| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

A guitar string stops oscillating a few seconds after being plucked. To keep a child happy on a swing, you must keep pushing. Although we can often make friction and other non-conservative forces negligibly small, completely undamped motion is rare. In fact, we may even want to damp oscillations, such as with car shock absorbers.
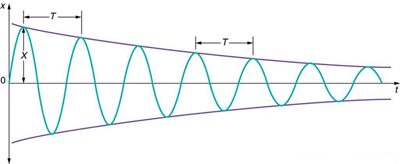
For a system that has a small amount of damping, the period and frequency are nearly the same as for simple harmonic motion, but the amplitude gradually decreases as shown in [link] . This occurs because the non-conservative damping force removes energy from the system, usually in the form of thermal energy. In general, energy removal by non-conservative forces is described as
where is work done by a non-conservative force (here the damping force). For a damped harmonic oscillator, is negative because it removes mechanical energy (KE + PE) from the system.
If you gradually increase the amount of damping in a system, the period and frequency begin to be affected, because damping opposes and hence slows the back and forth motion. (The net force is smaller in both directions.) If there is very large damping, the system does not even oscillate—it slowly moves toward equilibrium. [link] shows the displacement of a harmonic oscillator for different amounts of damping. When we want to damp out oscillations, such as in the suspension of a car, we may want the system to return to equilibrium as quickly as possible Critical damping is defined as the condition in which the damping of an oscillator results in it returning as quickly as possible to its equilibrium position The critically damped system may overshoot the equilibrium position, but if it does, it will do so only once. Critical damping is represented by Curve A in [link] . With less-than critical damping, the system will return to equilibrium faster but will overshoot and cross over one or more times. Such a system is underdamped ; its displacement is represented by the curve in [link] . Curve B in [link] represents an overdamped system. As with critical damping, it too may overshoot the equilibrium position, but will reach equilibrium over a longer period of time.
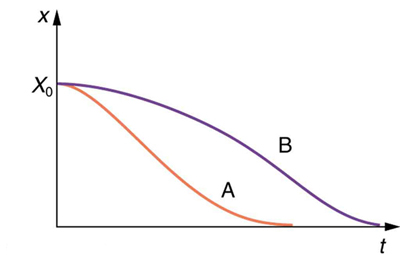
Critical damping is often desired, because such a system returns to equilibrium rapidly and remains at equilibrium as well. In addition, a constant force applied to a critically damped system moves the system to a new equilibrium position in the shortest time possible without overshooting or oscillating about the new position. For example, when you stand on bathroom scales that have a needle gauge, the needle moves to its equilibrium position without oscillating. It would be quite inconvenient if the needle oscillated about the new equilibrium position for a long time before settling. Damping forces can vary greatly in character. Friction, for example, is sometimes independent of velocity (as assumed in most places in this text). But many damping forces depend on velocity—sometimes in complex ways, sometimes simply being proportional to velocity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to physics for vanguard high school (derived from college physics)' conversation and receive update notifications?