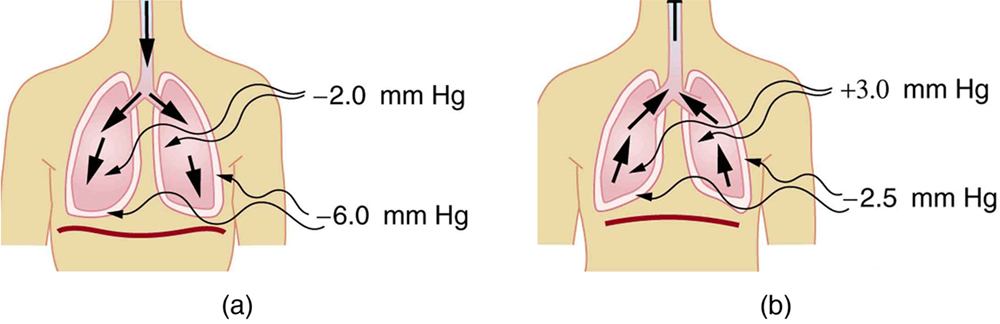
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Normally, there is a 5- to12-mm Hg pressure in the fluid surrounding the brain and filling the spinal column. This cerebrospinal fluid serves many purposes, one of which is to supply flotation to the brain. The buoyant force supplied by the fluid nearly equals the weight of the brain, since their densities are nearly equal. If there is a loss of fluid, the brain rests on the inside of the skull, causing severe headaches, constricted blood flow, and serious damage. Spinal fluid pressure is measured by means of a needle inserted between vertebrae that transmits the pressure to a suitable measuring device.
This bodily pressure is one of which we are often aware. In fact, there is a relationship between our awareness of this pressure and a subsequent increase in it. Bladder pressure climbs steadily from zero to about 25 mm Hg as the bladder fills to its normal capacity of . This pressure triggers the micturition reflex , which stimulates the feeling of needing to urinate. What is more, it also causes muscles around the bladder to contract, raising the pressure to over 100 mm Hg, accentuating the sensation. Coughing, straining, tensing in cold weather, wearing tight clothes, and experiencing simple nervous tension all can increase bladder pressure and trigger this reflex. So can the weight of a pregnant woman’s fetus, especially if it is kicking vigorously or pushing down with its head! Bladder pressure can be measured by a catheter or by inserting a needle through the bladder wall and transmitting the pressure to an appropriate measuring device. One hazard of high bladder pressure (sometimes created by an obstruction), is that such pressure can force urine back into the kidneys, causing potentially severe damage.
These pressures are the largest in the body, due both to the high values of initial force, and the small areas to which this force is applied, such as in the joints.. For example, when a person lifts an object improperly, a force of 5000 N may be created between vertebrae in the spine, and this may be applied to an area as small as . The pressure created is or about 50 atm! This pressure can damage both the spinal discs (the cartilage between vertebrae), as well as the bony vertebrae themselves. Even under normal circumstances, forces between vertebrae in the spine are large enough to create pressures of several atmospheres. Most causes of excessive pressure in the skeletal system can be avoided by lifting properly and avoiding extreme physical activity. (See Forces and Torques in Muscles and Joints .)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 101' conversation and receive update notifications?