| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Life is simpler if the beginning time is taken to be zero, as when we use a stopwatch. If we were using a stopwatch, it would simply read zero at the start of the lecture and 50 min at the end. If , then .
In this text, for simplicity's sake,
Your notion of velocity is probably the same as its scientific definition. You know that if you have a large displacement in a small amount of time you have a large velocity, and that velocity has units of distance divided by time, such as miles per hour or kilometers per hour.
Average velocity is displacement (change in position) divided by the time of travel ,
where is the average (indicated by the bar over the ) velocity, is the change in position (or displacement), and and are the final and beginning positions at times and , respectively. If the starting time is taken to be zero, then the average velocity is simply
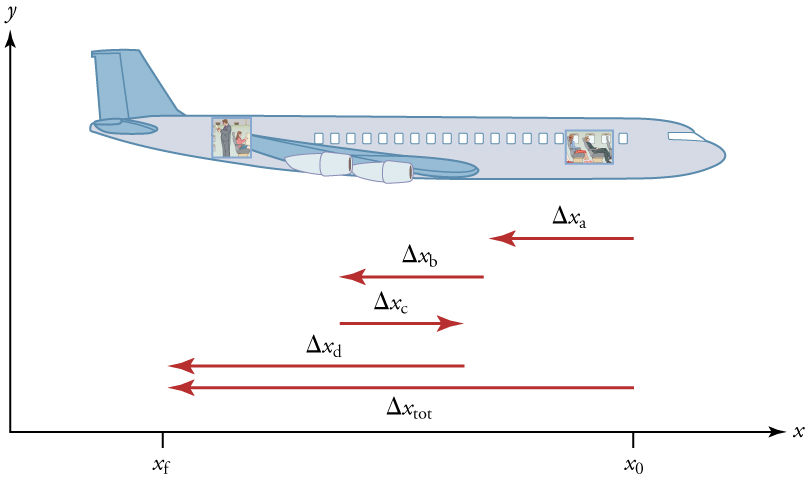
Notice that this definition indicates that velocity is a vector because displacement is a vector . It has both magnitude and direction. The SI unit for velocity is meters per second or m/s, but many other units, such as km/h, mi/h (also written as mph), and cm/s, are in common use. Suppose, for example, an airplane passenger took 5 seconds to move −4 m (the minus sign indicates that displacement is toward the back of the plane). His average velocity would be
The minus sign indicates the average velocity is also toward the rear of the plane.
The average velocity of an object does not tell us anything about what happens to it between the starting point and ending point, however. For example, we cannot tell from average velocity whether the airplane passenger stops momentarily or backs up before he goes to the back of the plane. To get more details, we must consider smaller segments of the trip over smaller time intervals.
The smaller the time intervals considered in a motion, the more detailed the information. When we carry this process to its logical conclusion, we are left with an infinitesimally small interval. Over such an interval, the average velocity becomes the instantaneous velocity or the velocity at a specific instant . A car's speedometer, for example, shows the magnitude (but not the direction) of the instantaneous velocity of the car. (Police give tickets based on instantaneous velocity, but when calculating how long it will take to get from one place to another on a road trip, you need to use average velocity.) Instantaneous velocity is the average velocity at a specific instant in time (or over an infinitesimally small time interval).
Mathematically, finding instantaneous velocity, , at a precise instant can involve taking a limit, a calculus operation beyond the scope of this text. However, under many circumstances, we can find precise values for instantaneous velocity without calculus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sample chapters: openstax college physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?