| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The relative amounts of reactants and products represented in a balanced chemical equation are often referred to as stoichiometric amounts . All the exercises of the preceding module involved stoichiometric amounts of reactants. For example, when calculating the amount of product generated from a given amount of reactant, it was assumed that any other reactants required were available in stoichiometric amounts (or greater). In this module, more realistic situations are considered, in which reactants are not present in stoichiometric amounts.
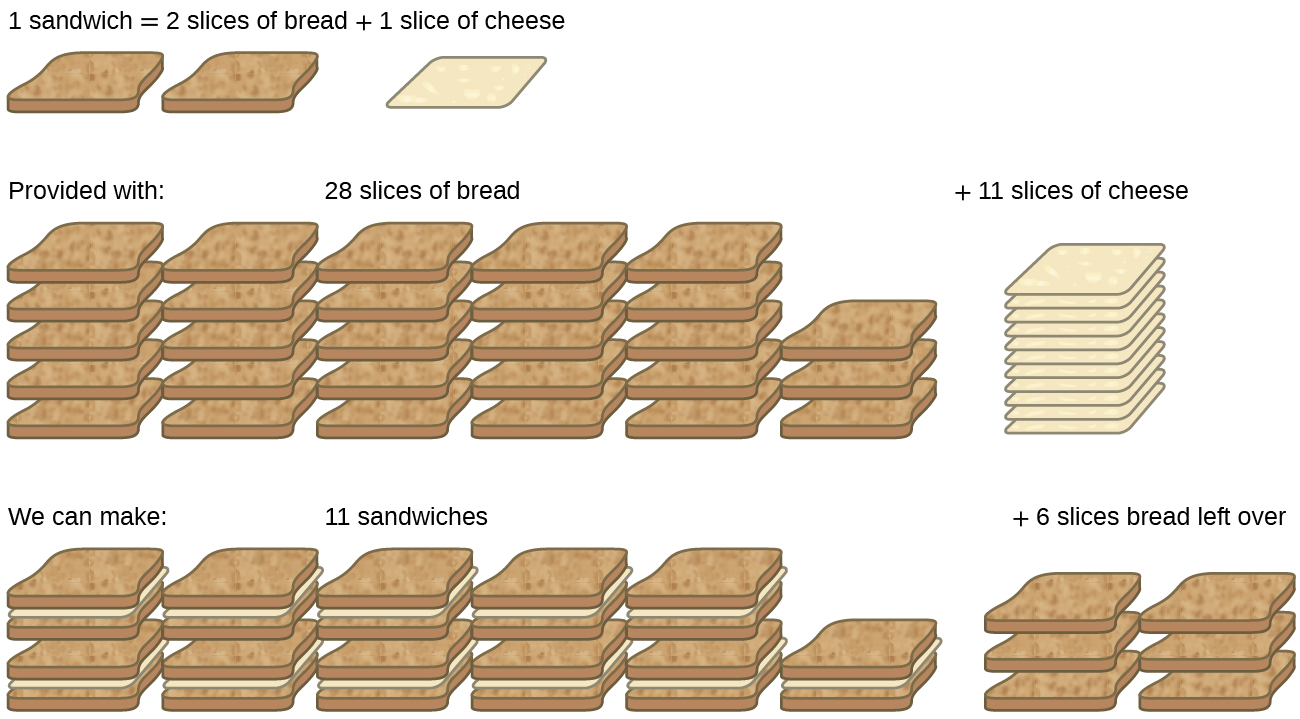
Consider another food analogy, making grilled cheese sandwiches ( [link] ):
Stoichiometric amounts of sandwich ingredients for this recipe are bread and cheese slices in a 2:1 ratio. Provided with 28 slices of bread and 11 slices of cheese, one may prepare 11 sandwiches per the provided recipe, using all the provided cheese and having six slices of bread left over. In this scenario, the number of sandwiches prepared has been limited by the number of cheese slices, and the bread slices have been provided in excess .
Consider this concept now with regard to a chemical process, the reaction of hydrogen with chlorine to yield hydrogen chloride:
The balanced equation shows the hydrogen and chlorine react in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio. If these reactants are provided in any other amounts, one of the reactants will nearly always be entirely consumed, thus limiting the amount of product that may be generated. This substance is the limiting reactant , and the other substance is the excess reactant . Identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant provided and comparing them to the stoichiometric amounts represented in the balanced chemical equation. For example, imagine combining 3 moles of H 2 and 2 moles of Cl 2 . This represents a 3:2 (or 1.5:1) ratio of hydrogen to chlorine present for reaction, which is greater than the stoichiometric ratio of 1:1. Hydrogen, therefore, is present in excess, and chlorine is the limiting reactant. Reaction of all the provided chlorine (2 mol) will consume 2 mol of the 3 mol of hydrogen provided, leaving 1 mol of hydrogen unreacted.
An alternative approach to identifying the limiting reactant involves comparing the amount of product expected for the complete reaction of each reactant. Each reactant amount is used to separately calculate the amount of product that would be formed per the reaction’s stoichiometry. The reactant yielding the lesser amount of product is the limiting reactant. For the example in the previous paragraph, complete reaction of the hydrogen would yield

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?