 5 plants. At the end of the growing period, each plant was measured, producing the following data (in inches):
| Tommy's Plants | Tara's Plants | Nick's Plants |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 25 | 23 |
| 21 | 31 | 27 |
| 23 | 23 | 22 |
| 30 | 20 | 30 |
| 23 | 28 | 20 |
Does it appear that the three media in which the bean plants were grown produce the same mean height? Test at a 3% level of significance.
This time, we will perform the calculations that lead to the F' statistic. Notice that each group has the same number of plants so we will use the formula .
First, calculate the sample mean and sample variance of each group.
| Tommy's Plants | Tara's Plants | Nick's Plants | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Mean | 24.2 | 25.4 | 24.4 |
| Sample Variance | 11.7 | 18.3 | 16.3 |
Next, calculate the variance of the three group means (Calculate the variance of 24.2, 25.4, and 24.4). Variance of the group means = 0.413 =
Then where is the sample size (number of plants each child grew).
Calculate the mean of the three sample variances (Calculate the mean of 11.7, 18.3, and 16.3). Mean of the sample variances = 15.433
Then .
The statistic (or ratio) is
The dfs for the numerator =
The dfs for the denominator =
The distribution for the test is and the F statistic is
The p-value is .
Decision: Since and the , do not reject . (Why?)
Conclusion: With a 3% the level of significance, from the sample data, the evidence is not sufficient to conclude that the mean heights of the bean plants are different.
(This experiment was actually done by three classmates of the son of one of the authors.)
Another fourth grader also grew bean plants but this time in a jelly-like mass. The heights were (in inches) 24, 28, 25, 30, and 32.
Do a One-Way ANOVA test on the 4 groups. You may use your calculator or computer to perform the test. Are the heights of the bean plants different? Use a solution sheet .
From the sample data, the evidence is not sufficient to conclude that the mean heights of the bean plants are different.
From the class, create four groups of the same size as follows: men under 22, men at least 22, women under 22, women at least 22. Have each member of each group record the number of states in the United States he or she has visited.Run an ANOVA test to determine if the average number of states visited in the four groups are the same. Test at a 1% level of significance. Use one of the solution sheets at the end of the chapter (after the homework).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Quantitative information analysis iii' conversation and receive update notifications?