| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The DNA of prokaryotes is organized into a circular chromosome supercoiled in the nucleoid region of the cell cytoplasm. Proteins that are needed for a specific function, or that are involved in the same biochemical pathway, are encoded together in blocks called operons . For example, all of the genes needed to use lactose as an energy source are coded next to each other in the lactose (or lac ) operon.
In prokaryotic cells, there are three types of regulatory molecules that can affect the expression of operons: repressors, activators, and inducers. Repressors are proteins that suppress transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus, whereas activators are proteins that increase the transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus. Finally, inducers are small molecules that either activate or repress transcription depending on the needs of the cell and the availability of substrate.
Bacteria such as E. coli need amino acids to survive. Tryptophan is one such amino acid that E. coli can ingest from the environment. E. coli can also synthesize tryptophan using enzymes that are encoded by five genes. These five genes are next to each other in what is called the tryptophan ( trp ) operon ( [link] ). If tryptophan is present in the environment, then E. coli does not need to synthesize it and the switch controlling the activation of the genes in the trp operon is switched off. However, when tryptophan availability is low, the switch controlling the operon is turned on, transcription is initiated, the genes are expressed, and tryptophan is synthesized.
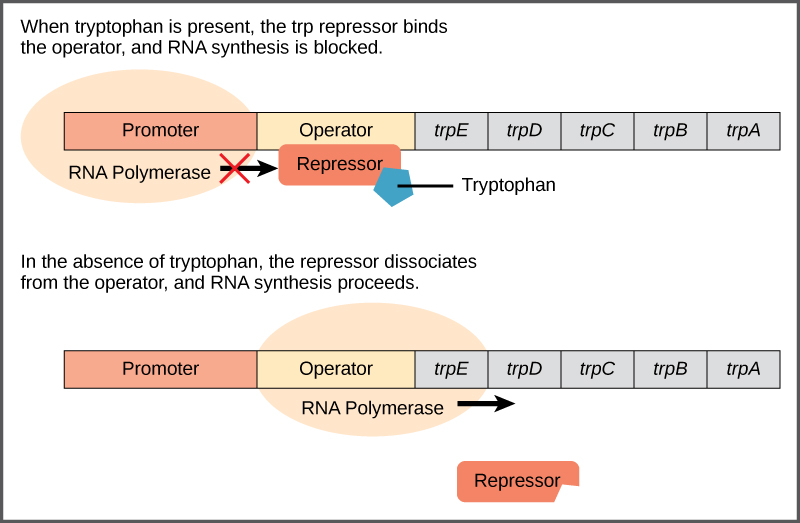
A DNA sequence that codes for proteins is referred to as the coding region. The five coding regions for the tryptophan biosynthesis enzymes are arranged sequentially on the chromosome in the operon. Just before the coding region is the transcriptional start site . This is the region of DNA to which RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription. The promoter sequence is upstream of the transcriptional start site; each operon has a sequence within or near the promoter to which proteins (activators or repressors) can bind and regulate transcription.
A DNA sequence called the operator sequence is encoded between the promoter region and the first trp coding gene. This operator contains the DNA code to which the repressor protein can bind. When tryptophan is present in the cell, two tryptophan molecules bind to the trp repressor, which changes shape to bind to the trp operator. Binding of the tryptophan–repressor complex at the operator physically prevents the RNA polymerase from binding, and transcribing the downstream genes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cell biology' conversation and receive update notifications?