| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
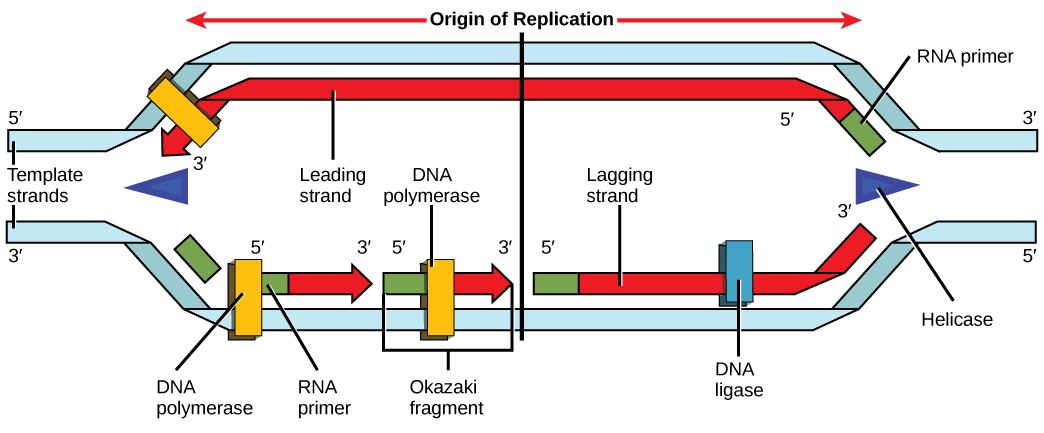
During elongation, an enzyme called DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of the template. Because DNA polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone, a primer sequence, which provides this starting point, is added with complementary RNA nucleotides. This primer is removed later, and the nucleotides are replaced with DNA nucleotides. One strand, which is complementary to the parental DNA strand, is synthesized continuously toward the replication fork so the polymerase can add nucleotides in this direction. This continuously synthesized strand is known as the leading strand . Because DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in a 5' to 3' direction, the other new strand is put together in short pieces called Okazaki fragments . The Okazaki fragments each require a primer made of RNA to start the synthesis. The strand with the Okazaki fragments is known as the lagging strand . As synthesis proceeds, an enzyme removes the RNA primer, which is then replaced with DNA nucleotides, and the gaps between fragments are sealed by an enzyme called DNA ligase .
The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows:
You isolate a cell strain in which the joining together of Okazaki fragments is impaired and suspect that a mutation has occurred in an enzyme found at the replication fork. Which enzyme is most likely to be mutated?
Because eukaryotic chromosomes are linear, DNA replication comes to the end of a line in eukaryotic chromosomes. As you have learned, the DNA polymerase enzyme can add nucleotides in only one direction. In the leading strand, synthesis continues until the end of the chromosome is reached; however, on the lagging strand there is no place for a primer to be made for the DNA fragment to be copied at the end of the chromosome. This presents a problem for the cell because the ends remain unpaired, and over time these ends get progressively shorter as cells continue to divide. The ends of the linear chromosomes are known as telomeres , which have repetitive sequences that do not code for a particular gene. As a consequence, it is telomeres that are shortened with each round of DNA replication instead of genes. For example, in humans, a six base-pair sequence, TTAGGG, is repeated 100 to 1000 times. The discovery of the enzyme telomerase ( [link] ) helped in the understanding of how chromosome ends are maintained. The telomerase attaches to the end of the chromosome, and complementary bases to the RNA template are added on the end of the DNA strand. Once the lagging strand template is sufficiently elongated, DNA polymerase can now add nucleotides that are complementary to the ends of the chromosomes. Thus, the ends of the chromosomes are replicated.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for slcc biol 1010' conversation and receive update notifications?