| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find the average rate of change of on the interval
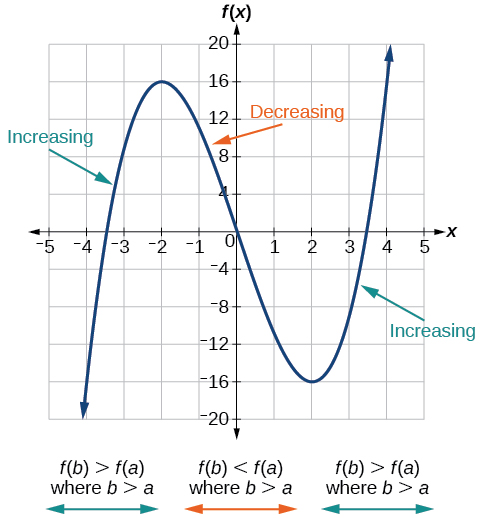
As part of exploring how functions change, we can identify intervals over which the function is changing in specific ways. We say that a function is increasing on an interval if the function values increase as the input values increase within that interval. Similarly, a function is decreasing on an interval if the function values decrease as the input values increase over that interval. The average rate of change of an increasing function is positive, and the average rate of change of a decreasing function is negative. [link] shows examples of increasing and decreasing intervals on a function.
While some functions are increasing (or decreasing) over their entire domain, many others are not. A value of the input where a function changes from increasing to decreasing (as we go from left to right, that is, as the input variable increases) is called a local maximum . If a function has more than one, we say it has local maxima. Similarly, a value of the input where a function changes from decreasing to increasing as the input variable increases is called a local minimum . The plural form is “local minima.” Together, local maxima and minima are called local extrema , or local extreme values, of the function. (The singular form is “extremum.”) Often, the term local is replaced by the term relative . In this text, we will use the term local .
Clearly, a function is neither increasing nor decreasing on an interval where it is constant. A function is also neither increasing nor decreasing at extrema. Note that we have to speak of local extrema, because any given local extremum as defined here is not necessarily the highest maximum or lowest minimum in the function’s entire domain.
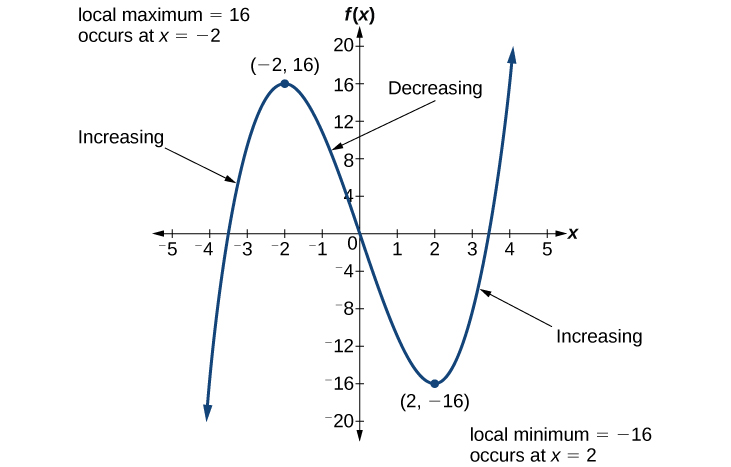
For the function whose graph is shown in [link] , the local maximum is 16, and it occurs at The local minimum is and it occurs at
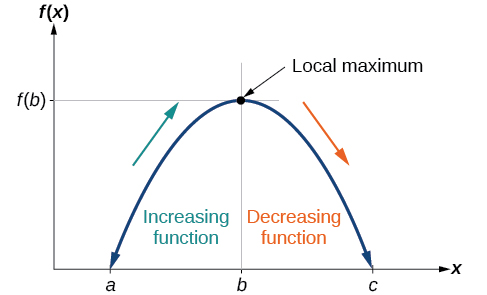
To locate the local maxima and minima from a graph, we need to observe the graph to determine where the graph attains its highest and lowest points, respectively, within an open interval. Like the summit of a roller coaster, the graph of a function is higher at a local maximum than at nearby points on both sides. The graph will also be lower at a local minimum than at neighboring points. [link] illustrates these ideas for a local maximum.
These observations lead us to a formal definition of local extrema.
A function is an increasing function on an open interval if for every , interval where
A function is a decreasing function on an open interval if for every , interval where
A function has a local maximum at a point in an open interval if is greater than or equal to for every point ( does not equal ) in the interval. Likewise, has a local minimum at a point in if is less than or equal to for every ( does not equal ) in the interval.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Essential precalculus, part 1' conversation and receive update notifications?