| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. 11; 25; 6; 12; 11; 15; 27; 34
24; 8; 14; 9; 17; 13; 11; 12
2.
2.1 519; 527; 535; 543
2.2 825; 810; 795; 780
2.3 3 770; 3 779; 3 797; 3 806
2.4 99 800; 9 760; 9 640; 9 600
3.
3.1 3 003; 333; 330; 303; 33
3.2 6 666; 6 606; 6 600; 6 060; 6 006
Leaner Section
1. It happens often that one has to think quickly. That is why mental arithmetic skills are very important. Let us see whether you can work faster than your friend. Work in pairs and see who can give the answer first. Start at the arrow every time and work clockwise.
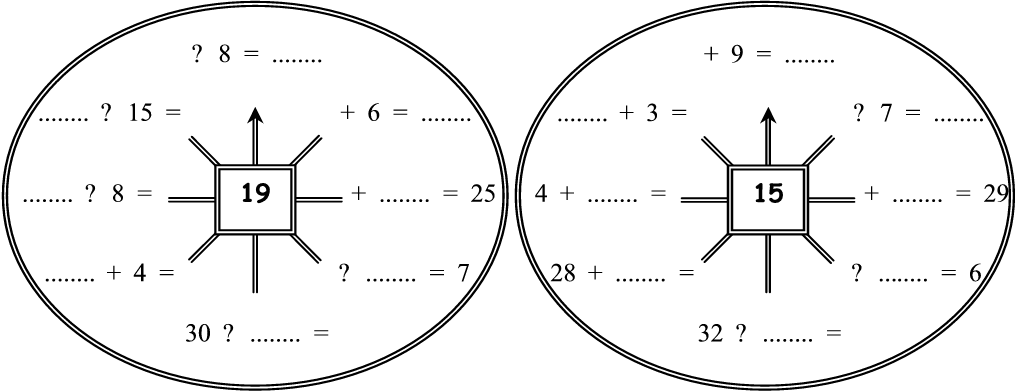
DO YOU STILL REMEMBER?
Rows of numbers sometimes provide very interesting patterns. If we, for instance, begin at 350 and keep adding 15, we'll get the following pattern:
350 ; 365 ; 380 ; 395 ; 410
2. Rows of numbers always have some sort of numeric pattern. Examine the following patterns and see whether you can complete the rows correctly (use your pocket calculator, if necessary, to check that you have worked correctly):
2.1 495 ; 503 ; 511 ; _________ ; _________ ; . _________ ; _________
2.2 870 ; 855 ; 840 ; _________ ; . _________ ; . _________ ; _________
2.3 3 752 ; 3 761 ; _________ ; _________ ; 3 788 ; _________ ; _______
2.4 _________ ; _________ ; 9 720 ; 9 680 : _________ ; _________
3. In our everyday life it is very important to be able to read and say numbers correctly. We also need to know which number is greater/smaller than the other. Just think of the number of times per day you work with money. If you save R220, for instance, you would certainly not want R202 to be written in your savings booklet! Look at the following numbers and write them down in order from the GREATEST to the SMALLEST (descending order).
3.1 303 ; 330 ; 333 ; 33 ; 3 003
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3.2 6 006 ; 6 600 ; 6 666 ; 6 060 ; 6 606
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.9: We know this when the learner performs mental calculations;
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.1: We know this when the learner investigates and extends numeric and geometric patterns looking for a relationship or rules, including patterns.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?