| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like prokaryotic cells, the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires the actions of an RNA polymerase to bind to a sequence upstream of a gene to initiate transcription. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, the eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires other proteins, or transcription factors, to facilitate transcription initiation. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to the promoter sequence and other regulatory sequences to control the transcription of the target gene. RNA polymerase by itself cannot initiate transcription in eukaryotic cells. Transcription factors must bind to the promoter region first and recruit RNA polymerase to the site for transcription to be established.
View the process of transcription—the making of RNA from a DNA template—at this site .
In some eukaryotic genes, there are regions that help increase or enhance transcription. These regions, called enhancers , are not necessarily close to the genes they enhance. They can be located upstream of a gene, within the coding region of the gene, downstream of a gene, or may be thousands of nucleotides away.
Enhancer regions are binding sequences, or sites, for transcription factors. When a DNA-bending protein binds, the shape of the DNA changes ( [link] ). This shape change allows for the interaction of the activators bound to the enhancers with the transcription factors bound to the promoter region and the RNA polymerase. Whereas DNA is generally depicted as a straight line in two dimensions, it is actually a three-dimensional object. Therefore, a nucleotide sequence thousands of nucleotides away can fold over and interact with a specific promoter.
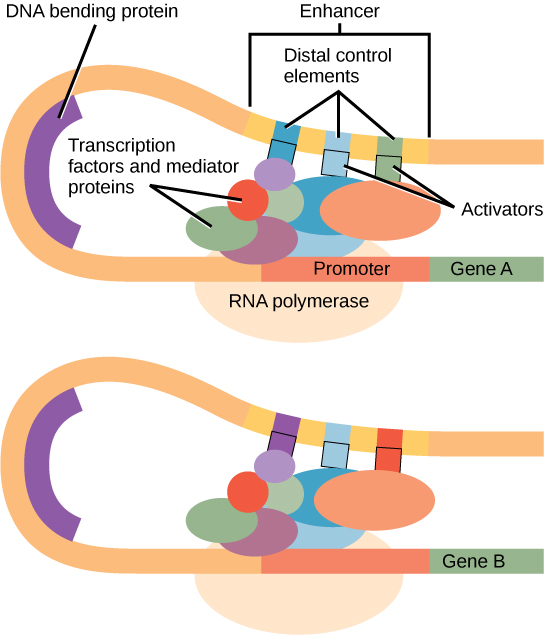
Like prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells also have mechanisms to prevent transcription. Transcriptional repressors can bind to promoter or enhancer regions and block transcription. Like the transcriptional activators, repressors respond to external stimuli to prevent the binding of activating transcription factors.
To start transcription, general transcription factors must first bind to the TATA box and recruit RNA polymerase to that location. The binding of additional regulatory transcription factors will either increase or prevent transcription. In addition to promoter sequences, enhancer regions help augment transcription. Enhancers can be upstream, downstream, within a gene itself, or on other chromosomes. Transcription factors bind to enhancer regions to increase or prevent transcription.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?