| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although you may not typically think of the skin as an organ, it is in fact made of tissues that work together as a single structure to perform unique and critical functions. The skin and its accessory structures make up the integumentary system , which provides the body with overall protection. The skin is made of multiple layers of cells and tissues, which are held to underlying structures by connective tissue ( [link] ). The deeper layer of skin is well vascularized (has numerous blood vessels). It also has numerous sensory, and autonomic and sympathetic nerve fibers ensuring communication to and from the brain.
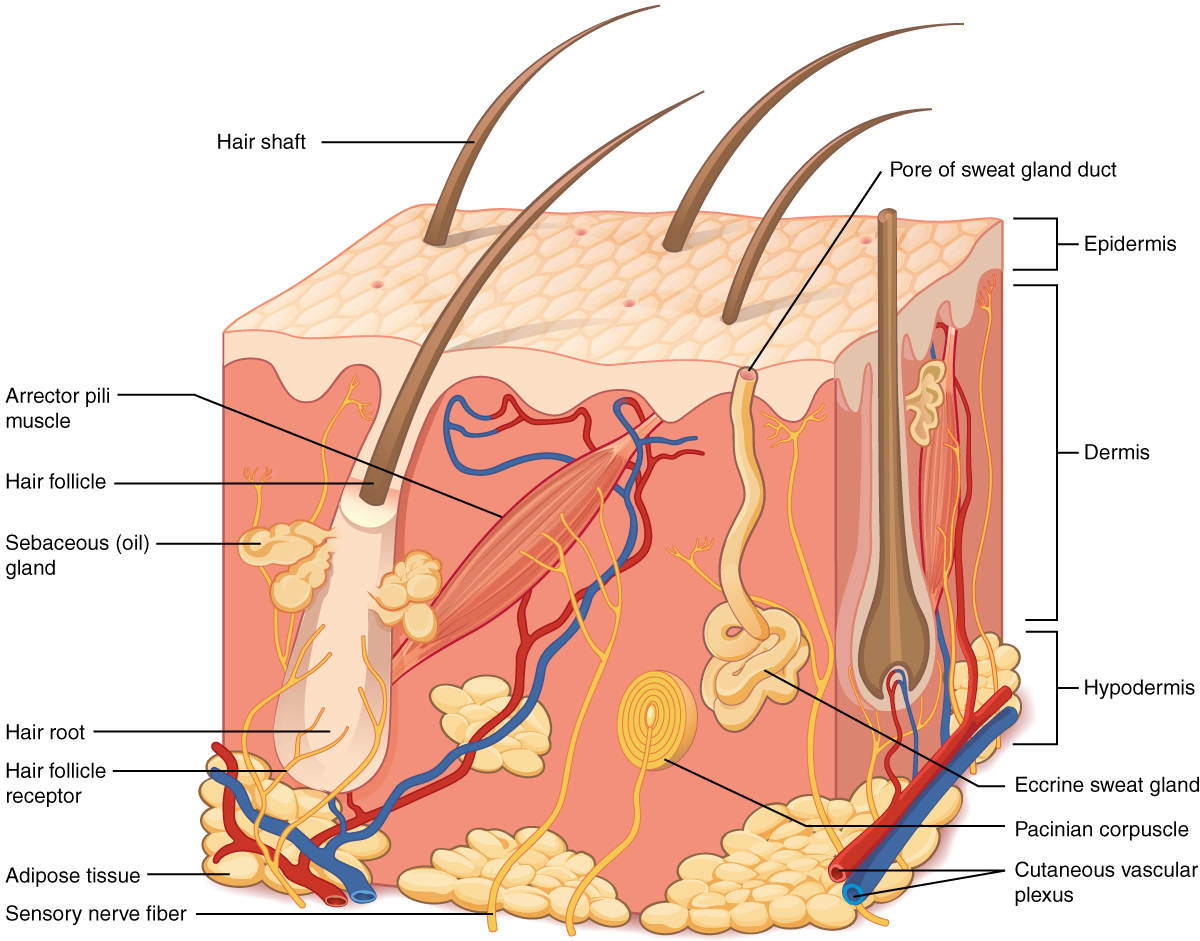
The skin consists of two main layers and a closely associated layer. View this animation to learn more about layers of the skin. What are the basic functions of each of these layers?
The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body. It does not have any blood vessels within it (i.e., it is avascular). Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as “thin skin.” From deep to superficial, these layers are the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum. Most of the skin can be classified as thin skin. “Thick skin” is found only on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It has a fifth layer, called the stratum lucidum, located between the stratum corneum and the stratum granulosum ( [link] ).
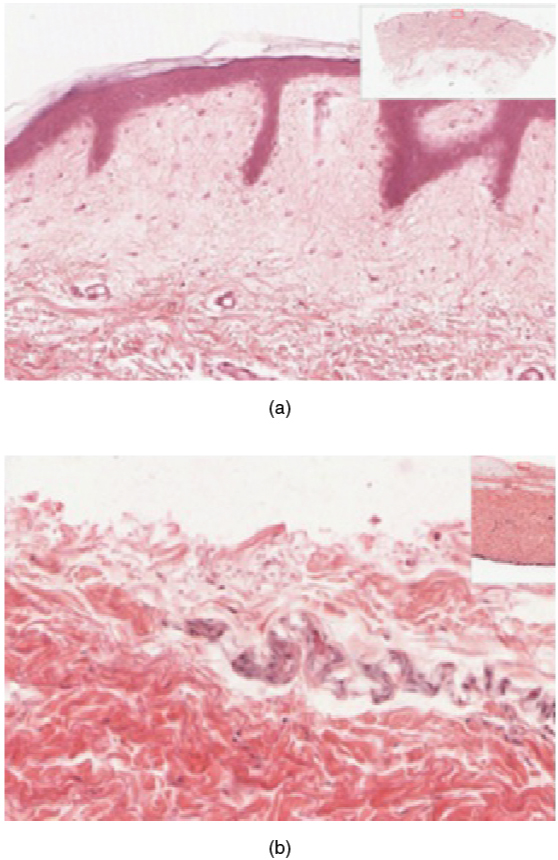
The cells in all of the layers except the stratum basale are called keratinocytes. A keratinocyte is a cell that manufactures and stores the protein keratin. Keratin is an intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their hardness and water-resistant properties. The keratinocytes in the stratum corneum are dead and regularly slough away, being replaced by cells from the deeper layers ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?