| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
Earlier we multiplied factors together to get a product. Now, we will be reversing this process; we will start with a product and then break it down into its factors. Splitting a product into factors is called factoring.
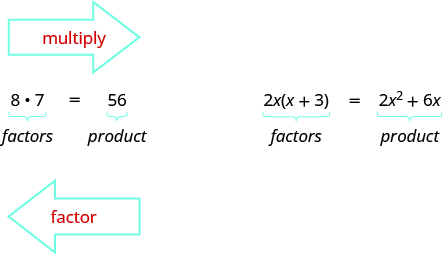
In The Language of Algebra we factored numbers to find the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. Now we will factor expressions and find the greatest common factor of two or more expressions. The method we use is similar to what we used to find the LCM.
The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more expressions is the largest expression that is a factor of all the expressions.
First we will find the greatest common factor of two numbers.
Find the greatest common factor of and
| Step 1: Factor each coefficient into primes. Write all variables with exponents in expanded form. | Factor 24 and 36. |
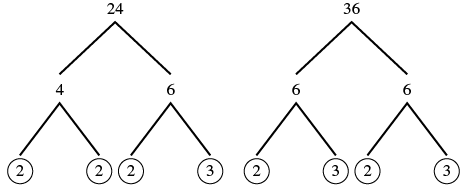 |
| Step 2: List all factors--matching common factors in a column. |
 | |
| In each column, circle the common factors. | Circle the 2, 2, and 3 that are shared by both numbers. |
 |
| Step 3: Bring down the common factors that all expressions share. | Bring down the 2, 2, 3 and then multiply. | |
| Step 4: Multiply the factors. | The GCF of 24 and 36 is 12. |
Notice that since the GCF is a factor of both numbers, and can be written as multiples of
In the previous example, we found the greatest common factor of constants. The greatest common factor of an algebraic expression can contain variables raised to powers along with coefficients. We summarize the steps we use to find the greatest common factor .
Find the greatest common factor of
| Factor each number into primes.
Circle the common factors in each column. Bring down the common factors. |
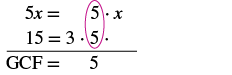 |
| The GCF of 5x and 15 is 5. |
In the examples so far, the greatest common factor was a constant. In the next two examples we will get variables in the greatest common factor.
Find the greatest common factor of and
| Factor each coefficient into primes and write
the variables with exponents in expanded form. Circle the common factors in each column. Bring down the common factors. Multiply the factors. |
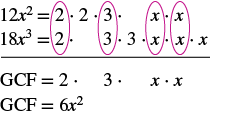 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?