| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SOCIAL SCIENCES: Geography
Grade 6
MAP WORK AND PRACTICAL WORK
Module 2
THE USE OF LINES OF LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE
1. How are lines of longitude and latitude used in your atlas?
Lines of latitude (N or S) and longitude (E or W) can also be used TOGETHER to describe the location of places exactly. Then they are called that place’s location co-ordinates.
Let’s say you have no idea where Sydney is on the globe. Rather than reading and searching a map for hours, you can go to the INDEX at the back of the atlas, where the names of places are arranged alphabetically.
Example:
Next to Sydney the following particulars are given:
Sydney 55 33.55 S 150.30 E
This means
55 - page 55 in the atlas (differs from atlas to atlas)
33.55 S - 33 degrees and 55 minutes south
150.30 E - 150 degrees and 30 minutes east
By using the degree reference, any place can be easily found. The degree reference refers to degrees of longitude and latitude.
Activity 1:
To determine the location of capital cities
[LO 1.3]
Find the following capitals in the index of your atlas, and write down the location of each one completely. Then indicate which one should have the coldest climate, which ones should have roughly the same climate, etc.
| Capitals | Location | Climate |
| Stockholm | 59.20 N 18.10 E | |
| Berlin | ||
| Rome | ||
| Tripoli | ||
| Kinshasa | ||
| Windhoek | ||
| Cape Town |
[LO 1.2]
Name the three kinds of scales indicated on the map of the world:
Measure the distance between the following places in centimetres. Use the map’s ratio scale and determine the real distance in kilometres. Show your calculations.
a) (4) Cape Town to (5) Melbourne _______________km
b) (6) New York to (7) London ______________________km
c) (8) Paris to (9) Johannesburg_________________km
Study the world map and say in which direction the following countries lie from one another:
South America to Europe
Europe to Africa
Australia to South Africa
Europe to Australia
If you want to fly from (9) Johannesburg to the nearest ocean, in which direction and how far will this be in kilometres?
Direction
Distance_______ km
In which two hemispheres are the following countries and continents situated?
h) Asia___________and_______________
i) Canada ___________and_________________
j) South Africa ____________ and_____________
k) India _______________and______________
l) USA _____________ and__________________
Which lines of latitude are represented by numbers (10), (11) and (12)?
Name the line of longitude that runs through London.
In the morning, will the sun “appear” at Australia or South Africa first? Give reasons for your answer.
Figure 4
***SORRY, THIS MEDIA TYPE IS NOT SUPPORTED.***

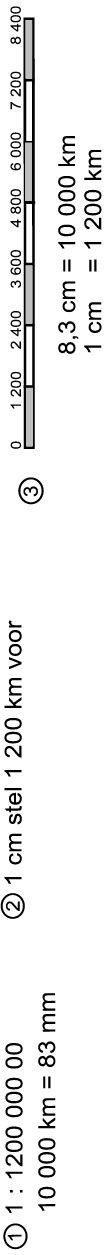
Activity 3:
To use an atlas index
[LO 1.3]
Find the place names in the following questions in your atlas index and answer each of the questions:
1. Which river flows through Munich?
2. Which channel connects Berlin with the North Sea?
3. Name the largest island in Japan
4. How high is the highest point of the Caucasus?
5. Name the capital of Taiwan
6. Between which two parts of the United Kingdom are the Cheviot Hills?
_________________ and_____________________
7. What is the time difference between Rosario and Manaus in South Africa?
8. Which city lies 25 km southeast of Amsterdam?
9. In which country can we find the city of Stuttgart?
10. Which river runs into Lake St Lucia?
11. How far is the Argentine capital from the capital of Uruguay?
12. What is so unique about Lake Titicaca? (Look at the colour of the surrounding area.)
13. Which of Ladismith or Ladysmith is closest to Cape Town?
14. On which island can you find the city of Palermo?
15. Roughly how many kilometres is the coastline of the Nigerian delta?
Assessment
| Learning Outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| GEOGRAPHICAL ENQUIRYThe learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and environmental concepts and processes. |
| Assessment standards(AS’s) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| selects and records relevant information from sources for specific purposes (including recording and observing in the field);locates relevant places on maps using latitude and longitude (degrees and minutes);uses information to propose solutions to problems; 1.5 reports on enquiries, through discussion, debate, structured writing, graphs, tables, maps and diagrams. |
Memorandum
Activity 1:
| Capitals | Location | Climate |
| Stockholm | 59.20 N 18.10 E | Cold |
| Berlin | 52.30 N 13.24 E | Cold |
| Rome | 41.55 N 12.30 E | Moderately cold |
| Tripoli | 32.30 N 13.15 E | Moderate |
| Kinshasa | 22.36 S 17.04 E | Warm |
| Windhoek | 22.36 S 17.04 E | Warm |
| Cape Town | 33.58 S 18.30 E | Moderate |
Activity 2:
Ratio scale
Word scale
Line scale
±10 000 km
±6 000 km
±7 000 km
NE
S
W
g) SE
E
±600 km
N and E
N and W
S and E
N and E
N and W
23,5ºC
0º
60ºN
Greenwich (0º)
Australia – E of SA
Activity 3:
Isar
Mitteland Canal
Honshu
Elbrus/ 5633 m
Taipei
Scotland and England
None
Hilversum
Germany
Umfolozi
250 - 300 km
Very high
Ladismith
Sicily
15. ±250 km

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?