| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To study the energy of a simple harmonic oscillator, we first consider all the forms of energy it can have We know from Hooke’s Law: Stress and Strain Revisited that the energy stored in the deformation of a simple harmonic oscillator is a form of potential energy given by:
Because a simple harmonic oscillator has no dissipative forces, the other important form of energy is kinetic energy . Conservation of energy for these two forms is:
or
This statement of conservation of energy is valid for all simple harmonic oscillators, including ones where the gravitational force plays a role
Namely, for a simple pendulum we replace the velocity with , the spring constant with , and the displacement term with . Thus
In the case of undamped simple harmonic motion, the energy oscillates back and forth between kinetic and potential, going completely from one to the other as the system oscillates. So for the simple example of an object on a frictionless surface attached to a spring, as shown again in [link] , the motion starts with all of the energy stored in the spring. As the object starts to move, the elastic potential energy is converted to kinetic energy, becoming entirely kinetic energy at the equilibrium position. It is then converted back into elastic potential energy by the spring, the velocity becomes zero when the kinetic energy is completely converted, and so on. This concept provides extra insight here and in later applications of simple harmonic motion, such as alternating current circuits.
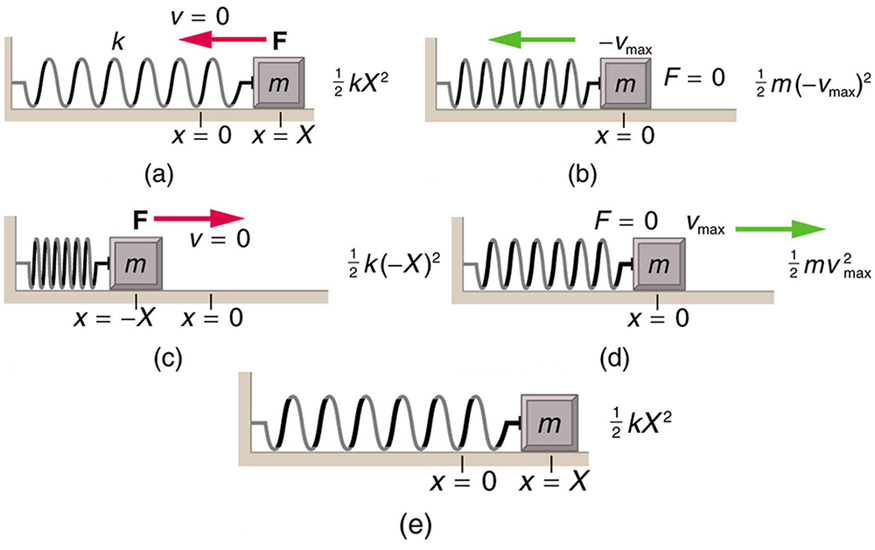
The conservation of energy principle can be used to derive an expression for velocity . If we start our simple harmonic motion with zero velocity and maximum displacement ( ), then the total energy is
This total energy is constant and is shifted back and forth between kinetic energy and potential energy, at most times being shared by each. The conservation of energy for this system in equation form is thus:
Solving this equation for yields:
Manipulating this expression algebraically gives:
and so
where
From this expression, we see that the velocity is a maximum ( ) at , as stated earlier in . Notice that the maximum velocity depends on three factors. Maximum velocity is directly proportional to amplitude. As you might guess, the greater the maximum displacement the greater the maximum velocity. Maximum velocity is also greater for stiffer systems, because they exert greater force for the same displacement. This observation is seen in the expression for it is proportional to the square root of the force constant . Finally, the maximum velocity is smaller for objects that have larger masses, because the maximum velocity is inversely proportional to the square root of . For a given force, objects that have large masses accelerate more slowly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 110 at une' conversation and receive update notifications?