| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An electrical conductor is a substance that allows an electrical current to pass through it. Electrical conductors are usually metals. Copper is one of the best electrical conductors, and this is why it is used to make conducting wire. In reality, silver actually has an even higher electrical conductivity than copper, but because silver is so expensive, it is not practical to use it for electrical wiring because such large amounts are needed. In the overhead power lines that we see above us, aluminium is used. The aluminium usually surrounds a steel core which adds tensile strength to the metal so that it doesn't break when it is stretched across distances. Occasionally gold is used to make wire, not because it is a particularly good conductor, but because it is very resistant to surface corrosion. Corrosion is when a material starts to deteriorate at the surface because of its reactions with the surroundings, for example oxygen and water in the air.
An insulator is a non-conducting material that does not carry any charge. Examples of insulators would be plastic and wood. Do you understand now why electrical wires are normally covered with plastic insulation? Semi-conductors behave like insulators when they are cold, and like conductors when they are hot. The elements silicon and germanium are examples of semi-conductors.
A conductor allows the easy movement or flow of something such as heat or electrical charge through it. Insulators are the opposite to conductors because they inhibit or reduce the flow of heat, electrical charge, sound etc through them.
Think about the materials around you. Are they electrical conductors or not? Why are different materials used? Think about the use of semiconductors in electronics? Can you think of why they are used there?
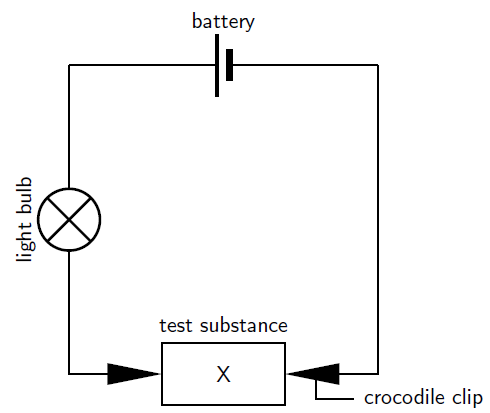
| Test substance | Metal/non-metal | Does the light bulb glow? | Conductor or insulator |
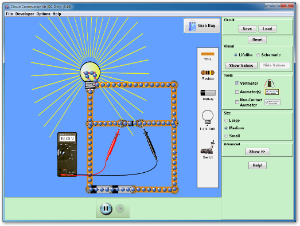
The following simulation allows you to work through the above activity. For this simulation use the grab bag option to get materials to test. Set up the circuit as described in the activity.
A thermal conductor is a material that allows energy in the form of heat, to be transferred within the material, without any movement of the material itself. An easy way to understand this concept is through a simple demonstration.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?