This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses variables, constants, and real numbers. By the end of the module students should be able to distinguish between variables and constants, be able to recognize a real number and particular subsets of the real numbers and understand the ordering of the real numbers.
Section overview
- Variables and Constants
- Real Numbers
- Subsets of Real Numbers
- Ordering Real Numbers
Variables and constants
A basic distinction between algebra and arithmetic is the use of symbols (usually letters) in algebra to represent numbers. So, algebra is a generalization of arithmetic. Let us look at two examples of situations in which letters are substituted for numbers:
- Suppose that a student is taking four college classes, and each class can have at most 1 exam per week. In any 1-week period, the student may have 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 exams. In algebra, we can let the letter
represent the number of exams this student may have in a 1-week period. The letter
may assume any of the
various values 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
- Suppose that in writing a term paper for a biology class a student needs to specify the average lifetime, in days, of a male housefly. If she does not know this number off the top of her head, she might represent it (at least temporarily) on her paper with the letter
(which reminds her of
time ). Later, she could look up the average time in a reference book and find it to be 17 days. The letter
can assume only the one value, 17, and no other values. The value
is
constant .
Variable, constant
- A letter or symbol that represents any member of a collection of two or more numbers is called a
variable .
- A letter or symbol that represents one specific number, known or unknown, is called a
constant .
In
example 1 , the letter
is a variable since it can represent any of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4. The letter
example 2 is a constant since it can only have the value 17.
Real numbers
Real number line
The study of mathematics requires the use of several collections of numbers. The
real number line allows us to visually display (graph) the numbers in which we are interested.
A line is composed of infinitely many points. To each point we can associate a unique number, and with each number, we can associate a particular point.
Coordinate
The
number associated with a point on the number line is called the
coordinate of the point.
Graph
The
point on a number line that is associated with a particular number is called the
graph of that number.
Constructing a real number line
We construct a real number line as follows:
-
Draw a horizontal line.

-
Origin
Choose any point on the line and label it 0. This point is called the
origin .
-
Choose a convenient length. Starting at 0, mark this length off in both directions, being careful to have the lengths look like they are about the same.
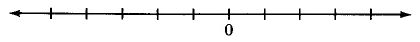
We now define a real number.
Real number
A
real number is any number that is the coordinate of a point on the real number line.
Positive numbers, negative numbers
Real numbers whose graphs are to the right of 0 are called
positive real numbers , or more simply,
positive numbers . Real numbers whose graphs appear to the left of 0 are called
negative real numbers , or more simply,
negative numbers .
![]()
![]()
![]()
