| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the connection between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The CNS is like the power plant of the nervous system. It creates the signals that control the functions of the body. The PNS is like the wires that go to individual houses. Without those “wires,” the signals produced by the CNS could not control the body (and the CNS would not be able to receive sensory information from the body either).
The PNS can be broken down into the autonomic nervous system , which controls bodily functions without conscious control, and the sensory-somatic nervous system , which transmits sensory information from the skin, muscles, and sensory organs to the CNS and sends motor commands from the CNS to the muscles.
Which of the following statements is false?
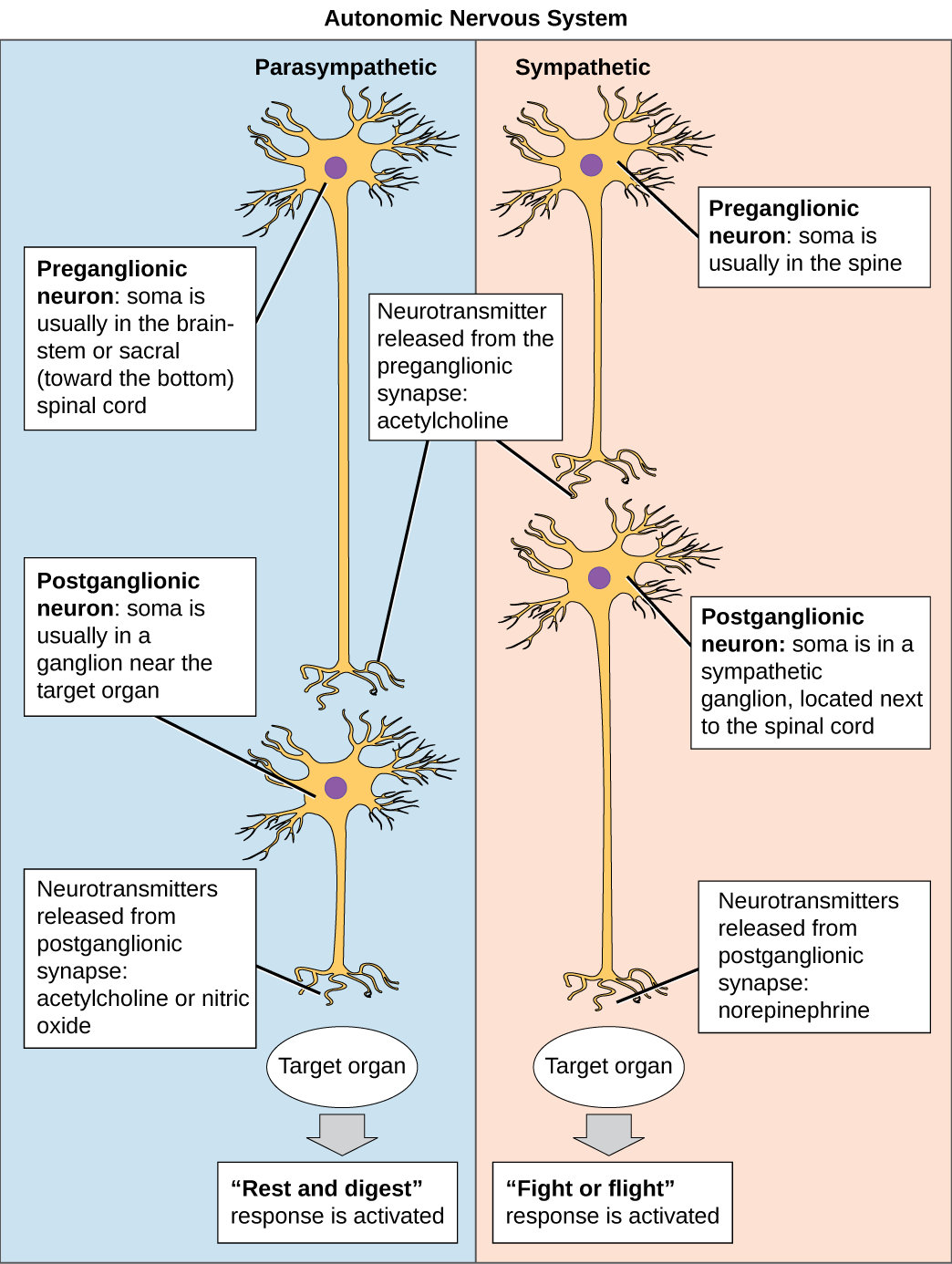
The autonomic nervous system serves as the relay between the CNS and the internal organs. It controls the lungs, the heart, smooth muscle, and exocrine and endocrine glands. The autonomic nervous system controls these organs largely without conscious control; it can continuously monitor the conditions of these different systems and implement changes as needed. Signaling to the target tissue usually involves two synapses: a preganglionic neuron (originating in the CNS) synapses to a neuron in a ganglion that, in turn, synapses on the target organ, as illustrated in [link] . There are two divisions of the autonomic nervous system that often have opposing effects: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response that occurs when an animal encounters a dangerous situation. One way to remember this is to think of the surprise a person feels when encountering a snake (“snake” and “sympathetic” both begin with “s”). Examples of functions controlled by the sympathetic nervous system include an accelerated heart rate and inhibited digestion. These functions help prepare an organism’s body for the physical strain required to escape a potentially dangerous situation or to fend off a predator.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of georgia concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?