| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Common Unit Prefixes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix | Symbol | Factor | Example |
| femto | f | 10 −15 | 1 femtosecond (fs) = 1 10 −15 s (0.000000000000001 s) |
| pico | p | 10 −12 | 1 picometer (pm) = 1 10 −12 m (0.000000000001 m) |
| nano | n | 10 −9 | 4 nanograms (ng) = 4 10 −9 g (0.000000004 g) |
| micro | µ | 10 −6 | 1 microliter (μL) = 1 10 −6 L (0.000001 L) |
| milli | m | 10 −3 | 2 millimoles (mmol) = 2 10 −3 mol (0.002 mol) |
| centi | c | 10 −2 | 7 centimeters (cm) = 7 10 −2 m (0.07 m) |
| deci | d | 10 −1 | 1 deciliter (dL) = 1 10 −1 L (0.1 L ) |
| kilo | k | 10 3 | 1 kilometer (km) = 1 10 3 m (1000 m) |
| mega | M | 10 6 | 3 megahertz (MHz) = 3 10 6 Hz (3,000,000 Hz) |
| giga | G | 10 9 | 8 gigayears (Gyr) = 8 10 9 yr (8,000,000,000 Gyr) |
| tera | T | 10 12 | 5 terawatts (TW) = 5 10 12 W (5,000,000,000,000 W) |

Need a refresher or more practice with scientific notation? Visit this site to go over the basics of scientific notation.
The initial units of the metric system, which eventually evolved into the SI system, were established in France during the French Revolution. The original standards for the meter and the kilogram were adopted there in 1799 and eventually by other countries. This section introduces four of the SI base units commonly used in chemistry. Other SI units will be introduced in subsequent chapters.
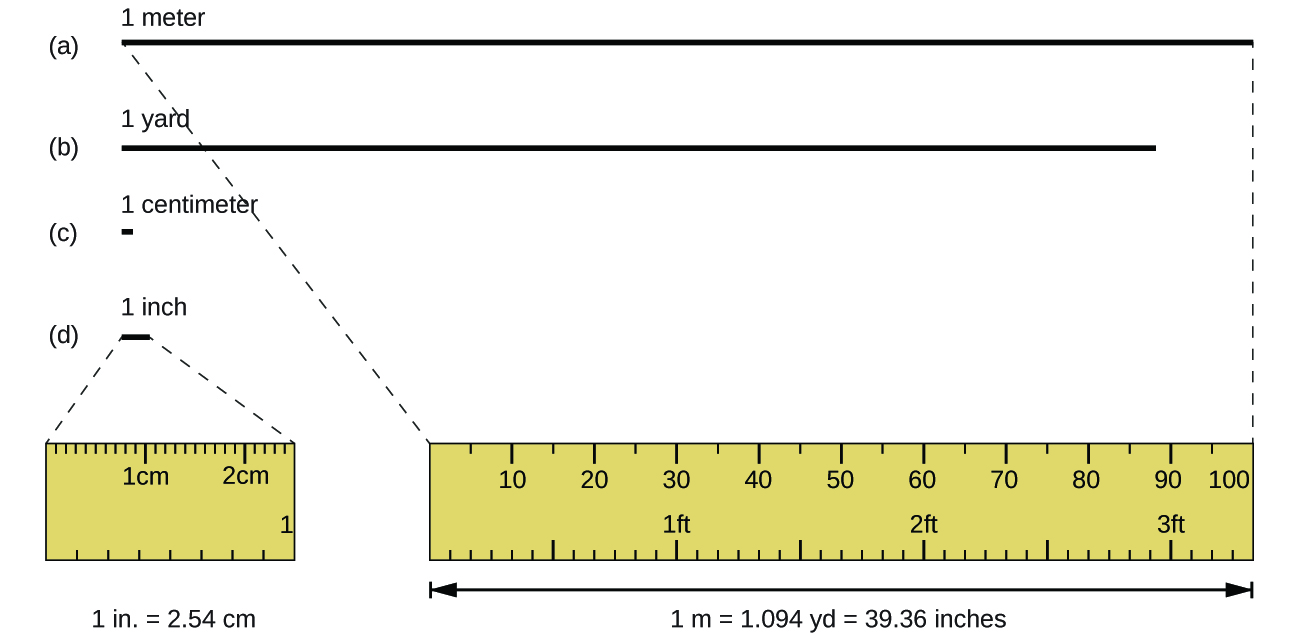
The standard unit of length in both the SI and original metric systems is the meter (m) . A meter was originally specified as 1/10,000,000 of the distance from the North Pole to the equator. It is now defined as the distance light in a vacuum travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second. A meter is about 3 inches longer than a yard ( [link] ); one meter is about 39.37 inches or 1.094 yards. Longer distances are often reported in kilometers (1 km = 1000 m = 10 3 m), whereas shorter distances can be reported in centimeters (1 cm = 0.01 m = 10 −2 m) or millimeters (1 mm = 0.001 m = 10 −3 m).
The standard unit of mass in the SI system is the kilogram (kg) . A kilogram was originally defined as the mass of a liter of water (a cube of water with an edge length of exactly 0.1 meter). It is now defined by a certain cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy, which is kept in France ( [link] ). Any object with the same mass as this cylinder is said to have a mass of 1 kilogram. One kilogram is about 2.2 pounds. The gram (g) is exactly equal to 1/1000 of the mass of the kilogram (10 −3 kg).

Temperature is an intensive property. The SI unit of temperature is the kelvin (K) . The IUPAC convention is to use kelvin (all lowercase) for the word, K (uppercase) for the unit symbol, and neither the word “degree” nor the degree symbol (°). The degree Celsius (°C) is also allowed in the SI system, with both the word “degree” and the degree symbol used for Celsius measurements. Celsius degrees are the same magnitude as those of kelvin, but the two scales place their zeros in different places. Water freezes at 273.15 K (0 °C) and boils at 373.15 K (100 °C) by definition, and normal human body temperature is approximately 310 K (37 °C). The conversion between these two units and the Fahrenheit scale will be discussed later in this chapter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?